Abstract
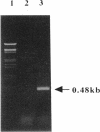
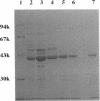
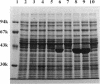
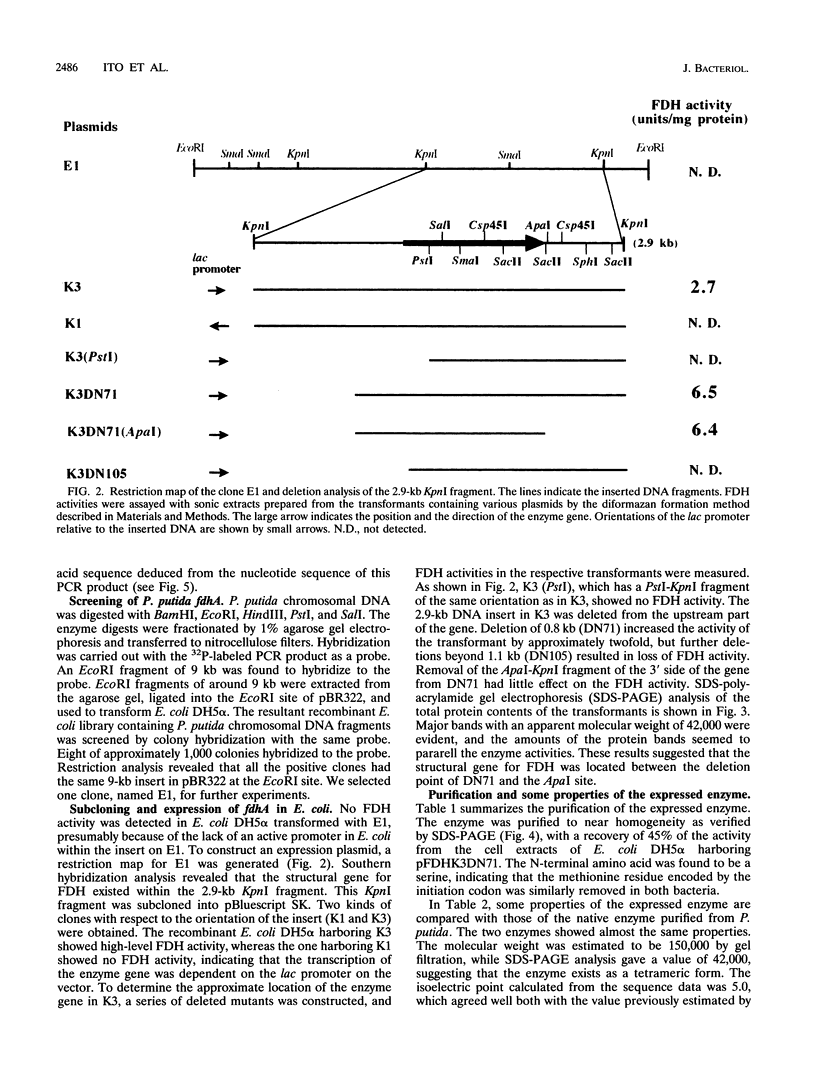
A DNA fragment of 485 bp was specifically amplified by PCR with primers based on the N-terminal sequence of the purified formaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.46) from Pseudomonas putida and on that of a cyanogen bromide-derived peptide. With this product as a probe, a gene coding for formaldehyde dehydrogenase (fdhA) in P. putida chromosomal DNA was cloned in Escherichia coli DH5 alpha. Sequencing analysis revealed that the fdhA gene contained 1,197-bp open reading frame, encoding a protein composed of 399 amino acid residues whose calculated molecular weight was 42,082. The transformant of E. coli DH5 alpha harboring the hybrid plasmid, pFDHK3DN71, showed about 50-fold-higher formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity than P. putida. The predicted amino acid sequence contained several features characteristic of the zinc-containing medium-chain alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) family. Most of the glycine residues strictly conserved within the family, including a Gly-Xaa-Gly-Xaa-Xaa-Gly pattern in the coenzyme binding domain, were well conserved in this enzyme. Regions around both the catalytic and the structural zinc atoms were also conserved. Analyses of structural and enzymatic characteristics indicated that P. putida FDH belongs to the medium-chain ADH family, with mixed properties of mammalian class I and III ADHs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammendola S., Raia C. A., Caruso C., Camardella L., D'Auria S., De Rosa M., Rossi M. Thermostable NAD(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase from Sulfolobus solfataricus: gene and protein sequence determination and relationship to other alcohol dehydrogenases. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12514–12523. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando M., Yoshimoto T., Ogushi S., Rikitake K., Shibata S., Tsuru D. Formaldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. Purification and some properties. J Biochem. 1979 May;85(5):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson B. D., Somerville R. L., Epperly B. R., Dekker E. E. The primary structure of Escherichia coli L-threonine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5226–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson O., Jörnvall H. "Enzymogenesis": classical liver alcohol dehydrogenase origin from the glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Sachs M. M., Gerlach W. L., Finnegan E. J., Peacock W. J. Molecular analysis of the alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (Adh2) gene of maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):727–743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggeling L., Sahm H. The formaldehyde dehydrogenase of Rhodococcus erythropolis, a trimeric enzyme requiring a cofactor and active with alcohols. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Horjales E., Jörnvall H., Brändén C. I., Jeffery J. Molecular aspects of functional differences between alcohol and sorbitol dehydrogenases. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8005–8012. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Müller-Wille P., Horjales E., Futer O., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L., Hög J. O., Kaiser R., Jörnvall H. Comparison of three classes of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Emphasis on different substrate binding pockets. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Nordström B., Zeppezauer E., Söderlund G., Ohlsson I., Boiwe T., Söderberg B. O., Tapia O., Brändén C. I., Akeson A. Three-dimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2-4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):27–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri P. R., Krug J. F., Kozak C., Moretti T., O'Brien S. J., Seuanez H. N., Goldman D. Cloning and comparative mapping of a human class III (chi) alcohol dehydrogenase cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91741-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutheil W. G., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Purification, characterization, and partial sequence of the glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli: a class III alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):475–481. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Human liver class III alcohol and glutathione dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase are the same enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1371–1377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91045-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Eklund H., Brändén C. I. Subunit conformation of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8414–8419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Hempel J., Vallee B. Structures of human alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases. Enzyme. 1987;37(1-2):5–18. doi: 10.1159/000469237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Persson B., Jeffery J. Characteristics of alcohol/polyol dehydrogenases. The zinc-containing long-chain alcohol dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser R., Holmquist B., Hempel J., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H. Class III human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: a novel structural type equidistantly related to the class I and class II enzymes. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1132–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser R., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H. Characteristics of mammalian class III alcohol dehydrogenases, an enzyme less variable than the traditional liver enzyme of class I. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8432–8438. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson C., Hög J. O. Zinc coordination in mammalian sorbitol dehydrogenase. Replacement of putative zinc ligands by site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):103–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazono A., Yoshimoto T., Tsuru D. Cloning, sequencing, and high expression of the proline iminopeptidase gene from Bacillus coagulans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):7919–7925. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.7919-7925.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi R., Tarr G. E. [Protein sequencing analysis by manual Edman degradation]. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1986 Aug;31(10):991–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivusalo M., Baumann M., Uotila L. Evidence for the identity of glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and class III alcohol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K., Ye R., Wu X. C., Wong S. L. Sorbitol dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis. Purification, characterization, and gene cloning. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24989–24994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogushi S., Ando M., Tsuru D. Formaldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida: a zinc metalloenzyme. J Biochem. 1984 Nov;96(5):1587–1591. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. H., Plapp B. V. Isoenzymes of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase active on ethanol and steroids. cDNA cloning, expression, and comparison of active sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13296–13302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakihama N., Ohmori H., Sugimoto N., Yamasaki Y., Oshino R., Shin M. Toyopearl HW-65C: ammonium sulfate as a new column chromatographic adsorbent for enzyme purification. J Biochem. 1983 Jan;93(1):129–134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Characterization of human alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes by high-performance liquid chromatographic peptide mapping. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):422–429. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila L., Koivusalo M. Formaldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Purification, properties, and evidence for the formation of glutathione thiol esters by the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7653–7663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner F. W., Parés X., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Physical and enzymatic properties of a class III isozyme of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: chi-ADH. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2193–2199. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Murayama N., Honda T., Tone H., Tsuru D. Cloning and expression of aminopeptidase P gene from Escherichia coli HB101 and characterization of expressed enzyme. J Biochem. 1988 Jul;104(1):93–97. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ophem P. W., Duine J. A. Microbial alcohol, aldehyde and formate ester oxidoreductases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;328:605–620. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2904-0_63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ophem P. W., Van Beeumen J., Duine J. A. NAD-linked, factor-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase or trimeric, zinc-containing, long-chain alcohol dehydrogenase from Amycolatopsis methanolica. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]