Abstract
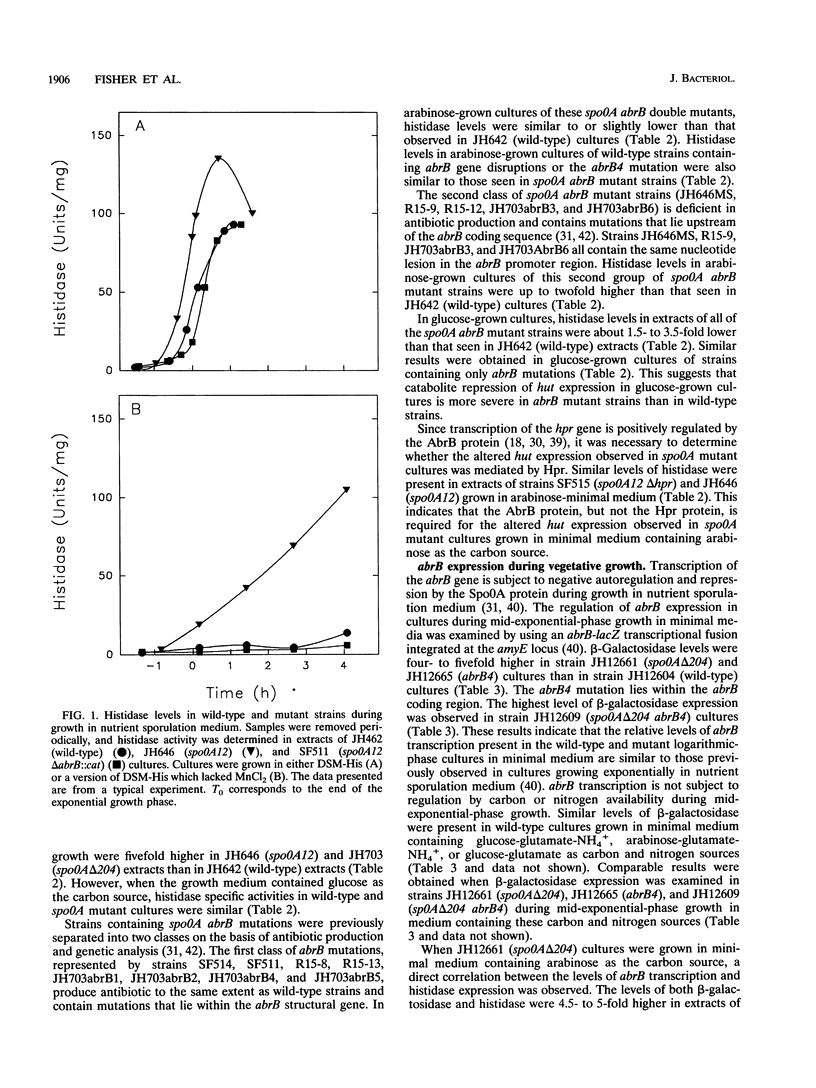
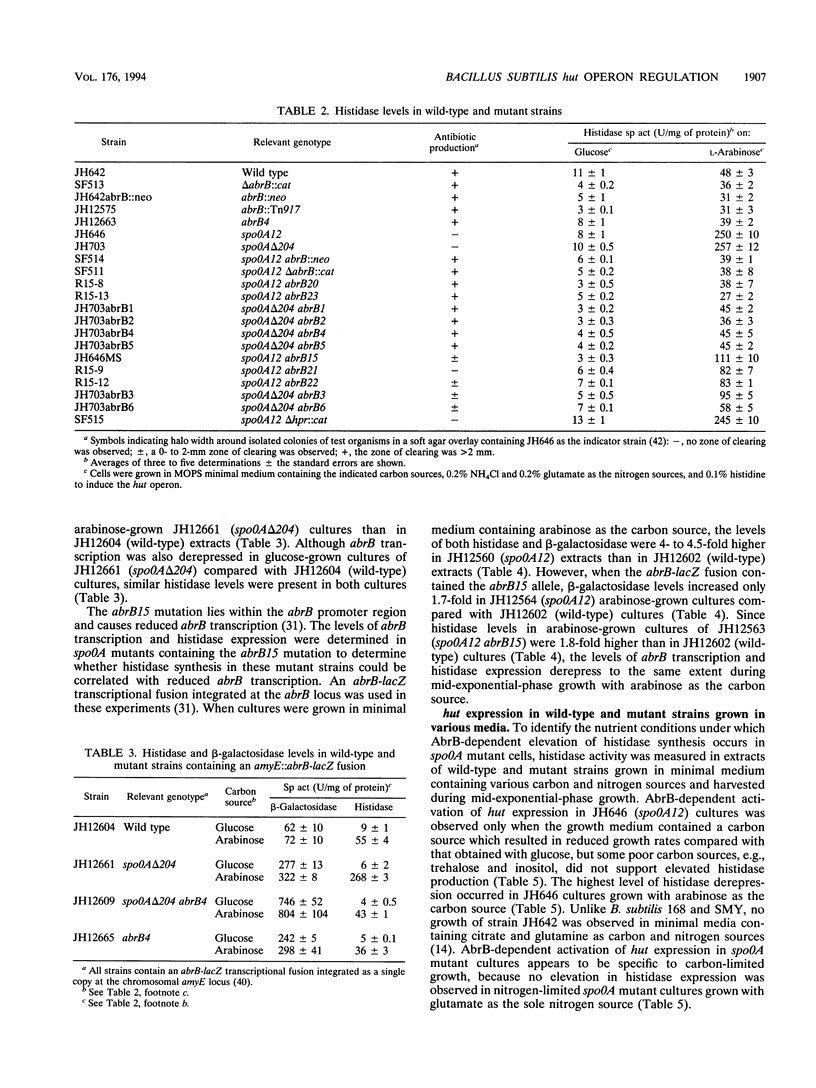
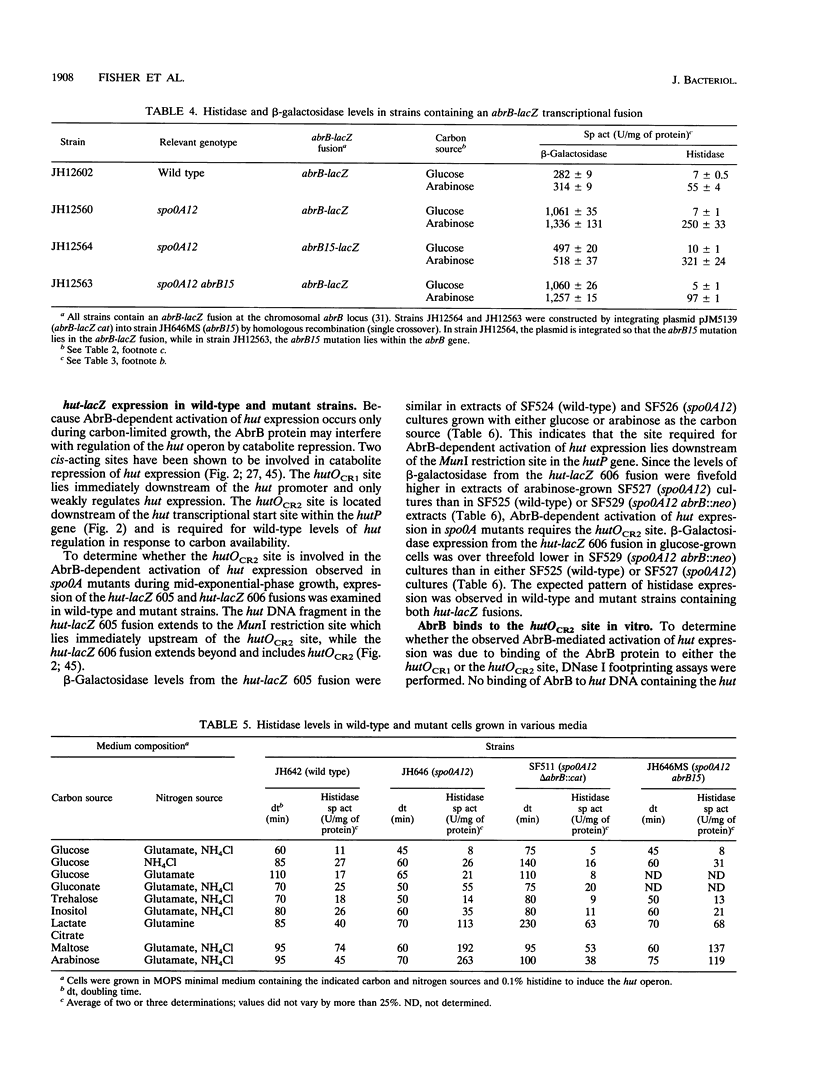
The first enzyme of the Bacillus subtilis histidine-degradative (hut) pathway, histidase, was expressed at higher levels during the onset of the stationary growth phase in nutrient sporulation medium in early-blocked sporulation mutants (spo0A) than in wild-type strains. Histidase expression was also elevated in spo0A mutant cultures compared with wild-type cultures during the logarithmic growth phase in minimal medium containing slowly metabolized carbon sources. Histidase expression was not derepressed in spo0A abrB mutant cultures under these growth conditions, suggesting that the AbrB protein is responsible for the derepression of histidase synthesis seen in spo0A mutant cultures. spo0A mutants contain higher levels of the AbrB protein than do wild-type strains because the Spo0A protein represses AbrB expression. A direct correlation between the levels of abrB transcription and histidase expression was found in spo0A mutant cultures. The hutOCR2 operator, which is required for wild-type regulation of hut expression by catabolite repression, was also required for AbrB-dependent derepression of hut expression in spo0A mutants. Purified AbrB protein bound to the hutOCR2 operator in vitro, suggesting that AbrB protein alters hut expression by competing with the hut catabolite repressor protein for binding to the hutOCR2 site. During the logarithmic growth phase in media containing slowly metabolized carbon sources, the expression of several other enzymes subject to catabolite repression was elevated in spo0A mutants but not in spo0A abrB mutants. This suggests that the AbrB protein acts as a global modulator of catabolite repression during carbon-limited growth.
Full text
PDF


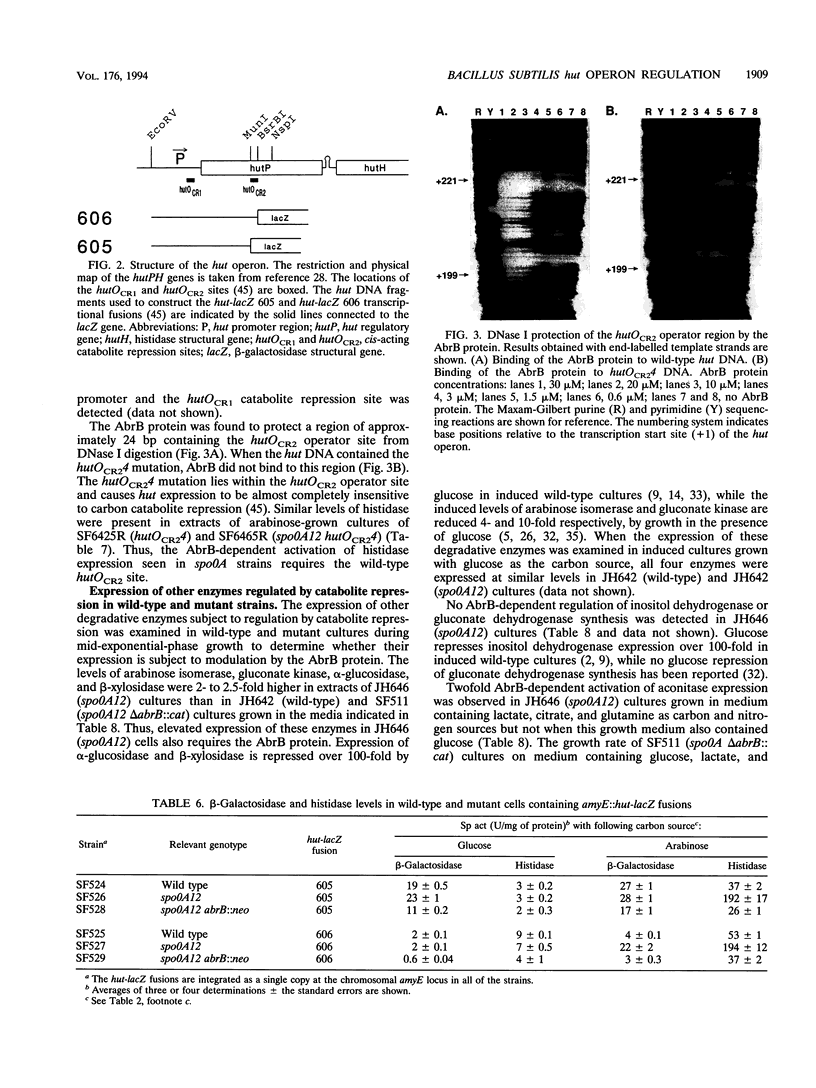
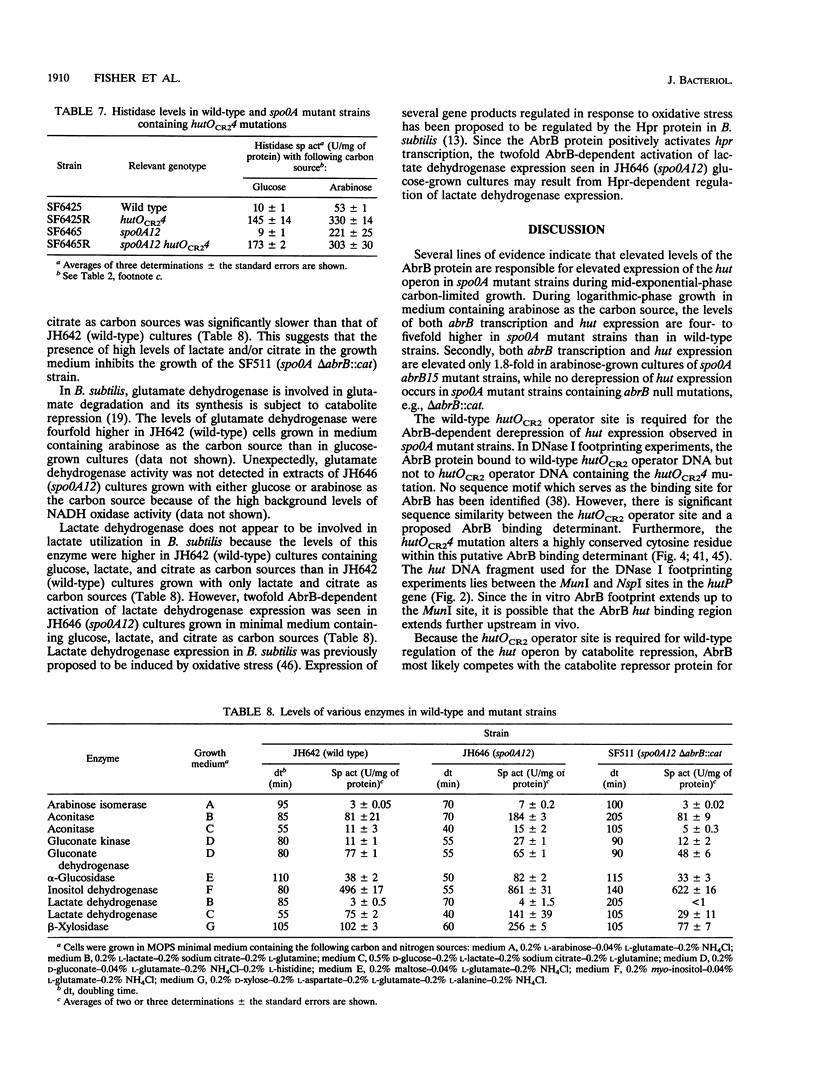


