Abstract
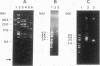
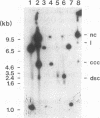
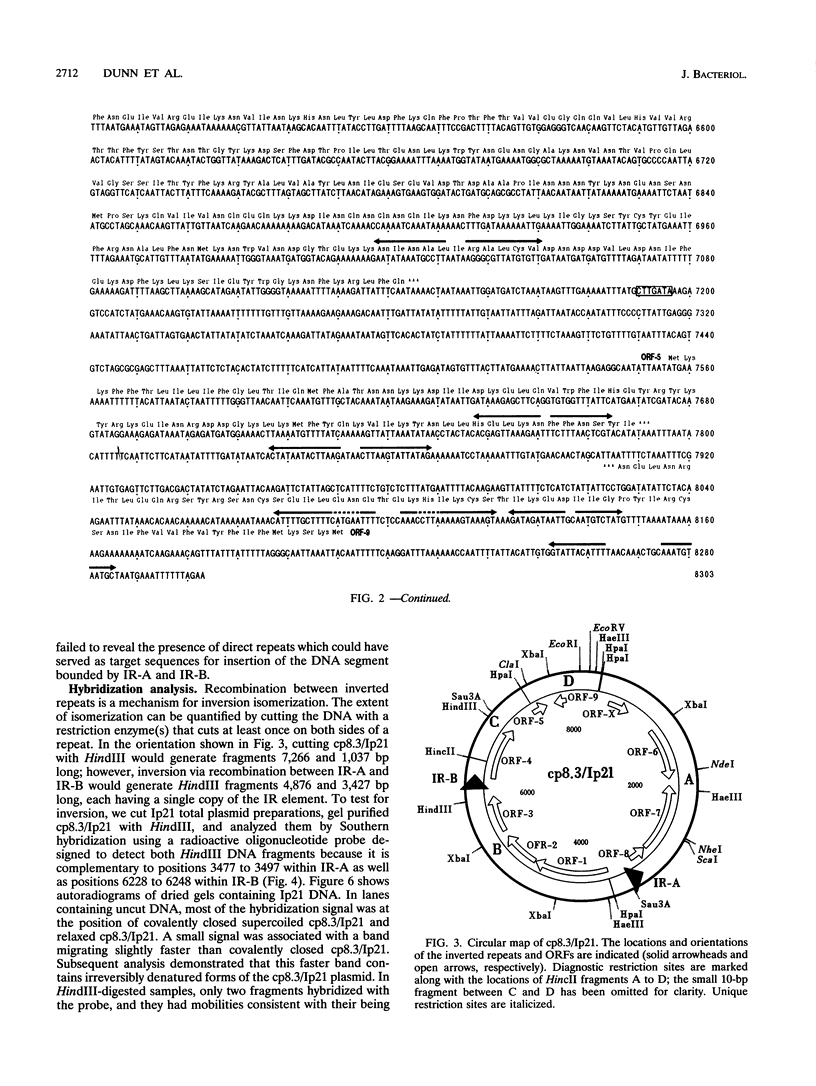
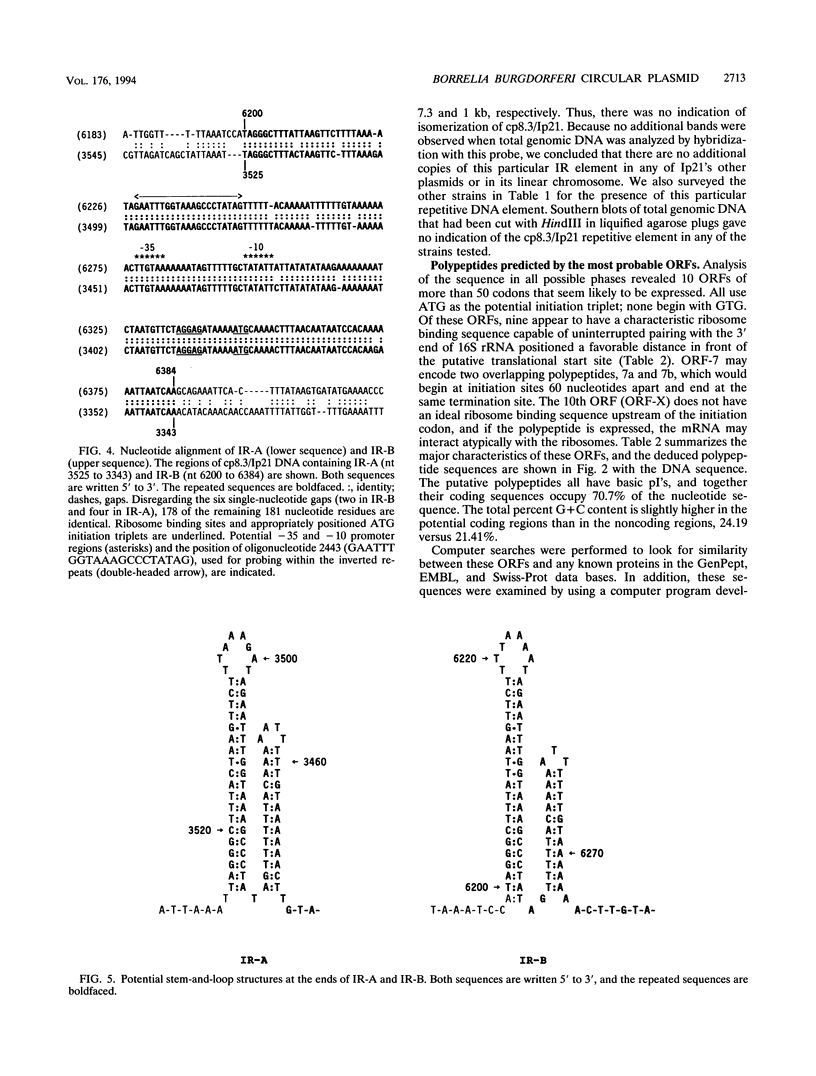
We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of a small circular plasmid from the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi Ip21, the agent of Lyme disease. The plasmid (cp8.3/Ip21) is 8,303 bp long, has a 76.6% A+T content, and is unstable upon passage of cells in vitro. An analysis of the sequence revealed the presence of two nearly perfect copies of a 184-bp inverted repeat sequence separated by 2,675 bp containing three closely spaced, but nonoverlapping, open reading frames (ORFs). Each inverted repeat ends in sequences that may function as signals for the initiation of transcription and translation of flanking plasmid sequences. A unique oligonucleotide probe based on the repeated sequence showed that the DNA between the repeats is present predominantly in a single orientation. Additional copies of the repeat were not detected elsewhere in the Ip21 genome. An analysis for potential ORFs indicates that the plasmid has nine highly probable protein-coding ORFs and one that is less probable; together, they occupy almost 71% of the nucleotide sequence. Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences of the ORFs revealed one (ORF-9) with features in common with Borrelia lipoproteins and another (ORF-2) having limited homology with a replication protein, RepC, from a gram-positive plasmid that replicates by a rolling circle (RC) mechanism. Known collectively as RC plasmids, such plasmids require a double-stranded origin at which the Rep protein nicks the DNA to generate a single-stranded replication intermediate. cp8.3/Ip21 has three copies of the heptameric motif characteristically found at a nick site of most RC plasmids. These observations suggest that cp8.3/Ip21 may replicate by an RC mechanism.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. The PROSITE dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins, its current status. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3097–3103. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfaiza J., Postic D., Bellenger E., Baranton G., Girons I. S. Genomic fingerprinting of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Nov;31(11):2873–2877. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.11.2873-2877.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Garon C. F., Barbour A. G., MacDougall J. Extrachromosomal elements of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):623–628. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90120-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Huang W. M. Linear chromosomal physical and genetic map of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):967–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9677–9686. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., MacDougall J., Saint Girons I. Physical map of the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi 212, a causative agent of Lyme disease, and localization of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3766–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3766-3774.