Abstract
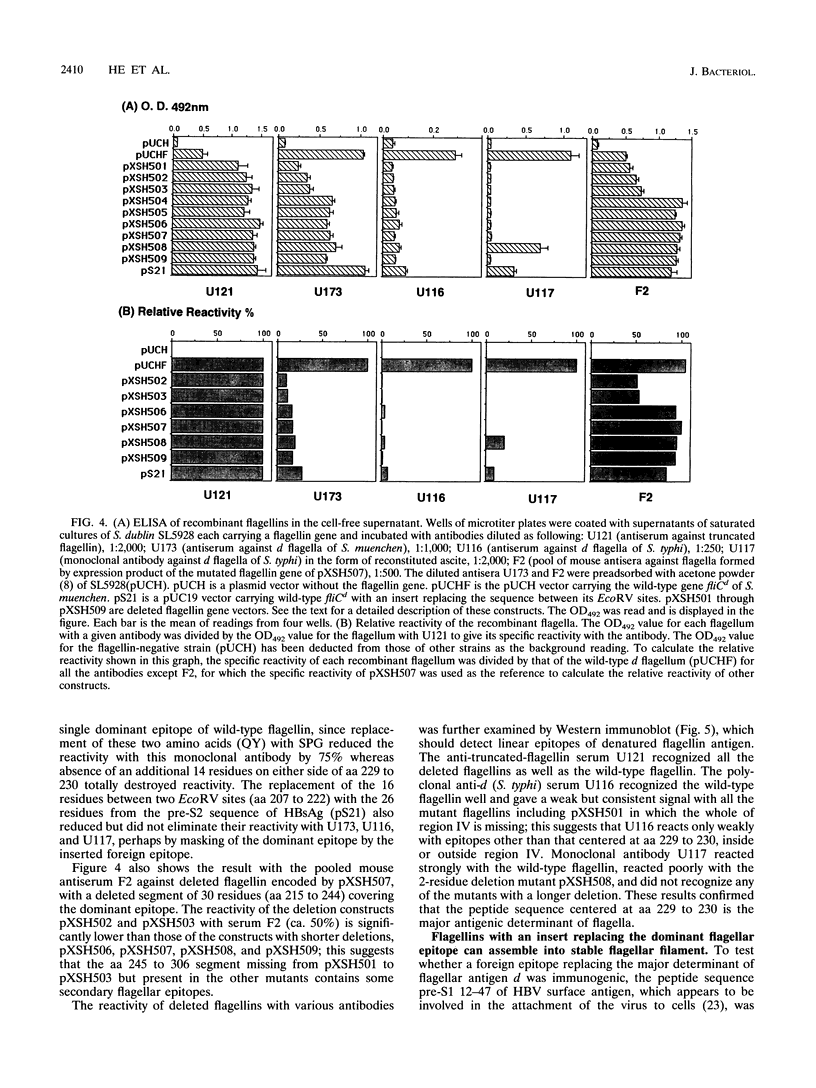
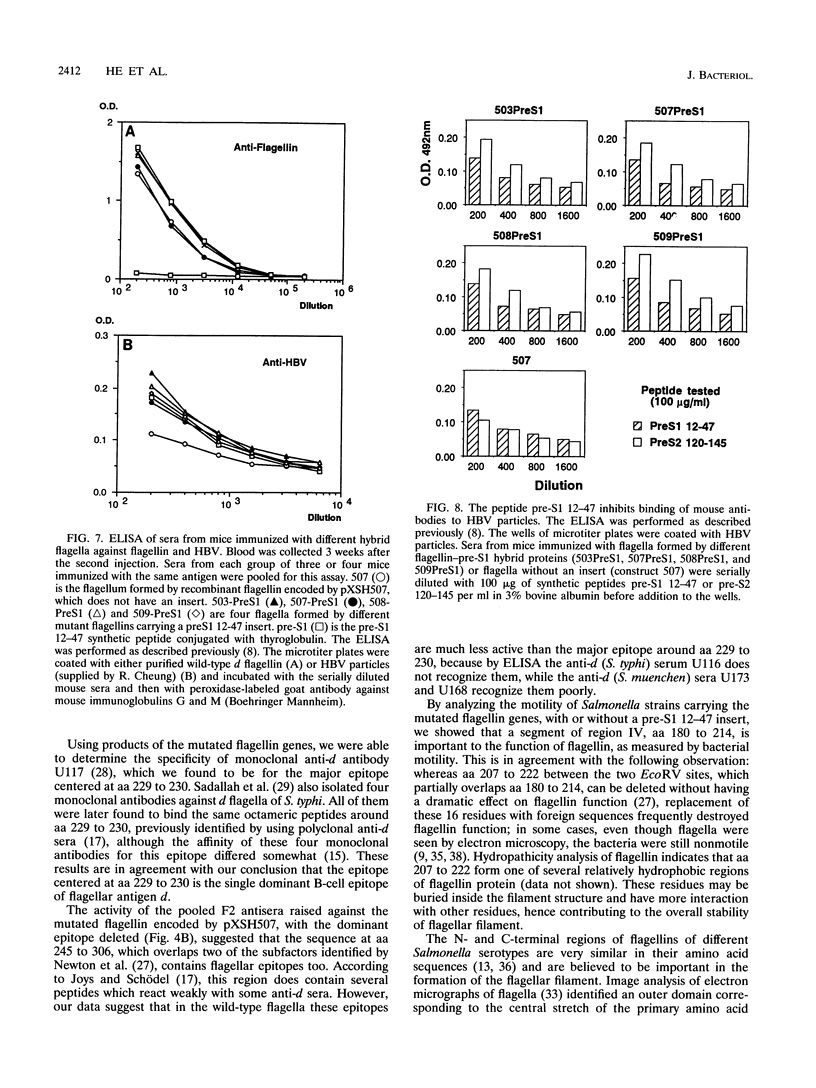
To identify the major antigenic determinant of native Salmonella flagella of antigenic type d, we constructed a series of mutated fliCd genes with deletions and amino acid alterations in hypervariable region IV and in region of putative epitopes as suggested by epitope mapping with synthetic octameric peptides (T.M. Joys and F. Schödel, Infect. Immun. 59:3330-3332, 1991). The expressed product of most of the mutant genes, with deletions of up to 92 amino acids in region IV, assembled into functional flagella and conferred motility on flagellin-deficient hosts. Serological analysis of these flagella with different anti-d antibodies revealed that the peptide sequence centered at amino acids 229 to 230 of flagellin was a dominant B-cell epitope at the surface of d flagella, because replacement of these two amino acids alone or together with their flanking sequence by a tripeptide specified by a linker sequence eliminated most reactivity with antisera against wild-type d flagella as tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or by Western immunoblot. Functional analysis of the mutated flagellin genes with or without an insert suggested that amino acids 180 to 214 in the 5' part of hypervariable region IV (residues 181 to 307 of the total of 505) is important to the function of flagella. The hybrid proteins formed by insertion of peptide sequence pre-S1 12-47 of hepatitis B virus surface antigen into the deleted flagellins assembled into functional flagella, and antibody to the pre-S1 sequence was detected after immunization of mice with the hybrid protein. This suggests that such mutant flagellins containing heterologous epitopes have potential as vaccines.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullas L. R., Ryu J. I. Salmonella typhimurium LT2 strains which are r- m+ for all three chromosomally located systems of DNA restriction and modification. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):471–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.471-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll L., Frankel G. Cloning and sequencing of two new fli genes, the products of which are essential for Salmonella flagellar biosynthesis. Gene. 1993 Apr 15;126(1):119–121. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto M., Stocker B. A. Transduction by phage P1kc in Salmonella typhimurium. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel G., Newton S. M., Schoolnik G. K., Stocker B. A. Intragenic recombination in a flagellin gene: characterization of the H1-j gene of Salmonella typhi. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3149–3152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel G., Newton S. M., Schoolnik G. K., Stocker B. A. Unique sequences in region VI of the flagellin gene of Salmonella typhi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1379–1383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim G. F., Fleet G. H., Lyons M. J., Walker R. A. Method for the isolation of highly purified Salmonella flagellins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1040–1044. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1040-1044.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics and chemistry of bacterial flagella. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):454–475. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.454-475.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOYS T. M., STOCKER B. A. Mutation and recombination of flagellar antigen i of Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1963 Jan 26;197:413–414. doi: 10.1038/197413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M., Schödel F. Epitope mapping of the d flagellar antigen of Salmonella muenchen. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3330–3332. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3330-3332.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M., Stocker B. A. Isolation and serological analysis of mutant forms of flagellar antigen i of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jul;44(1):121–138. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M., Stocker B. A. Recombination in H1, the gene determining the flagellar antigen-i of Salmonella typhimurium; mapping of H1 and fla mutations. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Oct;58(2):267–275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G. Construction of a minimum-size functional flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3305–3309. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3305-3309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Yamashita I., Vonderviszt F. Structure of the core and central channel of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):648–654. doi: 10.1038/342648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Jacob C. O., Stocker B. A. Immune response to cholera toxin epitope inserted in Salmonella flagellin. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2468182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Kotb M., Poirier T. P., Stocker B. A., Beachey E. H. Expression and immunogenicity of a streptococcal M protein epitope inserted in Salmonella flagellin. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2158–2165. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2158-2165.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Wasley R. D., Wilson A., Rosenberg L. T., Miller J. F., Stocker B. A. Segment IV of a Salmonella flagellin gene specifies flagellar antigen epitopes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):419–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri A., Ghosh S., Upadhyay S., Talwar G. P. Monoclonal antibodies against flagellar antigen of Salmonella typhi. Hybridoma. 1989 Jun;8(3):353–360. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadallah F., Brighouse G., Del Giudice G., Drager-Dayal R., Hocine M., Lambert P. H. Production of specific monoclonal antibodies to Salmonella typhi flagellin and possible application to immunodiagnosis of typhoid fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):59–64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Ground squirrel hepatitis virus DNA: molecular cloning and comparison with hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):393–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.393-397.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the flagellar filament of Caulobacter crescentus. A flagellin lacking the outer domain and its amino acid sequence lacking an internal segment. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):787–808. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional structure of the frozen-hydrated flagellar filament. The left-handed filament of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):581–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. The nucleotide sequence of the H-1r gene of Salmonella rubislaw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8227–8227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Newton S., Judd A., Stocker B., Robinson W. S. Expression of immunogenic epitopes of hepatitis B surface antigen with hybrid flagellin proteins by a vaccine strain of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]