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Activation of the Bacillus subtilis hut operon at the onset of stationary growth phase in nutrient sporulation medium results primarily from the relief of amino acid repression of histidine transport. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4282–4289. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4282-4289.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Regulation of histidine and proline degradation enzymes by amino acid availability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4758–4765. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4758-4765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisschop A., de Jong L., Lima Costa M. E., Konings W. N. Relation between reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidation and amino acid transport in membrane vesicles from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):807–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Chun K. T., Edson B. A., Price C. W. Early-blocked sporulation mutations alter expression of enzymes under carbon control in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00334696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm S. P., Staal S. P., Hoch J. A. Phenotypes of pleiotropic-negative sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1063-1070.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. P., Prior S. E., Barstow D. A., Minton N. P. The pMTL nic- cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A., Magasanik B. Induction and repression of the histidine-degrading enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5165–5178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney P. H., Whiteman P. F., Freese E. Media dependence of commitment in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):901–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.901-907.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. 8. Patterns of enzyme development during growth and sporulation of Baccillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4653–4660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman D. W., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Relationship between aconitase gene expression and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3068–3075. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3068-3075.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowds B. C., Hoch J. A. Regulation of the oxidative stress response by the hpr gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 May;137(5):1121–1125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-5-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Sonenshein A. L. A target for carbon source-dependent negative regulation of the citB promoter of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):835–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.835-844.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Freese E. Isolation and properties of a Bacillus subtilis mutant unable to produce fructose-bisphosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.760-767.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürbass R., Gocht M., Zuber P., Marahiel M. A. Interaction of AbrB, a transcriptional regulator from Bacillus subtilis with the promoters of the transition state-activated genes tycA and spoVG. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):347–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00261673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallio P. T., Fagelson J. E., Hoch J. A., Strauch M. A. The transition state regulator Hpr of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13411–13417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. F., Wakim J., Fischer R. S. Regulation of glutamate dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):1002–1005. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.1002-1005.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiopoulos C., Mueller J. P., Slack F. J., Murphy C. G., Patankar S., Bukusoglu G., Sonenshein A. L. A Bacillus subtilis dipeptide transport system expressed early during sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1903–1913. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa Y., Fujita Y. Promoter-independent catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis gnt operon. J Biochem. 1993 Jun;113(6):665–671. