Abstract
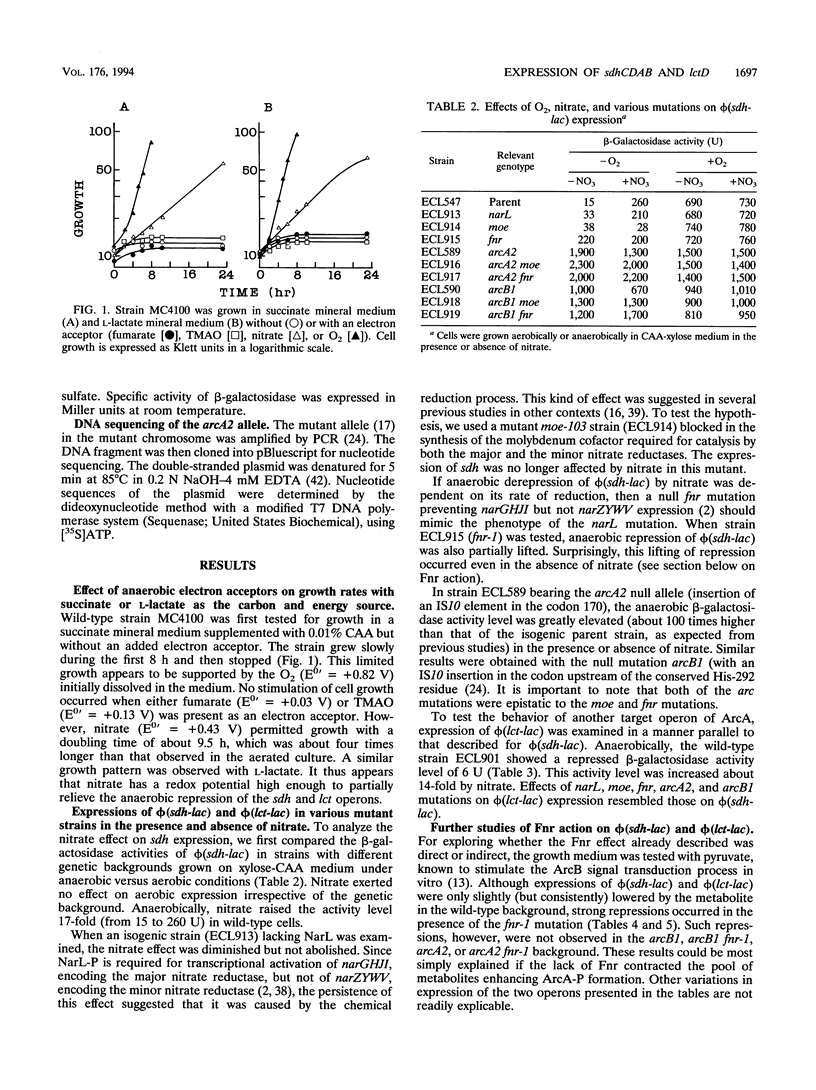
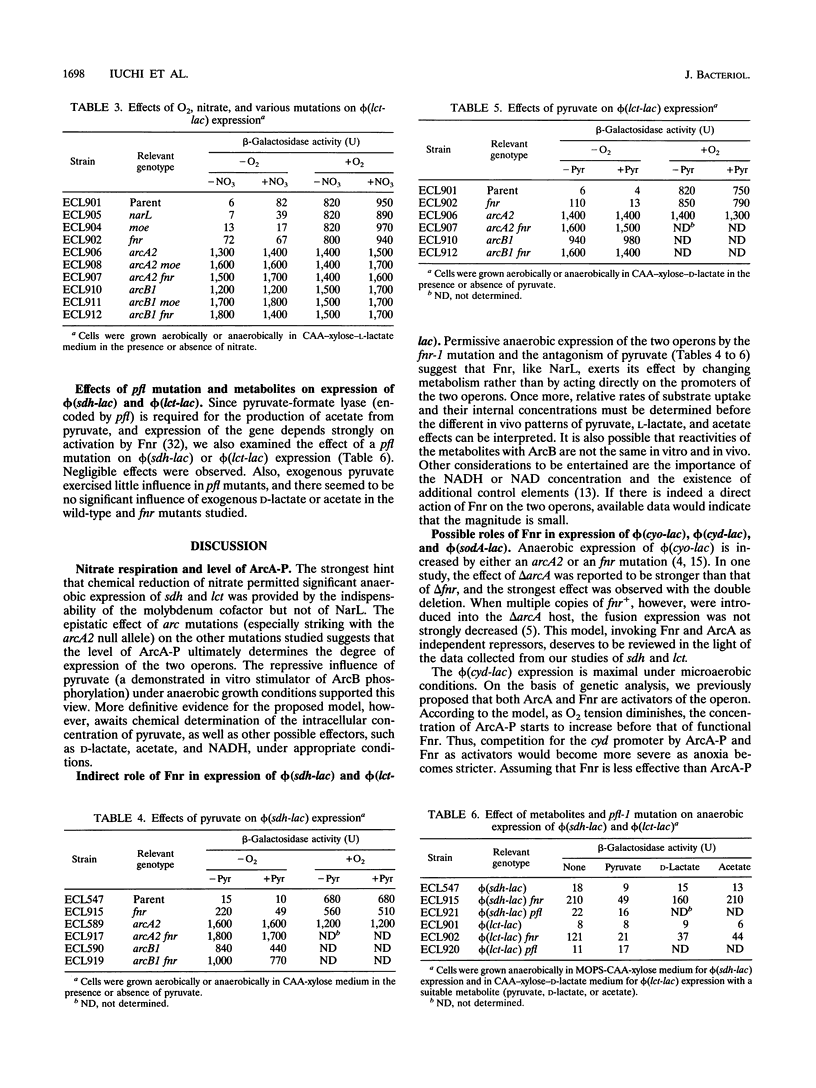
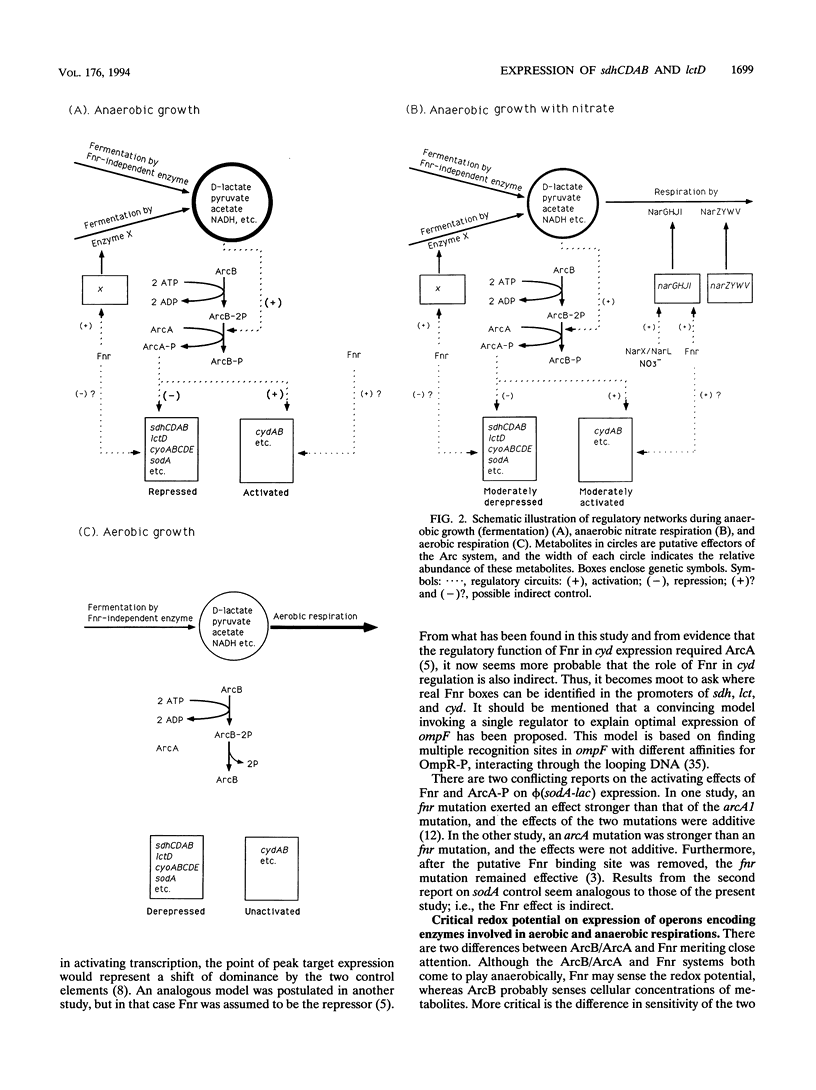
Expression of sdhCDAB (encoding succinate dehydrogenase) and lctD (encoding the flavin-linked L-lactate dehydrogenase) is elevated aerobically and repressed anaerobically in Escherichia coli. The repression is initiated by autophosphorylation of the sensor protein ArcB, followed by phosphoryl group transfer to the regulator ArcA. ArcA-P, a global transcriptional regulator, then prevents sdh and lct expression. The stimulus for ArcB is not O2 deficiency per se. In vitro experiments showed that ArcB phosphorylation is enhanced by pyruvate, D-lactate, acetate, and NADH, the concentrations of which are likely to increase with the lack of an effective exogenous electron sink. In addition to their aerobic function, the two primary dehydrogenases also have roles in anaerobic nitrate respiration. Results presented here indicate that the increase of sdh and lct expression by nitrate depended on its chemical reduction, which in turn diminished the ArcA-P pool. Unexpectedly, a mutation in the fnr gene (encoding a global regulator involved in anaerobic metabolism) also alleviated the anaerobic repressions. Mutations in arcB or arcA were epistatic over that of fnr. Moreover, since this relief was counteracted by pyruvate in the growth medium, Fnr appears to affect formation of stimuli for ArcB. It is possible that Fnr also indirectly affects some of the other members of the arcA modulon, e.g., cyoABCDE (encoding the cytochrome o complex), cydAB (encoding the cytochrome d complex), and sodA (encoding the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg B. L., Stewart V. Structural genes for nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):691–702. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy V., Burini J. F., Giordano G., Pascal M. C., Chippaux M. Presence in the 'silent' terminus region of the Escherichia coli K12 chromosome of cryptic gene(s) encoding a new nitrate reductase. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compan I., Touati D. Interaction of six global transcription regulators in expression of manganese superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1687-1696.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter P. A., Chepuri V., Gennis R. B., Gunsalus R. P. Cytochrome o (cyoABCDE) and d (cydAB) oxidase gene expression in Escherichia coli is regulated by oxygen, pH, and the fnr gene product. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6333–6338. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6333-6338.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter P. A., Gunsalus R. P. Contribution of the fnr and arcA gene products in coordinate regulation of cytochrome o and d oxidase (cyoABCDE and cydAB) genes in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Feb 1;70(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90558-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong J., Iuchi S., Kwan H. S., Lu Z., Lin E. C. The deduced amino-acid sequence of the cloned cpxR gene suggests the protein is the cognate regulator for the membrane sensor, CpxA, in