Abstract
In the photosynthetic cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942, the sphS and sphR genes were previously suggested to encode a typical pair of two-component signal transduction proteins. A deletion mutant strain lacking these genes failed to exhibit induction of alkaline phosphatase, the phoA gene product, in response to phosphate limitation in the medium. The SphR protein was overexpressed in Escherichia coli and then purified to near homogeneity. A truncated form of the SphS polypeptide (named SphS*) was also isolated. Here, we demonstrate that purified SphR is phosphorylated by phosphotransfer from SphS and binds to two distinct sites upstream from the phoA promoter. From these results, we conclude that the SphS and SphR proteins are directly involved in the regulation of phoA transcription in response to phosphate limitation in Synechococcus species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Nagaya M., Mizuno T. Sensor and regulator proteins from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus species PCC7942 that belong to the bacterial signal-transduction protein families: implication in the adaptive response to phosphate limitation. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):81–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Nakasai F., Mizushima S., Mizuno T. Evidence for the physiological importance of the phosphotransfer between the two regulatory components, EnvZ and OmpR, in osmoregulation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14090–14094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Grossman A. R. Identification and Purification of a Derepressible Alkaline Phosphatase from Anacystis nidulans R2. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1179–1184. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis P. R., Reilly P. A., Miedel M. C., Nelson N. Structure and targeted mutagenesis of the gene encoding 8-kDa subunit of photosystem I from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18374–18380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. L., Grossman A. R. Chlorosis induced by nutrient deprivation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942: not all bleaching is the same. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4718–4726. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4718-4726.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillo J. F., Gibson J. Regulation of phosphate accumulation in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):508–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.508-517.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihlenfeldt M. J., Gibson J. Phosphate utilization and alkaline phosphatase activity in Anacystis nidulans (Synechococcus). Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00428340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo Y. L., Nara F., Ichihara S., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Purification and characterization of the OmpR protein, a positive regulator involved in osmoregulatory expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15252–15256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J., Scappino L., Haselkorn R. The patA gene product, which contains a region similar to CheY of Escherichia coli, controls heterocyst pattern formation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., McCleary W. R., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Phosphorylation of bacterial response regulator proteins by low molecular weight phospho-donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Kawamoto T., Yamada M., Nakata A. Signal transduction in the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli involves phosphotransfer between PhoR and PhoB proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Kimura S., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Regulation of the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. Activation of pstS transcription by PhoB protein in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Tokishita S., Aiba H., Mizuno T. A novel sensor-regulator protein that belongs to the homologous family of signal-transduction proteins involved in adaptive responses in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Sugiura A., Kanamaru K., Mizuno T. Signal transduction between the two regulatory components involved in the regulation of the kdpABC operon in Escherichia coli: phosphorylation-dependent functioning of the positive regulator, KdpE. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):109–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
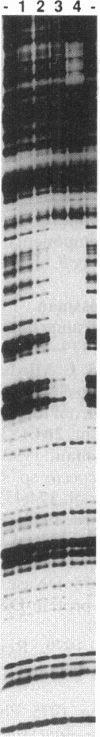
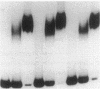
- Ray J. M., Bhaya D., Block M. A., Grossman A. R. Isolation, transcription, and inactivation of the gene for an atypical alkaline phosphatase of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4297–4309. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4297-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluchter W. M., Bryant D. A. Molecular characterization of ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase in cyanobacteria: cloning and sequence of the petH gene of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 and studies on the gene product. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3092–3102. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Wilmes-Riesenberg M. R. Involvement of phosphotransacetylase, acetate kinase, and acetyl phosphate synthesis in control of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2124–2130. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2124-2130.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]