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nihashi J., Fujita Y. Catabolite repression of inositol dehydrogenase and gluconate kinase syntheses in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 22;798(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Katagai T., Tomura D., Shoun H., Hoshino T., Furukawa K. Analysis of the transcriptional activity of the hut promoter in Bacillus subtilis and identification of a cis-acting regulatory region associated with catabolite repression downstream from the site of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2573–2582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Sugishita A., Furukawa K. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of histidase and regulatory genes in the Bacillus subtilis hut operon and positive regulation of the operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3199–3205. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3199-3205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohné M. Regulation of the dicarboxylic acid part of the citric acid cycle in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):224–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.224-234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Hoch J. A. Sequence analysis and regulation of the hpr locus, a regulatory gene for protease production and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2560–2567. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2560-2567.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Spiegelman G. B., Hoch J. A. Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer A., Deutscher J., Saier M. H., Jr, Reizer J. Analysis of the gluconate (gnt) operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1081–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncero M. I. Genes controlling xylan utilization by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):257–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.257-263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz M. S., Dingman D. W., Sonenshein A. L. Bacillus subtilis citB gene is regulated synergistically by glucose and glutamine. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):155–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.155-164.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Cami B., Brevet J., Cote R. Isolation and characterization of rifampin-resistant and streptolydigin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis with altered sporulation properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):253–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.253-265.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Hoch J. A. Transition-state regulators: sentinels of Bacillus subtilis post-exponential gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(3):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Perego M., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator AbrB of Bacillus subtilis is autoregulated during vegetative growth. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1203–1209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Spiegelman G. B., Perego M., Johnson W. C., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1615–1621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sá-Nogueira I., Paveia H., de Lencastre H. Isolation of constitutive mutants for L-arabinose utilization in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2855–2857. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2855-2857.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Freese E. The role of manganese in growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):329–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickert M. J., Chambliss G. H. Site-directed mutagenesis of a catabolite repression operator sequence in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6238–6242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Pettengill F. K., Fisher S. H. Catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis hut operon requires a cis-acting site located downstream of the transcription initiation site. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):1894–1902. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.1894-1902.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashphe J., Hoch J. A., Kaplan N. O. Regulation of lactate dehydrogenase synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]