Abstract
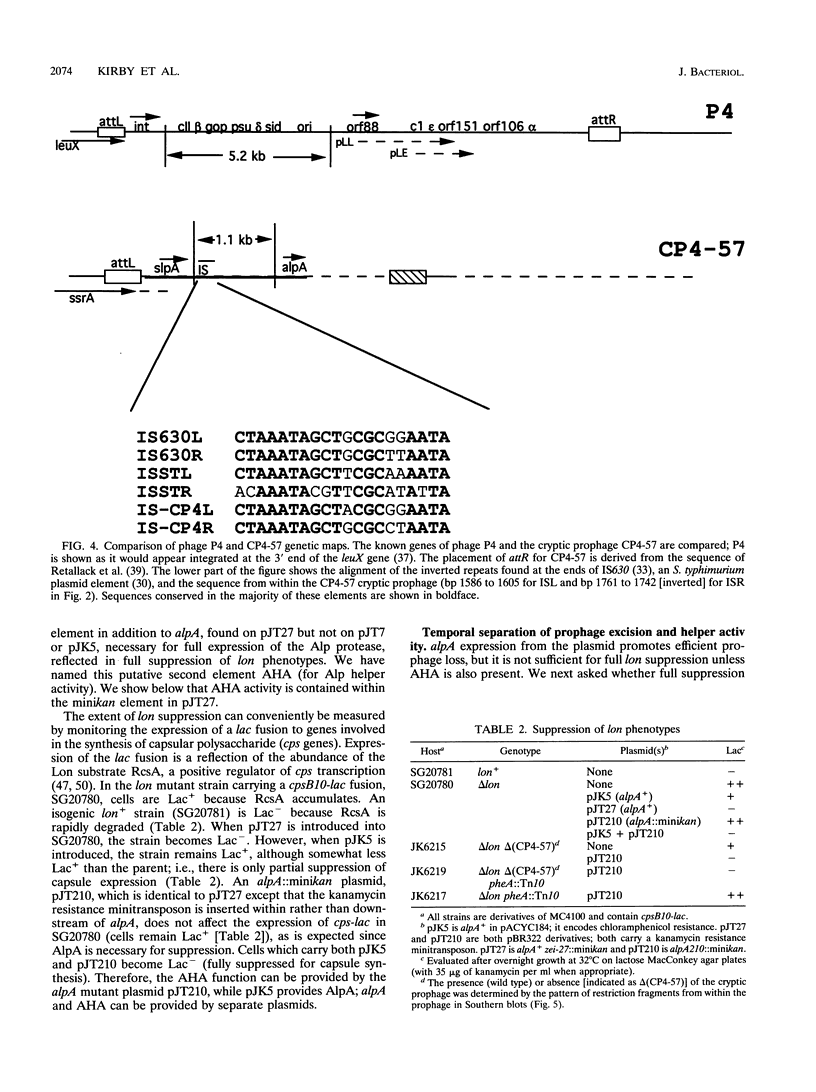
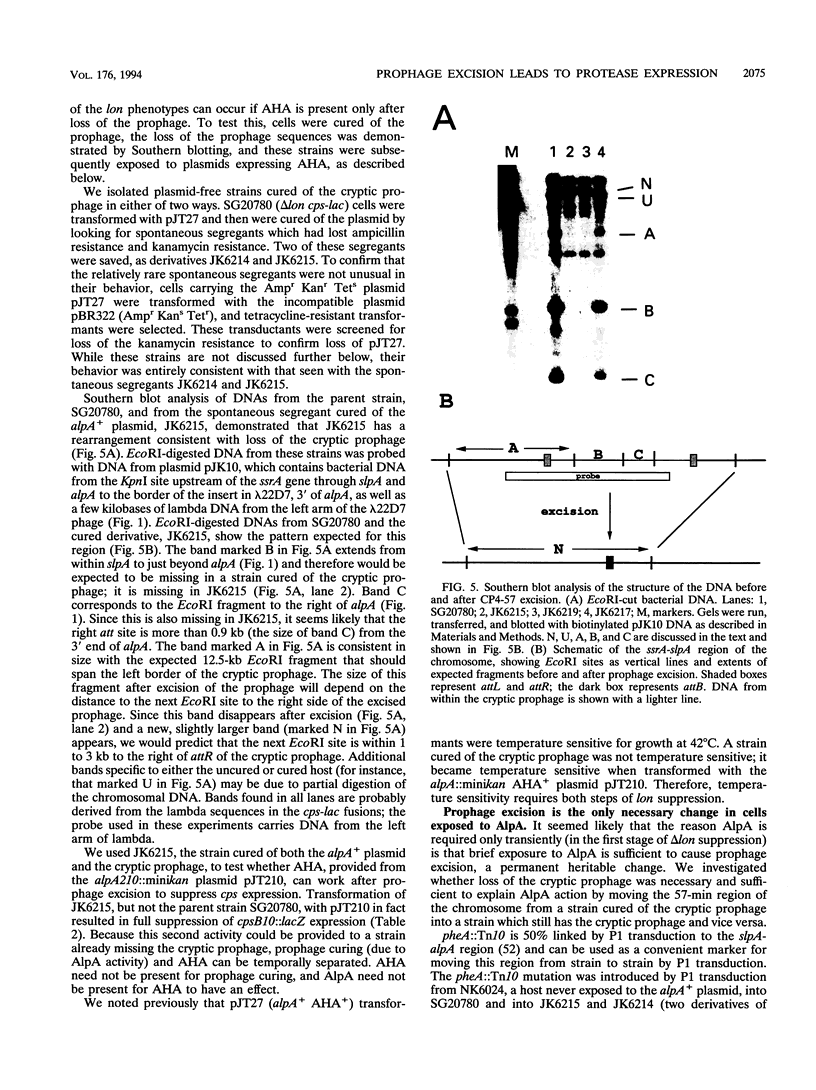
The Escherichia coli K-12 alpA gene product, when overproduced from a multicopy plasmid, leads to suppression of the capsule overproduction and UV sensitivity phenotypes of cells mutant for the Lon ATP-dependent protease. This suppression has previously been shown to correlate with increased in vivo activity of a previously unknown energy-dependent proteolytic activity capable of degrading Lon substrates, the Alp protease. We show in an accompanying paper that alpA, which has homology to a short open reading frame in bacteriophage P4, acts as a positive transcriptional regulator of slpA, a gene linked to alpA and necessary for suppression of lon mutants (J. E. Trempy, J. E. Kirby, and S. Gottesman, J. Bacteriol. 176:2061-2067). The sequence of slpA suggests that it encodes an integrase gene closely related to P4 int and that both alpA and slpA are part of a cryptic P4-like prophage. AlpA expression increases SlpA synthesis. Increased SlpA leads, in turn, to the excision and loss of the cryptic prophage. Excision is dependent on integration host factor as well as on SlpA. Prophage excision is necessary but not sufficient for full expression of the Alp protease. A second function (named AHA) allows full protease expression; this function can be provided by the kanamycin resistance element from Tn903 when the element is present on a multicopy plasmid. Excision and loss of the cryptic prophage apparently allow expression of the Alp protease by inactivating a small stable RNA (10Sa RNA) encoded by the ssrA gene. The precursor of this RNA has its 3' end within the cryptic prophage; the mature 3' end lies within the prophage attL site. Inactivation of ssrA by insertional mutagenesis is sufficient to allow expression of the suppressing Alp protease, even in the presence of the cryptic prophage. Therefore, 10Sa RNA acts as a negative regulator of protease synthesis or activity, and prophage excision must inactivate this inhibitory function of the RNA.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K. E., Hoess R. H. Evidence for a second conserved arginine residue in the integrase family of recombination proteins. Protein Eng. 1992 Jan;5(1):87–91. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. Phosphotransferase sequence homology. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):21–21. doi: 10.1038/329021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill J. A., Quinlan-Walshe C., Gottesman S. Fine-structure mapping and identification of two regulators of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2599–2611. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2599-2611.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Hunt D. A., Pace N. R. Nucleotide sequence of the 10Sa RNA gene of the beta-purple eubacterium Alcaligenes eutrophus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2820–2820. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Ljungquist E., Deho G., Usher D. C., Goldstein R., Youderian P., Sironi G., Six E. W. Lysogenization by satellite phage P4. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):20–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M. Chromosomal insertion sites for phages and plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7495–7499. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7495-7499.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan A. K., Apirion D. The gene for a small stable RNA (10Sa RNA) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1481–1485. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Calendar R. Interactions between satellite bacteriophage P4 and its helpers. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:465–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. A., Beltrame J., Manning P. A. The oac gene encoding a lipopolysaccharide O-antigen acetylase maps adjacent to the integrase-encoding gene on the genome of Shigella flexneri bacteriophage Sf6. Gene. 1991 Oct 30;107(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90295-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehó G., Zangrossi S., Ghisotti D., Sironi G. Alternative promoters in the development of bacteriophage plasmid P4. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1697-1704.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua W. C. An improved chloramphenicol resistance gene cassette for site-directed marker replacement mutagenesis. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):223–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Genetics of proteolysis in Escherichia coli*. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:163–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Maurizi M. R. Regulation by proteolysis: energy-dependent proteases and their targets. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):592–621. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.592-621.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Stout V. Regulation of capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1599–1606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling C., Sunshine M. G., Lane K. B., Six E. W., Calendar R. A mutation of the transactivation gene of satellite bacteriophage P4 that suppresses the rpoA109 mutation of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3541–3548. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3541-3548.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser M. A., Scocca J. J. Location of the host attachment site for phage HPl within a cluster of Haemophilus influenzae tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5305–5305. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser M. A., Scocca J. J. Site-specific integration of the Haemophilus influenzae bacteriophage HP1. Identification of the points of recombinational strand exchange and the limits of the host attachment site. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6859–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., Gottesman S. Cell-division control in Escherichia coli: specific induction of the SOS function SfiA protein is sufficient to block septation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Sunshine M. G., Six E. W., Inouye M. Retronphage phi R73: an E. coli phage that contains a retroelement and integrates into a tRNA gene. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):969–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1709758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby R. Evolutionary origin of aminoglycoside phosphotransferase resistance genes. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jun;30(6):489–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02101103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Harwood J., Fierer J., Guiney D. Genetic analysis of homology between the virulence plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1860–1863. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1860-1863.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. The phi 80 and P22 attachment sites. Primary structure and interaction with Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4468–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey D. F., Martínez C., Walker J. R. Physical map location of the Escherichia coli attachment site for the P22 prophage (attP22). J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3834–3835. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3834-3835.