Abstract
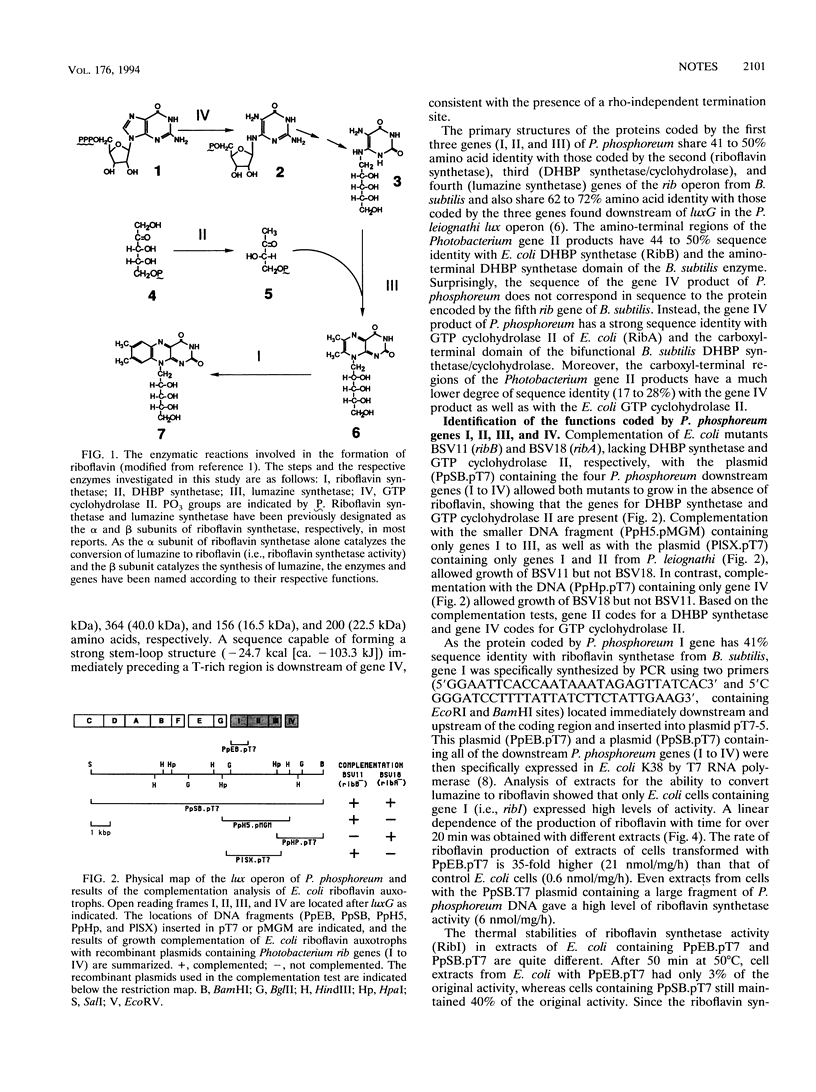
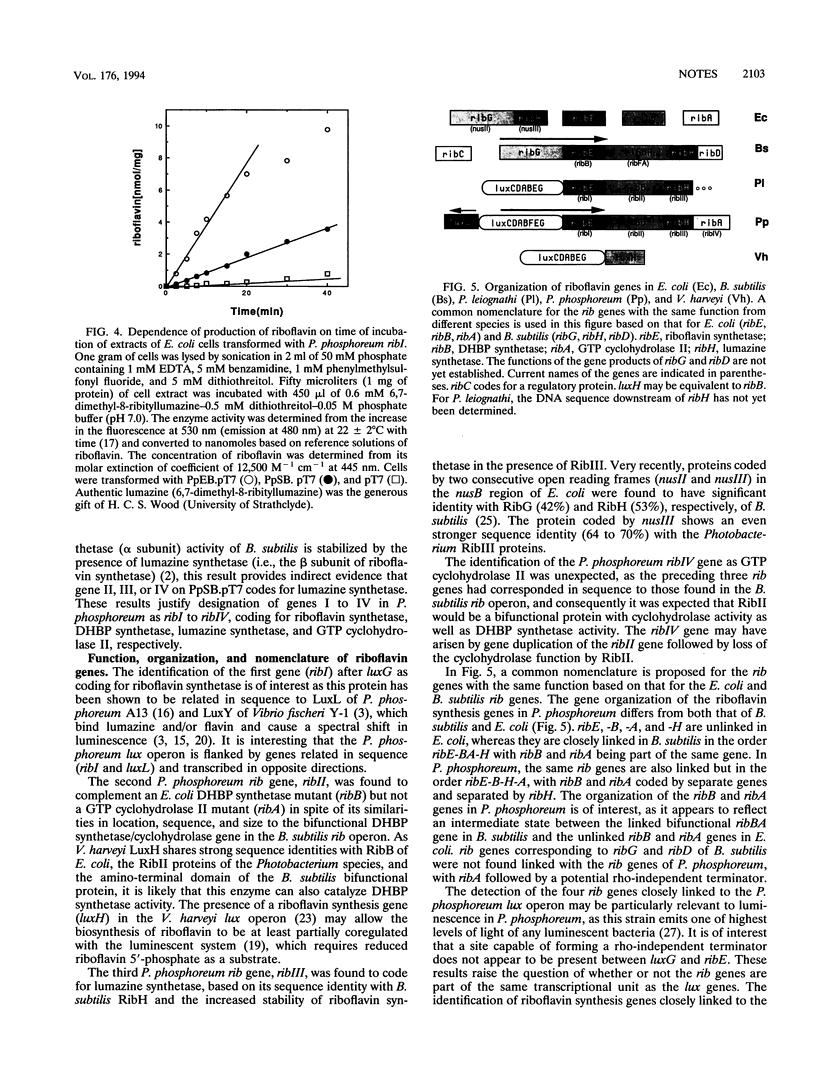
Four genes immediately downstream of luxG in the Photobacterium phosphoreum lux operon (ribEBHA) have been sequenced and shown to be involved in riboflavin synthesis. Sequence analyses and complementation of Escherichia coli riboflavin auxotrophs showed that the gene products of ribB and ribA are 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate (DHBP) synthetase and GTP cyclohydrolase II, respectively. By expression of P. phosphoreum ribE in E. coli using the bacteriophage T7 promoter-RNA polymerase system, ribE was shown to code for riboflavin synthetase, which catalyzes the conversion of lumazine to riboflavin. Increased thermal stability of RibE on expression with RibH indicated that ribH coded for lumazine synthetase. The organization of the rib genes in P. phosphoreum is quite distinct, with ribB and ribA being linked but separated by ribH, whereas in E. coli, they are unlinked and in Bacillus subtilis, RibB and RibA functions are coded by a single gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacher A., Baur R., Eggers U., Harders H. D., Otto M. K., Schnepple H. Riboflavin synthases of Bacillus subtilis. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):632–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. O., Treat M. L., Daubner S. C. Cloning and expression of the luxY gene from Vibrio fischeri strain Y-1 in Escherichia coli and complete amino acid sequence of the yellow fluorescent protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5509–5515. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandrin S. V., Rabinovich P. M., Stepanov A. I. Tri gruppy stsepleniia genov biosinteza riboflavina Escherichia coli. Genetika. 1983 Sep;19(9):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikindas M. L., Luk'ianov E. V., Rabinovich P. M., Stepanov A. I. Izuchenie oblasti 210 gradusov khromosomy Bacillus subtilis s pomoshch'iu rekombinantnykh plazmid. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1987 Feb;(2):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Meighen E. A. The lux genes in Photobacterium leiognathi are closely linked with genes corresponding in sequence to riboflavin synthesis genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90802-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H. C., Lottspeich F., Henschen A., Ladenstein R., Bacher A. Heavy riboflavin synthase of Bacillus subtilis. Primary structure of the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1016–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini J. A., Boylan M., Soly R. R., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Cloning and expression of the Photobacterium phosphoreum luminescence system demonstrates a unique lux gene organization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14308–14314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Dunlap P. V. Physiological, biochemical and genetic control of bacterial bioluminescence. Adv Microb Physiol. 1993;34:1–67. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):123–142. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.123-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironov V. N., Chikindas M. L., Kraev A. S., Stepanov A. I., Skriabin K. G. Operonnaia organozatsiia genov biosinteza riboflavina Bacillus subtilis. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1990;312(1):237–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironov V. N., Kraev A. S., Chernov B. K., Ul'ianov A. V., Golova Iu B. Geny biosinteza riboflavina Bacillus subtilis--polnaia pervichnaia struktura i model' organizatsii. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1989;305(2):482–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Meighen E. A., Graham A. F. Transcriptional regulation of lux genes transferred into Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2046–2054. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2046-2054.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane D. J., Prasher D. C. Evolutionary origins of bacterial bioluminescence. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane D. J., Woodward B., Lee J., Prasher D. C. Borrowed proteins in bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. K., Bacher A. Ligand-binding studies on light riboflavin synthase from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):511–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter G., Ritz H., Katzenmeier G., Volk R., Kohnle A., Lottspeich F., Allendorf D., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin: cloning, sequencing, mapping, and expression of the gene coding for GTP cyclohydrolase II in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4045–4051. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4045-4051.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter G., Volk R., Krieger C., Lahm H. W., Röthlisberger U., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin: cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4050–4056. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4050-4056.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. A luminous bacterium that emits yellow light. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):432–434. doi: 10.1126/science.850787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott K., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Bacher A. Riboflavin synthases of Bacillus subtilis. Purification and amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4204–4209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzman E., Miyamoto C., Graham A., Meighen E. Delineation of the transcriptional boundaries of the lux operon of Vibrio harveyi demonstrates the presence of two new lux genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3513–3517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taura T., Ueguchi C., Shiba K., Ito K. Insertional disruption of the nusB (ssyB) gene leads to cold-sensitive growth of Escherichia coli and suppression of the secY24 mutation. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):429–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00538702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesliar G. E., Shavlovskii G. M. Lokalizatsiia genov, kodiruiushchikh GTF-tsiklogidrolazu II i riboflavinsintazu na khromosome Escherichia coli K-12. Tsitol Genet. 1983 Sep-Oct;17(5):54–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., Rodriquez A., Meighen E. Differential acylation in vitro with tetradecanoyl coenzyme A and tetradecanoic acid (+ATP) of three polypeptides shown to have induced synthesis in Photobacterium phosphoreum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