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen D. E., Polin D. S., Dunn J. J., Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Dattwyler R. J., Luft B. J. Borrelia burgdorferi is clonal: implications for taxonomy and vaccine development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10163–10167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi M., Champion C. I., Haake D. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. F., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Use of the "blue halo" assay in the identification of genes encoding exported proteins with cleavable signal peptides: cloning of a Borrelia burgdorferi plasmid gene with a signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4129–4136. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4129-4136.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss A., Ehrlich S. D. The family of highly interrelated single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):231–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.231-241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear- and circular-plasmid copy numbers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5251–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5251-5257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C. Characterization of a circular plasmid from Borrelia burgdorferi, etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2203–2205. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2203-2205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivic A., MacDougall J., Russell R. R., Penn C. W. Isolation and characterization of a plasmid from Treponema denticola. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 1;62(2-3):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenson T. G. The epidemiology of lyme borreliosis. Parasitol Today. 1991 Feb;7(2):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90187-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Hyde F. W., Rumpel C. M. Taxonomy of the Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieleczawa J., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. DNA sequencing by primer walking with strings of contiguous hexamers. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1787–1791. doi: 10.1126/science.1465615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriuchechnikov V. N., Korenberg E. I., Shcherbakov S. V., Kovalevskii Iu V., Levin M. L. Identifikatsiia borrelii, izolirovannykh v SSSR ot kleshchei Ixodes persulcatus Schulze. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1988 Dec;(12):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougall J., Margarita D., Saint Girons I. Homology of a plasmid from the spirochete Treponema denticola with the single-stranded DNA plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2724–2728. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2724-2728.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Samuels D. S., Garon C. F. Transcriptional analyses and mapping of the ospC gene in Lyme disease spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):926–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Illegitimate recombination occurs between the replication origin of the plasmid pC194 and a progressing replication fork. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3691–3696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Recombination between repeated DNA sequences occurs more often in plasmids than in the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(1):46–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00327921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson T. A., Dean M. Preparation of high titer lambda phage lysates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6298–6298. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Wilske B., Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. The cryptic ospC gene of Borrelia burgdorferi B31 is located on a circular plasmid. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2192–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2192-2195.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint Girons I., Norris S. J., Göbel U., Meyer J., Walker E. M., Zuerner R. Genome structure of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Mudri S., Dattwyler R. J., Luft B. J. Mapping antibody-binding domains of the major outer surface membrane protein (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1911–1915. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1911-1915.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. Identification of Borrelia burgdorferi and B. hermsii using DNA hybridization probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1734-1738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. J., Gazumyan A., Schwartz I. rRNA gene organization in the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3757–3765. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3757-3765.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seery L. T., Nolan N. C., Sharp P. M., Devine K. M. Comparative analysis of the pC194 group of rolling circle plasmids. Plasmid. 1993 Nov;30(3):185–196. doi: 10.1006/plas.1993.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Garon C. F., Schwan T. G. Analysis of supercoiled circular plasmids in infectious and non-infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb Pathog. 1990 Feb;8(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Göbel U. B., Graf B., Jauris S., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Zumstein G. An OspA serotyping system for Borrelia burgdorferi based on reactivity with monoclonal antibodies and OspA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):340–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.340-350.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Jauris S., Hofmann A., Pradel I., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Will G., Wanner G. Immunological and molecular polymorphisms of OspC, an immunodominant major outer surface protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2182–2191. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2182-2191.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Weisberg R. A., Studier F. W. Gene 3 endonuclease of bacteriophage T7 resolves conformationally branched structures in double-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):359–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G., Moscoso M., Espinosa M. Rolling circle-replicating plasmids from gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a wall falls. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):789–796. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]