Abstract
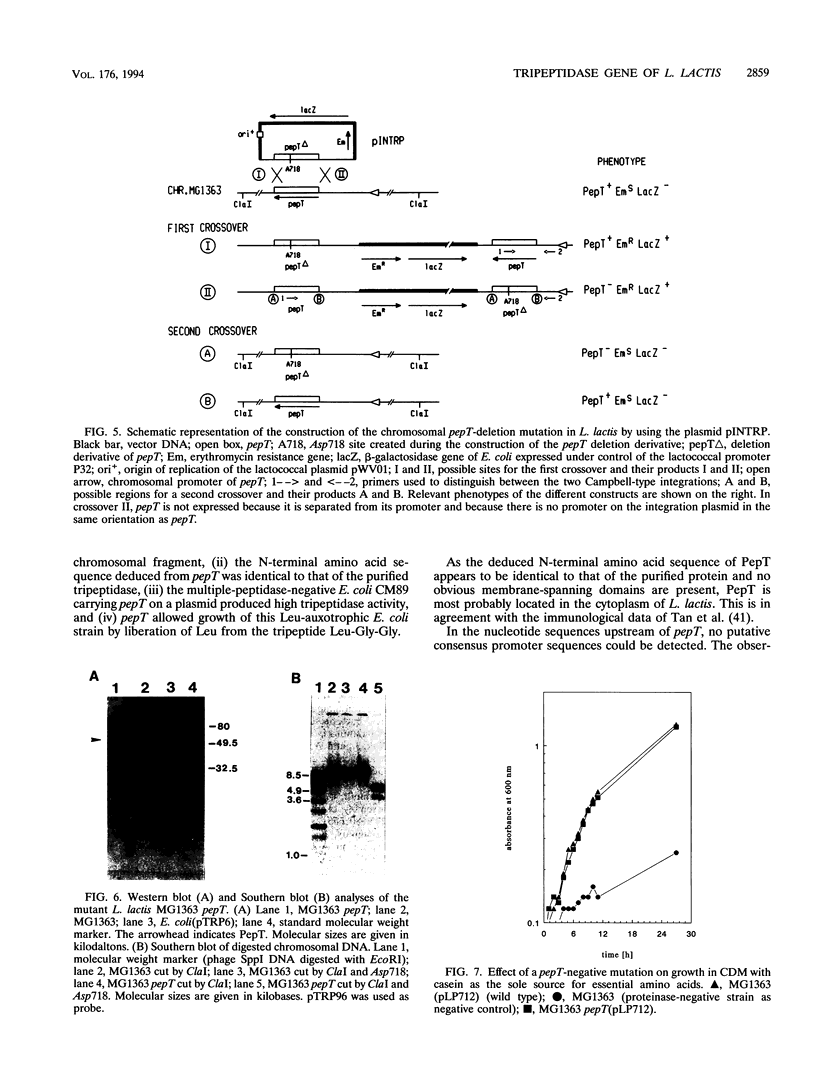
The gene encoding a tripeptidase (pepT) of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris (formerly subsp. lactis) MG1363 was cloned from a genomic library in pUC19 and subsequently sequenced. The tripeptidase of L. lactis was shown to be homologous to PepT of Salmonella typhimurium with 47.4% identity in the deduced amino acid sequences. L. lactis PepT was enzymatically active in Escherichia coli and allowed growth of a peptidase-negative leucine-auxotrophic E. coli strain by liberation of Leu from a tripeptide. Using a two-step integration-excision system, a pepT-negative mutant of L. lactis was constructed. No differences between the growth of the mutant and that of the wild-type strain in milk or in chemically defined medium with casein as the sole source of essential amino acids were observed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosman B. W., Tan P. S., Konings W. N. Purification and Characterization of a Tripeptidase from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1839–1843. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1839-1843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapot-Chartier M. P., Nardi M., Chopin M. C., Chopin A., Gripon J. C. Cloning and sequencing of pepC, a cysteine aminopeptidase gene from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris AM2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):330–333. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.330-333.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Qasba P. K. Alkaline transfer of DNA to plastic membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi E., Shibata D., Matoba T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J., Davies F. L. High-frequency conjugation associated with Streptococcus lactis donor cell aggregation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1260–1264. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1260-1264.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Monnerjahn U., Plapp R. Peptidase D gene (pepD) of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, transcript mapping, and comparison with other peptidase genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4641–4651. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4641-4651.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nes I. F. High-Frequency Transformation, by Electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Grown with Glycine in Osmotically Stabilized Media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3119–3123. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3119-3123.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino Y., Shinagawa H., Makino K., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the iap gene, responsible for alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5429–5433. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5429-5433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Campbell-like integration of heterologous plasmid DNA into the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.394-400.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Stability of Integrated Plasmids in the Chromosome of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2726–2735. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2726-2735.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo M. J., Miller C. G., Rudd K. E. Physical mapping of the Escherichia coli pepT and potABCD genes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7745–7746. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7745-7746.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Seewaldt E., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H., Magrum L., Woese C. R., Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E. The phylogenetic position of Streptococcus and Enterococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):543–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo B., Kok J., Bockelmann W., Haandrikman A., Leenhouts K. J., Venema G. Effect of X-Prolyl Dipeptidyl Aminopeptidase Deficiency on Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jul;59(7):2049–2055. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.7.2049-2055.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo B., Kok J., Venema K., Bockelmann W., Teuber M., Reinke H., Venema G. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase gene from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.38-44.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierau I., Tan P. S., Haandrikman A. J., Mayo B., Kok J., Leenhouts K. J., Konings W. N., Venema G. Cloning and sequencing of the gene for a lactococcal endopeptidase, an enzyme with sequence similarity to mammalian enkephalinase. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2087–2096. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2087-2096.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Miller J. L., Bagga D. A. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the anaerobically regulated pepT gene of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3554–3558. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3554-3558.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Schwartz G. Peptidase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.603-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P., Atkinson T., Bruton C. J., Sherwood R. F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas gene coding for carboxypeptidase G2. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardi M., Chopin M. C., Chopin A., Cals M. M., Gripon J. C. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of an X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase gene from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis NCDO 763. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.45-50.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., de Vos W. M., Gavrieli J. Plasmid DNA in Streptococcus cremoris Wg2: Influence of pH on Selection in Chemostats of a Variant Lacking a Protease Plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1272–1277. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1272-1277.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Konings W. N. Relation of growth of Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris to amino acid transport. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.700-707.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard G. G., Coolbear T. The physiology and biochemistry of the proteolytic system in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;12(1-3):179–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1993.tb00018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., FRANKLIN J. G., PERRY K. D. Correlation of the vitamin requirements with cultural and biochemical characters of Lactobacillus spp. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jul;25:473–482. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottländer E., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B, subtilis phage SP 50. I. Phage mutants with restricted growth on B. subtilis strain 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00343184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strøman P. Sequence of a gene (lap) encoding a 95.3-kDa aminopeptidase from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris Wg2. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90676-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. S., Chapot-Chartier M. P., Pos K. M., Rousseau M., Boquien C. Y., Gripon J. C., Konings W. N. Localization of peptidases in lactococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):285–290. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.285-290.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. S., Poolman B., Konings W. N. Proteolytic enzymes of Lactococcus lactis. J Dairy Res. 1993 May;60(2):269–286. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900027606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. S., van Alen-Boerrigter I. J., Poolman B., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Konings W. N. Characterization of the Lactococcus lactis pepN gene encoding an aminopeptidase homologous to mammalian aminopeptidase N. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 13;306(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80827-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynkkynen S., Buist G., Kunji E., Kok J., Poolman B., Venema G., Haandrikman A. Genetic and biochemical characterization of the oligopeptide transport system of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7523–7532. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7523-7532.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. New pUC-derived cloning vectors with different selectable markers and DNA replication origins. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:189–194. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90365-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabarovsky E. R., Winberg G. High efficiency electroporation of ligated DNA into bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5912–5912. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alen-Boerrigter I. J., Baankreis R., de Vos W. M. Characterization and overexpression of the Lactococcus lactis pepN gene and localization of its product, aminopeptidase N. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2555–2561. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2555-2561.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boven A., Konings W. N. Energetics of Leucyl-Leucine Hydrolysis in Streptococcus cremoris Wg(2). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):95–100. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.95-100.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., de Vos W. M. Molecular cloning, transcriptional analysis, and nucleotide sequence of lacR, a gene encoding the repressor of the lactose phosphotransferase system of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18499–18503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Guchte M., Kodde J., van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Heterologous gene expression in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis: synthesis, secretion, and processing of the Bacillus subtilis neutral protease. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2606–2611. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2606-2611.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Guchte M., Kok J., Venema G. Gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Feb;8(2):73–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., van der Lelie D., Venema G. Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2-specific promoters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2452–2457. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2452-2457.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]