Abstract
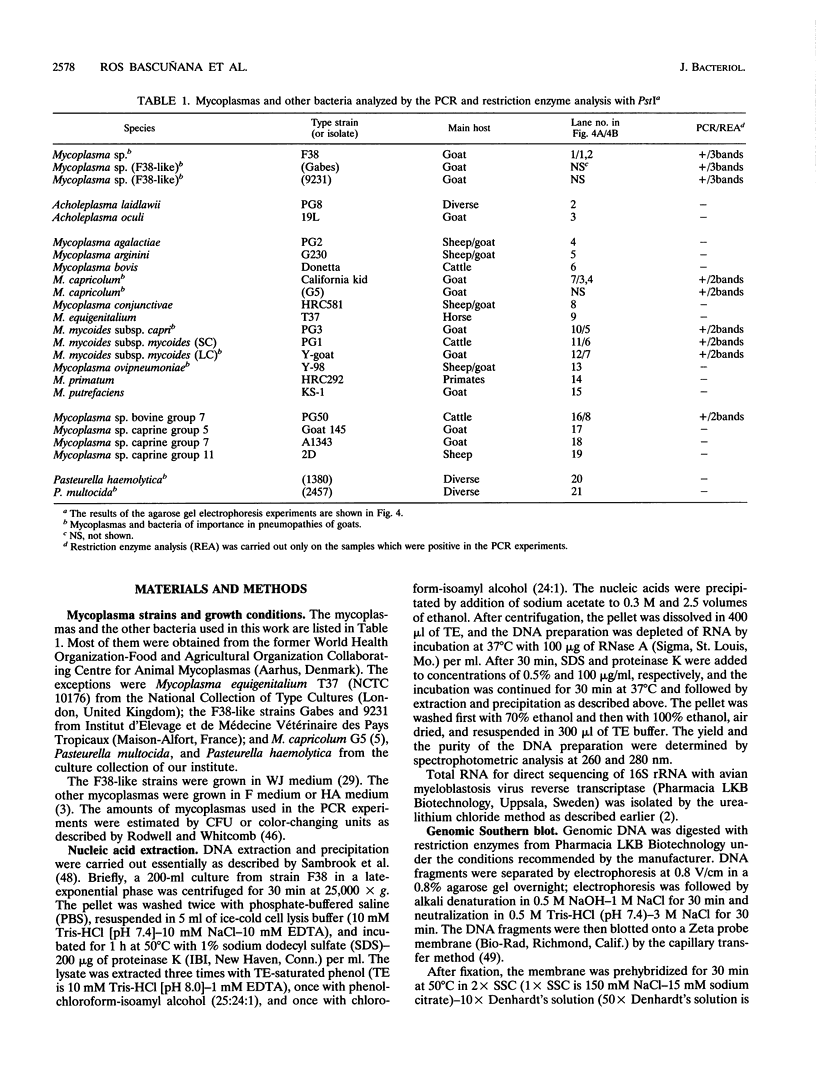
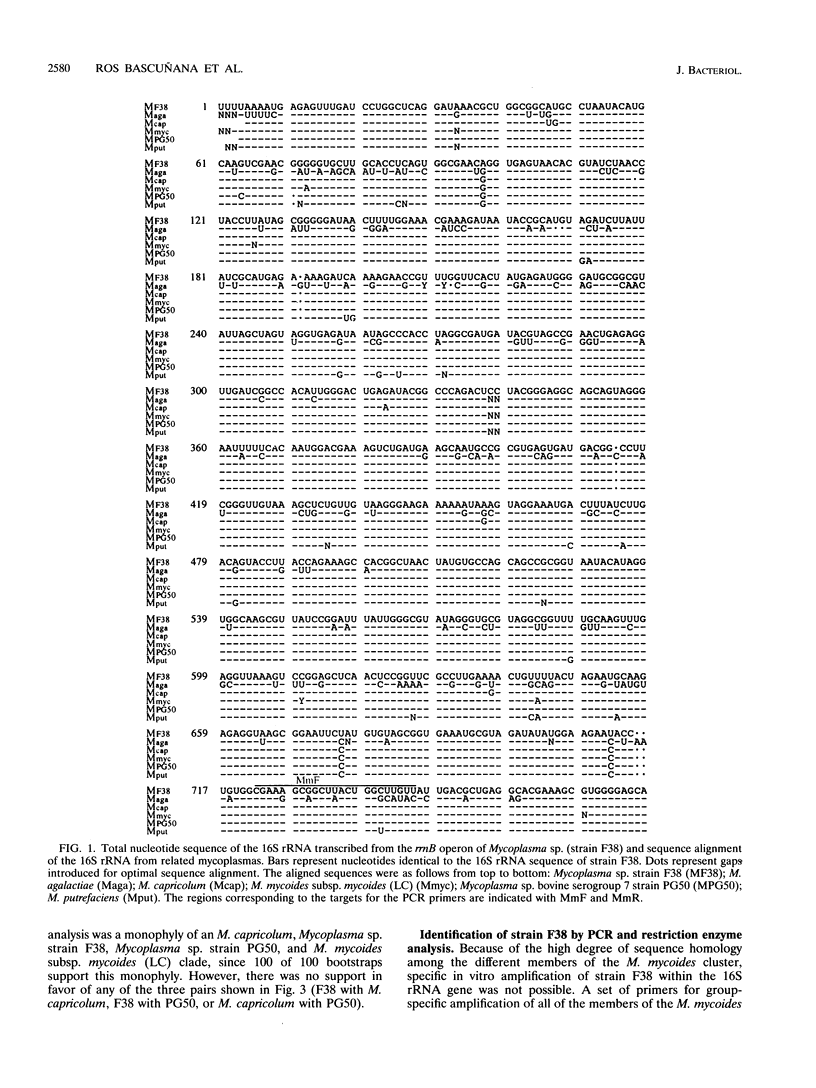
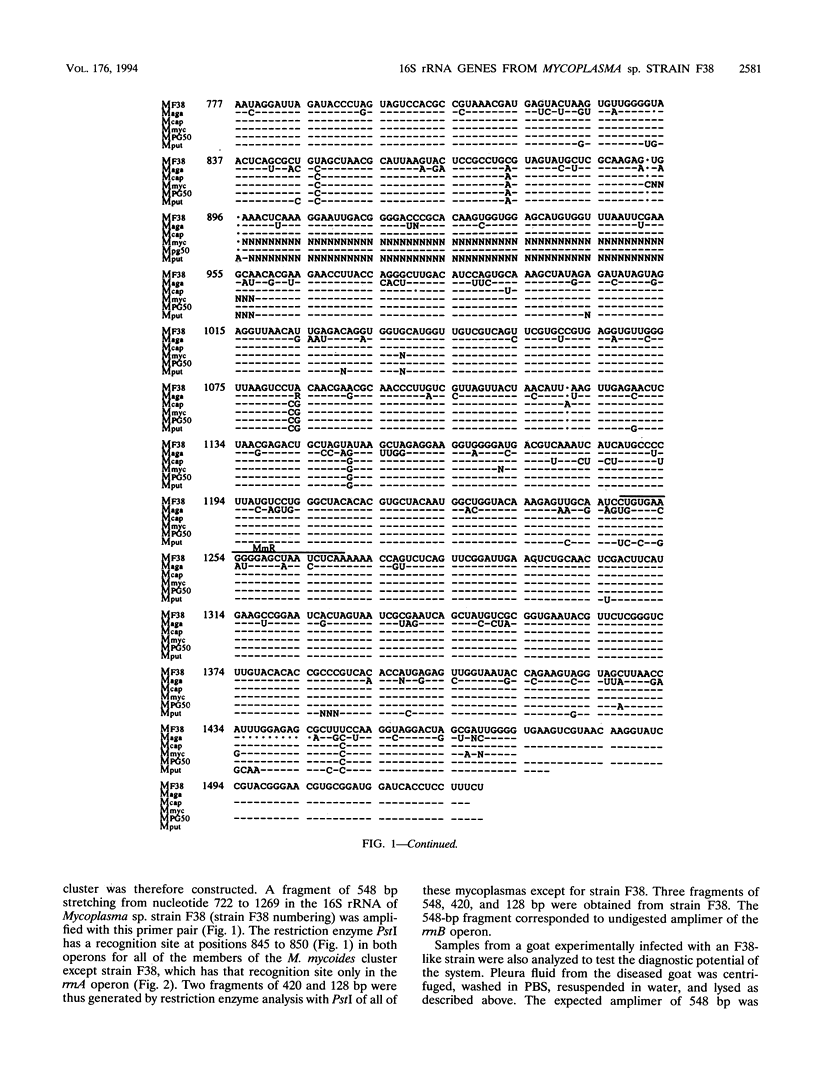
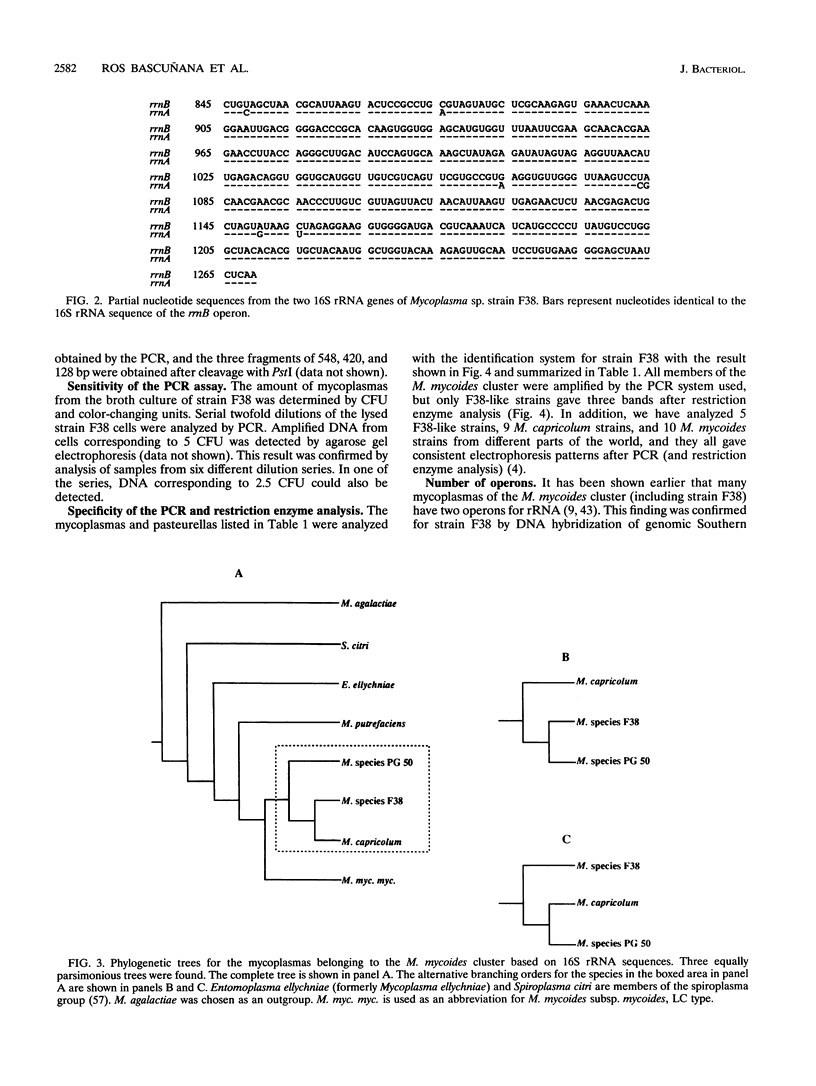
Mycoplasma sp. (strain F38) is the causative agent of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia, which is a goat disease of great global concern. Strain F38 belongs to the so-called "Mycoplasma mycoides cluster," and the members of this cluster have many biochemical and serological properties in common, which makes it difficult to differentiate between them by conventional methods. Their phylogenetic interrelationship are thus uncertain. The 16S rRNA gene of the rrnB operon from strain F38 was cloned and sequenced. The sequence was compared with the 16S rRNA sequences of related mycoplasmas, and phylogenetic trees were constructed by parsimony analysis. A three-way ambiguity among strain F38, Mycoplasma capricolum, and Mycoplasma sp. strain PG50 was observed in the trees. This observation is in agreement with a recent proposal to reclassify strain F38 and M. capricolum. A primer set was designed for in vitro amplification by PCR of a fragment of the 16S rRNA genes from the M. mycoides cluster. The amplimers of strain F38 could be distinguished easily from the corresponding amplimers from other members of the M. mycoides cluster by restriction enzyme analysis with PstI. This observation was utilized to design an identification system for strain F38. Part of the 16S rRNA gene of the rrnA operon from strain F38 was also cloned, and several sequence differences between the two rRNA operons were discovered, revealing microheterogeneity between the two 16S rRNA genes of this organism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Saillard C., Bové J. M., Leach R. H., Rose D. L., Cottew G. S., Tully J. G. DNA relatedness between field isolates of Mycoplasma F38 group, the agent of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia, and strains of Mycoplasma capricolum. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;43(3):597–602. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-3-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Pace N. R. Ribonuclease P RNA and protein subunits from bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1451–1456. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölske G., Msami H., Humlesjö N. E., Ernø H., Jönsson L. Mycoplasma capricolum in an outbreak of polyarthritis and pneumonia in goats. Acta Vet Scand. 1988;29(3-4):331–338. doi: 10.1186/BF03548626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölske G. Survey of Mycoplasma infections in cell cultures and a comparison of detection methods. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(3):331–340. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Q., Russell M., Birch D. E., Raymond J., Bloch W. Prevention of pre-PCR mis-priming and primer dimerization improves low-copy-number amplifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1717–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Niemela S. L., Miller R. H. One-step preparation of competent Escherichia coli: transformation and storage of bacterial cells in the same solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottew G. S., Breard A., DaMassa A. J., Ernø H., Leach R. H., Lefevre P. C., Rodwell A. W., Smith G. R. Taxonomy of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):632–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaMassa A. J., Wakenell P. S., Brooks D. L. Mycoplasmas of goats and sheep. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Jan;4(1):101–113. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East A. K., Thompson D. E., Collins M. D. Analysis of operons encoding 23S rRNA of Clostridium botulinum type A. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8158–8162. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8158-8162.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Wisotzkey J. D., Jurtshuk P., Jr How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):166–170. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydenberg J., Christiansen C. The sequence of 16S rRNA from Mycoplasma strain PG50. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):127–137. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L., Wollett G., Hollingdale M., de la Cruz V. F., Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Structurally distinct, stage-specific ribosomes occur in Plasmodium. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):933–937. doi: 10.1126/science.3672135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U. B., Geiser A., Stanbridge E. J. Oligonucleotide probes complementary to variable regions of ribosomal RNA discriminate between Mycoplasma species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1969–1974. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U., Maas R., Clad A. Quantitative electroelution of oligonucleotides and large DNA fragments from gels and purification by electrodialysis. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1987 Aug;14(5):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(87)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwami M., Muto A., Yamao F., Osawa S. Nucleotide sequence of the rrnB 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Mycoplasma capricolum. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00328065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Mattsson J. G., Jacobsson K., Fernandez C., Bergström K., Bölske G., Wallgren P., Göbel U. B. Specificity of oligonucleotide probes complementary to evolutionarily variable regions of 16S rRNA from Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Res Vet Sci. 1992 Mar;52(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(92)90010-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. H., Ernø H., MacOwan K. J. Proposal for designation of F38-type caprine mycoplasmas as Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae subsp. nov. and consequent obligatory relegation of strains currently classified as M. capricolum (Tully, Barile, Edward, Theodore, and Ernø 1974) to an additional new subspecies, M. capricolum subsp. capricolum subsp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;43(3):603–605. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-3-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacOwan K. J. Role of mycoplasma strain F38 in contagious caprine pleuropneumonia. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):979–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson J. G., Gersdorf H., Göbel U. B., Johansson K. E. Detection of Mycoplasma bovis and Mycoplasma agalactiae by oligonucleotide probes complementary to 16S rRNA. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Feb;5(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(91)90035-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson J. G., Johansson K. E. Oligonucleotide probes complementary to 16S rRNA for rapid detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Mar 1;107(2-3):139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMartin D. A., MacOwan K. J., Swift L. L. A century of classical contagious caprine pleuropneumonia: from original description to aetiology. Br Vet J. 1980 Sep-Oct;136(5):507–515. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)32196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylvaganam S., Dennis P. P. Sequence heterogeneity between the two genes encoding 16S rRNA from the halophilic archaebacterium Haloarcula marismortui. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):399–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Uemori T., Asada K., Kato I., Harasawa R. Acholeplasma laidlawii has tRNA genes in the 16S-23S spacer of the rRNA operon. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8163–8165. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8163-8165.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Ribosomal RNA: a key to phylogeny. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):113–123. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Jukes T. H., Watanabe K., Muto A. Recent evidence for evolution of the genetic code. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):229–264. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.229-264.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Taylor T., Finch L. R. Genomic maps of some strains within the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7265–7268. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7265-7268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell A. W. Emmy Klieneberger-Nobel Award Lecture: The protein fingerprints of mycoplasmas. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S8–17. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen D., Jones C., Schofield J. P. A rapid method for isolating high quality plasmid DNA suitable for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7463–7464. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svärd S. G., Mattsson J. G., Johansson K. E., Kirsebom L. A. Cloning and characterization of the RNase P RNA genes from two porcine mycoplasmas. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(5):849–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschke C., Herrmann R. Analysis of transcription and processing signals in the 5' regions of the two Mycoplasma capricolum rRNA operons. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jun;212(3):522–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00330859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschke C., Herrmann R. Analysis of transcription and processing signals of the 16S-23S rRNA operon of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):434–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00338079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. K., Bashiruddin J. B., Gould A. R. Relationships between members of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster as shown by DNA probes and sequence analysis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;42(4):593–601. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-4-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Petzel J. P., Oyaizu H., Yang D., Mandelco L., Sechrest J., Lawrence T. G., Van Etten J. A phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas: basis for their classification. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6455–6467. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6455-6467.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kuppeveld F. J., van der Logt J. T., Angulo A. F., van Zoest M. J., Quint W. G., Niesters H. G., Galama J. M., Melchers W. J. Genus- and species-specific identification of mycoplasmas by 16S rRNA amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2606–2615. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2606-2615.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]