Abstract
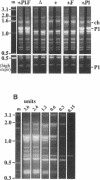
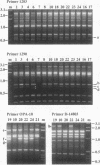
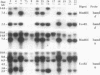
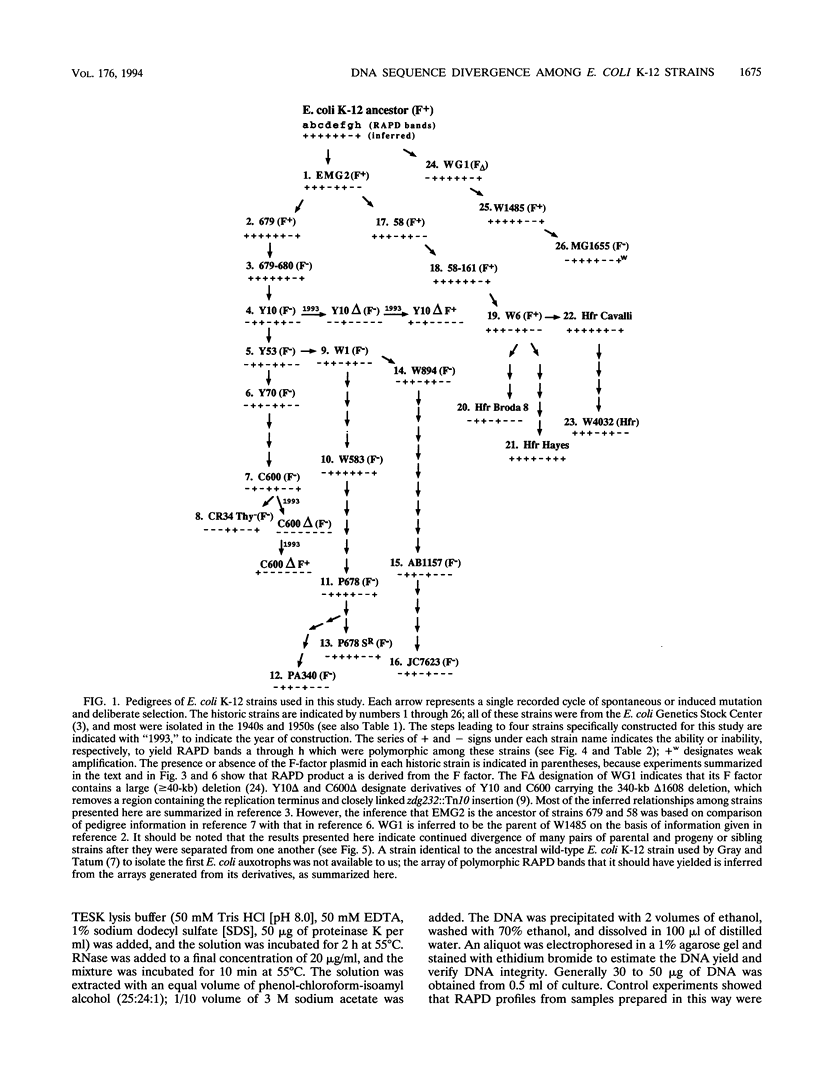
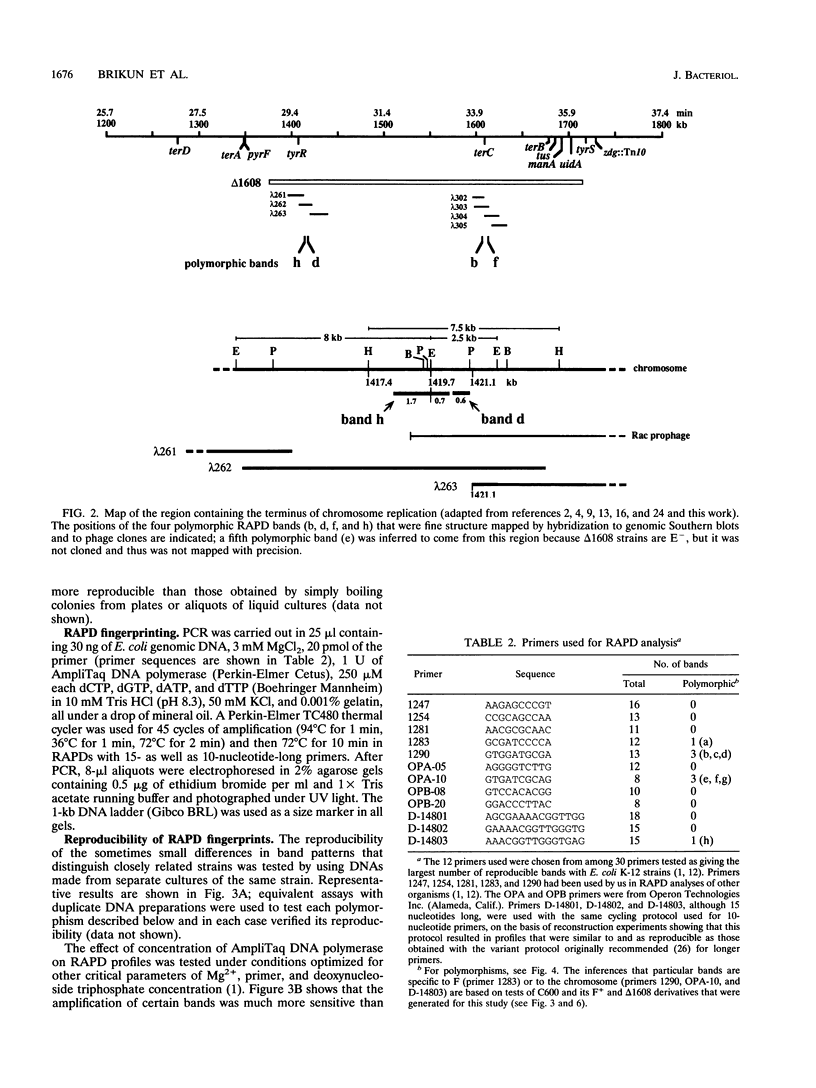
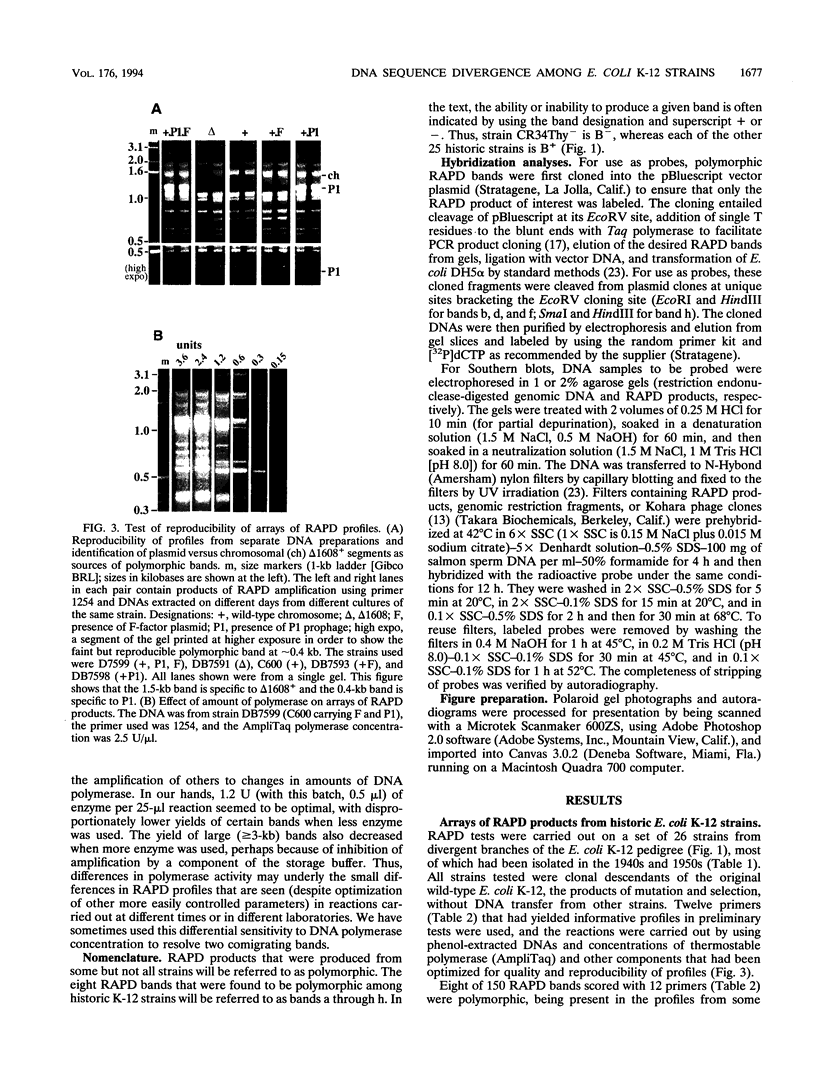
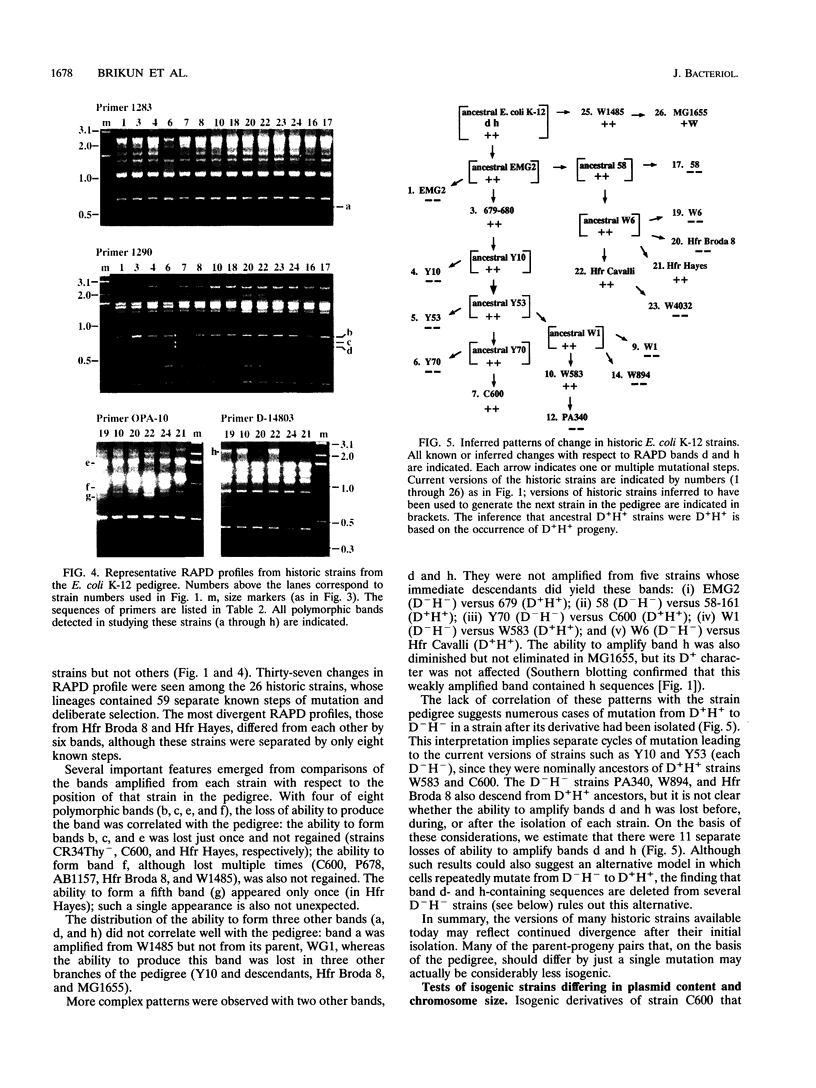
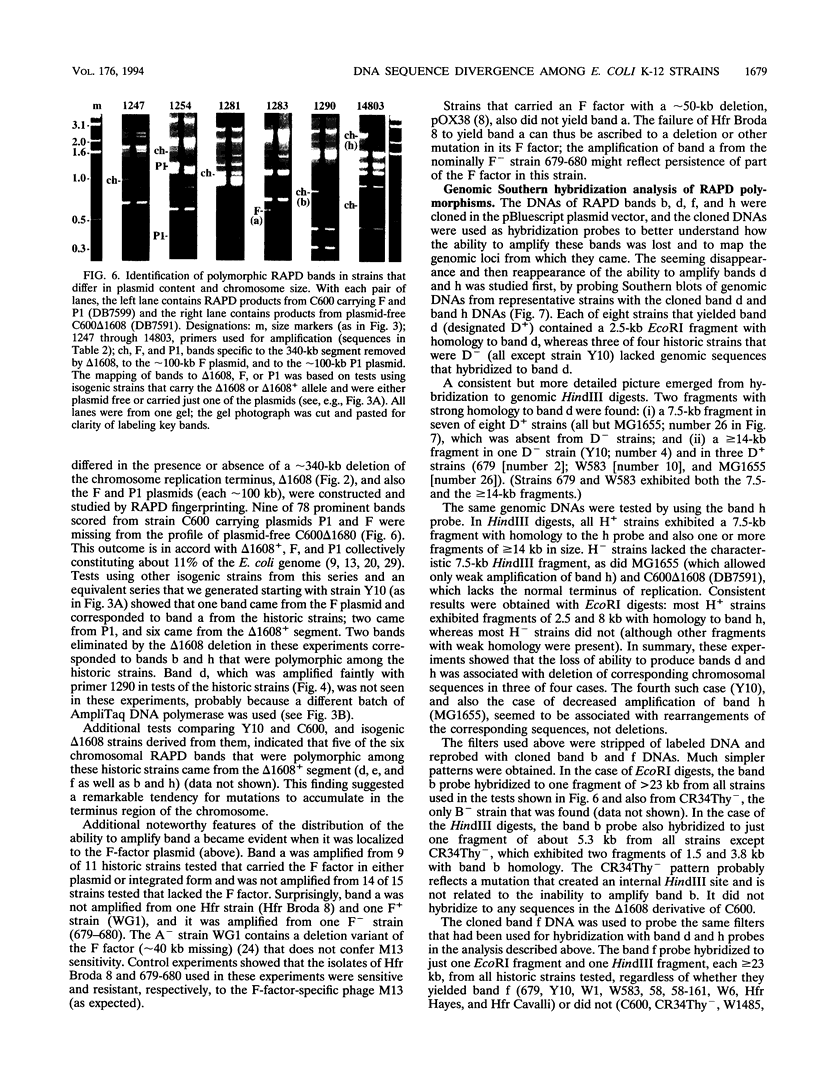
Derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12 of known ancestry were characterized by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprinting to better understand genome evolution in this family of closely related strains. This sensitive method entails PCR amplification with arbitrary primers at low stringency and yields arrays of anonymous DNA fragments that are strain specific. Among 150 fragments scored, eight were polymorphic in that they were produced from some but not all strains. Seven polymorphic bands were chromosomal, and one was from the F-factor plasmid. Five of the six mapped polymorphic chromosomal bands came from just 7% of the genome, a 340-kb segment that includes the terminus of replication. Two of these were from the cryptic Rac prophage, and the inability to amplify them from strains was