a two-component signal transduction system of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1993 Dec 22;136(1-2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90469-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. R., Li S. F., DeMoss J. A. Upstream sequence elements required for NarL-mediated activation of transcription from the narGHJI promoter of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14122–14128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H. A., Iuchi S., Lin E. C. The requirement of ArcA and Fnr for peak expression of the cyd operon in Escherichia coli under microaerobic conditions. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00273605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Sharrocks A. D., Green B., Geisow M., Guest J. R. Properties of FNR proteins substituted at each of the five cysteine residues. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P. Control of electron flow in Escherichia coli: coordinated transcription of respiratory pathway genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7069–7074. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7069-7074.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Kalman L. V., Stewart R. R. Nucleotide sequence of the narL gene that is involved in global regulation of nitrate controlled respiratory genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1965–1975. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Sun H. C. Regulatory roles of Fnr, Fur, and Arc in expression of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3217–3221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Cameron D. C., Lin E. C. A second global regulator gene (arcB) mediating repression of enzymes in aerobic pathways of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):868–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.868-873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Chepuri V., Fu H. A., Gennis R. B., Lin E. C. Requirement for terminal cytochromes in generation of the aerobic signal for the arc regulatory system in Escherichia coli: study utilizing deletions and lac fusions of cyo and cyd. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6020–6025. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6020-6025.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Cole S. T., Lin E. C. Multiple regulatory elements for the glpA operon encoding anaerobic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and the glpD operon encoding aerobic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli: further characterization of respiratory control. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.179-184.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Furlong D., Lin E. C. Differentiation of arcA, arcB, and cpxA mutant phenotypes of Escherichia coli by sex pilus formation and enzyme regulation. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2889–2893. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2889-2893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Kuritzkes D. R., Lin E. C. Escherichia coli mutant with altered respiratory control of the frd operon. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1023–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1023-1028.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Adaptation of Escherichia coli to redox environments by gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Adaptation of Escherichia coli to respiratory conditions: regulation of gene expression. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Molybdenum effector of fumarate reductase repression and nitrate reductase induction in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3720–3725. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3720-3725.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Mutational analysis of signal transduction by ArcB, a membrane sensor protein responsible for anaerobic repression of operons involved in the central aerobic pathways in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3972–3980. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3972-3980.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Purification and phosphorylation of the Arc regulatory components of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5617–5623. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5617-5623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. The narL gene product activates the nitrate reductase operon and represses the fumarate reductase and trimethylamine N-oxide reductase operons in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3901–3905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. arcA (dye), a global regulatory gene in Escherichia coli mediating repression of enzymes in aerobic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1888–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Matsuda Z., Fujiwara T., Lin E. C. The arcB gene of Escherichia coli encodes a sensor-regulator protein for anaerobic repression of the arc modulon. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):715–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the receiver module at the conserved aspartate residue controls transphosphorylation activity of histidine kinase in sensor protein ArcB of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23972–23980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. F., DeMoss J. A. Location of sequences in the nar promoter of Escherichia coli required for regulation by Fnr and NarL. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13700–13705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C., Iuchi S. Regulation of gene expression in fermentative and respiratory systems in Escherichia coli and related bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:361–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Taniguchi S., Saito T. The narX and narL genes encoding the nitrate-sensing regulators of Escherichia coli are homologous to a family of prokaryotic two-component regulatory genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2947–2957. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page L., Griffiths L., Cole J. A. Different physiological roles of two independent pathways for nitrite reduction to ammonia by enteric bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(4):349–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00276530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Böck A. Anaerobic regulation of pyruvate formate-lyase from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5330–5336. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5330-5336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Suppmann B. Anaerobic induction of pyruvate formate-lyase gene expression is mediated by the ArcA and FNR proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3474–3478. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3474-3478.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slauch J. M., Silhavy T. J. cis-acting ompF mutations that result in OmpR-dependent constitutive expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4039–4048. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4039-4048.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Roberts R. E., Guest J. R. FNR-dependent repression of the ndh gene of Escherichia coli and metal ion requirement for FNR-regulated gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Berg B. L. Influence of nar (nitrate reductase) genes on nitrate inhibition of formate-hydrogen lyase and fumarate reductase gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4437–4444. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4437-4444.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., MacGregor C. H. Nitrate reductase in Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of chlC, chlE, and chlG loci. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):788–799. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.788-799.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V. Nitrate regulation of anaerobic respiratory gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):425–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Parales J., Jr, Merkel S. M. Structure of genes narL and narX of the nar (nitrate reductase) locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2229–2234. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2229-2234.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trageser M., Unden G. Role of cysteine residues and of metal ions in the regulatory functioning of FNR, the transcriptional regulator of anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson K. L., Bell A. I., Cole J. A., Busby S. J. Definition of nitrite and nitrate response elements at the anaerobically inducible Escherichia coli nirB promoter: interactions between FNR and NarL. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varenne S., Casse F., Chippaux M., Pascal M. C. A mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in pyruvate formate lyase. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Nov 24;141(2):181–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00267683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. S., DeMoss J. A. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation catalyzed in vitro by purified components of the nitrate sensing system, NarX and NarL. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8391–8393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