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsutani S., Ohtsubo H., Maeda Y., Ohtsubo E. Isolation and characterization of IS elements repeated in the bacterial chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh B. K., Apirion D. 10Sa RNA, a small stable RNA of Escherichia coli, is functional. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Sep;229(1):52–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00264212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh B. K., Chauhan A. K., Isono K., Apirion D. Location of a gene (ssrA) for a small, stable RNA (10Sa RNA) in the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4708–4709. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4708-4709.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson L. S., 3rd, Kahn M. L. Integration of satellite bacteriophage P4 in Escherichia coli. DNA sequences of the phage and host regions involved in site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Yeats S. Transfer RNA genes frequently serve as integration sites for prokaryotic genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retallack D. M., Johnson L. L., Friedman D. I. Role for 10Sa RNA in the growth of lambda-P22 hybrid phage. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):2082–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.2082-2089.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Miller W., Werner C., Ostell J., Tolstoshev C., Satterfield S. G. Mapping sequenced E.coli genes by computer: software, strategies and examples. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):637–647. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Haggård-Ljungquist E., Nordström K. Activation of prophage P4 by the P2 Cox protein and the sites of action of the Cox protein on the two phage genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker J. M., Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: SOS induction and cellular location of the sulA protein, a key to lon-associated filamentation and death. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.551-561.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Baumann M., Friedman D. I., Baron L. S. Identification and characterization of mutations in Escherichia coli that selectively influence the growth of hybrid lambda bacteriophages carrying the immunity region of bacteriophage P22. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):191–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.191-200.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Inouye M., Inouye S. Association of a retroelement with a P4-like cryptic prophage (retronphage phi R73) integrated into the selenocystyl tRNA gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4171–4181. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4171-4181.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Cabassa A. S., Gottesman S. Capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 is regulated by proteolysis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):981–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.981-989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Gottesman S. Alp, a suppressor of lon protease mutants in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3348–3353. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3348-3353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Kirby J. E., Gottesman S. Alp suppression of Lon: dependence on the slpA gene. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):2061–2067. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.2061-2067.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi J. S., Kinger A. K. Identification of the 10Sa RNA structural gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):138–138. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