attributable to deletion (excision) or to rearrangement of Rac. Two other terminus-region segments that resulted in polymorphic bands appeared to have sustained point mutations that affected the ability to amplify them. Control experiments showed that RAPD bands from the 340-kb terminus-region segment and also from two plasmids (P1 and F) were represented in approximate proportion to their size. Optimization experiments showed that the concentration of thermostable polymerase strongly affected the arrays of RAPD products obtained. Comparison of RAPD polymorphisms and positions of strains exhibiting them in the pedigree suggests that many sequence changes occurred in these historic E. coli strains during their storage. We propose that the clustering of such mutations near the terminus reflects errors during completion of chromosome replication, possibly during slow growth in the stab cultures that were often used to store E. coli strains in the early years of bacterial genetics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akopyanz N., Bukanov N. O., Westblom T. U., Kresovich S., Berg D. E. DNA diversity among clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori detected by PCR-based RAPD fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5137–5142. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
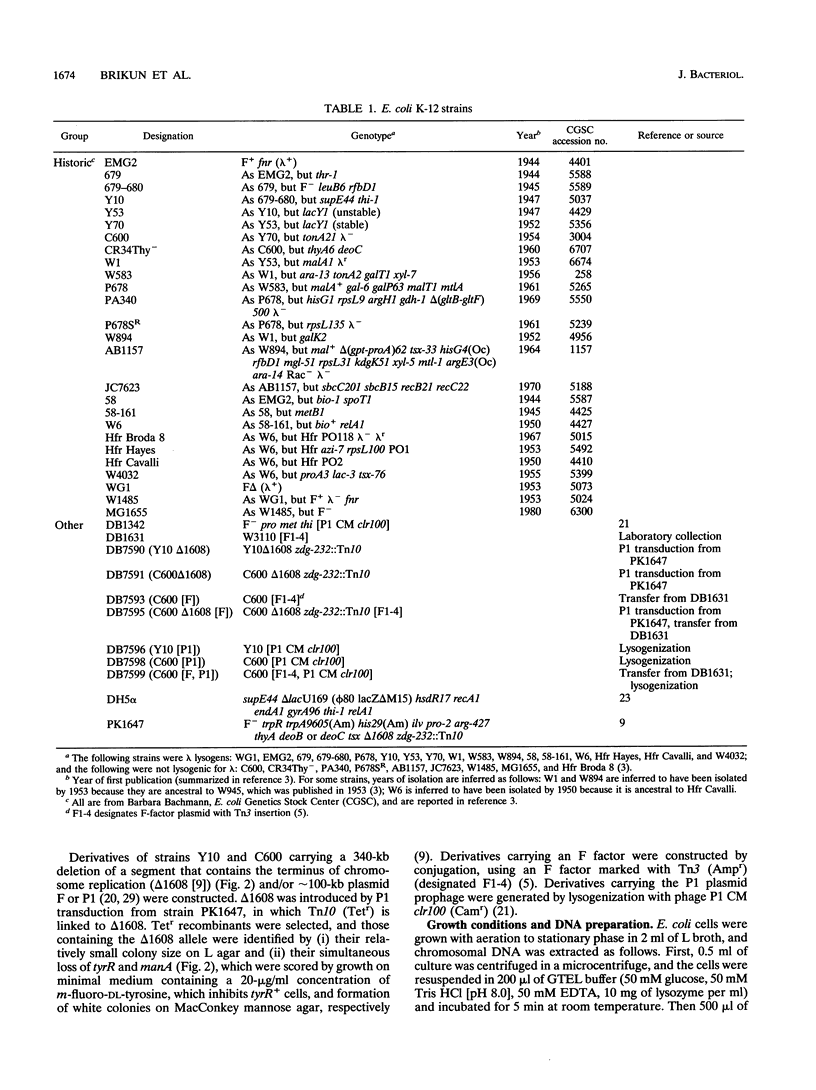
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. H., Tatum E. L. X-Ray Induced Growth Factor Requirements in Bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1944 Dec 15;30(12):404–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.30.12.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S., Reed R. R., Steitz J. A., Low K. B. Identification of a sex-factor-affinity site in E. coli as gamma delta. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):135–140. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. M., Kuempel P. L. Deletion of the terminus region (340 kilobase pairs of DNA) from the chromosome of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3766–3770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Tecklenburg M. L., Pelletier A. J., Kuempel P. L. tus, the trans-acting gene required for termination of DNA replication in Escherichia coli, encodes a DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser K., Murray N. E. Physical characterisation of the "Rac prophage" in E. coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):159–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00425532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersulyte D., Woods J. P., Keath E. J., Goldman W. E., Berg D. E. Diversity among clinical isolates of Histoplasma capsulatum detected by polymerase chain reaction with arbitrary primers. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7075–7079. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7075-7079.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louarn J. M., Louarn J., François V., Patte J. Analysis and possible role of hyperrecombination in the termination region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5097–5104. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5097-5104.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Restoration by the rac locus of recombinant forming ability in recB - and recC - merozygotes of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Apr 12;122(2):119–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00435185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan S. K., Chu C. C., Willis D. K., Templin A., Clark A. J. Physical analysis of spontaneous and mutagen-induced mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 expressing DNA exonuclease VIII activity. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):261–273. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. D., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. XbaI and BlnI genomic cleavage maps of Escherichia coli K-12 strain MG1655 and comparative analysis of other strains. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):419–445. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. C., Sternberg N. L. Using bacteriophage P1 system to clone high molecular weight genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:549–574. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16049-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Whittam T. S., Berg C. M., Berg D. E. RAPD (arbitrary primer) PCR is more sensitive than multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for distinguishing related bacterial strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5930–5933. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]