Abstract
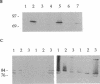
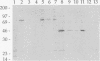
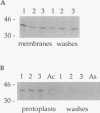
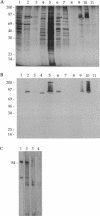
Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae has been found to utilize a novel mechanism for anchoring to the bacterial cell surface. In contrast to that of surface proteins from other gram-positive bacteria, PspA anchoring required choline-mediated interactions between the membrane-associated lipoteichoic acid and the C-terminal repeat region of PspA. Release of PspA from the cell surface could be effected by deletion of 5 of the 10 C-terminal repeat units, by high concentrations of choline, or by growth in choline-deficient medium. Other pneumococcal proteins, including autolysin, which has a similar C-terminal repeat region, were not released by these treatments. The attachment mechanism utilized by PspA thus appears to be uniquely adapted to exploit the unusual structure of the pneumococcal cell surface. Further, it has provided the means for rapid and simple isolation of immunogenic PspA from S. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr T., Fischer W., Peter-Katalinić J., Egge H. The structure of pneumococcal lipoteichoic acid. Improved preparation, chemical and mass spectrometric studies. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;207(3):1063–1075. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. M., Lock R. A., Hansman D., Paton J. C. Contribution of autolysin to virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2324–2330. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2324-2330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briese T., Hakenbeck R. Interaction of the pneumococcal amidase with lipoteichoic acid and choline. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):417–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Crain M. J., Gray B. M., Forman C., Yother J. Strong association between capsular type and virulence for mice among human isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):111–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.111-116.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Nahm M., Schroer K., Davie J., Baker P., Kearney J., Barletta R. Antiphosphocholine antibodies found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous infection with type 3 streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):694–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Yother J., McDaniel L. S. Role of pneumococcal surface protein A in the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S372–S374. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Physiological studies on the pneumococcal Forssman antigen: a choline-containing lipoteichoic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):267–274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Pneumococcal Forssman antigen. A choline-containing lipoteichoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6394–6397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundish D. E., Baddiley J. Pneumococcal C-substance, a ribitol teichoic acid containing choline phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):573–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1100573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain M. J., Waltman W. D., 2nd, Turner J. S., Yother J., Talkington D. F., McDaniel L. S., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) is serologically highly variable and is expressed by all clinically important capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3293–3299. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3293-3299.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz E., García E., Ascaso C., Méndez E., López R., García J. L. Subcellular localization of the major pneumococcal autolysin: a peculiar mechanism of secretion in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1238–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Alexander P., Nagle J., Filpula D. Gene for an immunoglobulin-binding protein from a group G streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.870-880.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Russell R. R., Dao M. L. Sequence analysis of the wall-associated protein precursor of Streptococcus mutans antigen A. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Behr T., Hartmann R., Peter-Katalinić J., Egge H. Teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus pneumoniae possess identical chain structures. A reinvestigation of teichoid acid (C polysaccharide). Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):851–857. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Pancholi V., Schneewind O. Conservation of a hexapeptide sequence in the anchor region of surface proteins from gram-positive cocci. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1603–1605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García E., García J. L., García P., Arrarás A., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., López R. Molecular evolution of lytic enzymes of Streptococcus pneumoniae and its bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):914–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., García J. L., García E., López R. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the pneumococcal autolysin gene from its own promoter in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;43(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., García J. L., García E., López R. Purification and characterization of the autolytic glycosidase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., García J. L., García E., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., López R. Modular organization of the lytic enzymes of Streptococcus pneumoniae and its bacteriophages. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie S. H., McWhinney P. H., Patel S., Raynes J. G., McAdam K. P., Whiley R. A., Hardie J. M. Species of alpha-hemolytic streptococci possessing a C-polysaccharide phosphorylcholine-containing antigen. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3076–3077. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3076-3077.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicelli S., Tomasz A. Attachment of pneumococcal autolysin to wall teichoic acids, an essential step in enzymatic wall degradation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1188–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1188-1190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtje J. V., Tomasz A. Biological effects of lipoteichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1023–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1023-1027.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Pneumococcal Forssman antigen: enrichment in mesosomal membranes and specific binding to the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.18-24.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Specific recognition of choline residues in the cell wall teichoic acid by the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase of Pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6072–6076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriki Y. Response to temperature shifts of expression of the amp gene on pBR322 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2294–2297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2294-2297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Neuberger M. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1321–1329. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1321-1329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Garcia E., Garcia P., Ronda C., Tomasz A. Choline-containing bacteriophage receptors in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1581–1590. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1581-1590.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Scott G., Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Monoclonal antibodies against protease-sensitive pneumococcal antigens can protect mice from fatal infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Scott G., Widenhofer K., Carroll J. M., Briles D. E. Analysis of a surface protein of Streptococcus pneumoniae recognised by protective monoclonal antibodies. Microb Pathog. 1986 Dec;1(6):519–531. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Sheffield J. S., Delucchi P., Briles D. E. PspA, a surface protein of Streptococcus pneumoniae, is capable of eliciting protection against pneumococci of more than one capsular type. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):222–228. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.222-228.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Sheffield J. S., Swiatlo E., Yother J., Crain M. J., Briles D. E. Molecular localization of variable and conserved regions of pspA and identification of additional pspA homologous sequences in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1992 Oct;13(4):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90036-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Yother J., Vijayakumar M., McGarry L., Guild W. R., Briles D. E. Use of insertional inactivation to facilitate studies of biological properties of pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA). J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):381–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonnell M., Lain R., Tomasz A. "Diplophage": a bacteriophage of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane L., Subbarow Y. Nutritional Requirements of the Pneumococcus: I. Growth Factors for Types I, II, V, VII, VIII. J Bacteriol. 1940 Nov;40(5):695–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.5.695-704.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronda-Lain C., Lopez R., Tapia A., Tomasz A. Role of the pneumococcal autolysin (murein hydrolase) in the release of progeny bacteriophage and in the bacteriophage-induced lysis of the host cells. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.366-374.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz J. M., Lopez R., Garcia J. L. Structural requirements of choline derivatives for 'conversion' of pneumococcal amidase. A new single-step procedure for purification of this autolysin. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):308–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneewind O., Model P., Fischetti V. A. Sorting of protein A to the staphylococcal cell wall. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90101-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Destruction of low efficiency markers is a slow process occurring at a heteroduplex stage of transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):283–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00268516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe I. C., Shaw N. Atypical lipoteichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7065–7069. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7065-7069.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Puelles J. M., Sanz J. M., García J. L., García E. Cloning and expression of gene fragments encoding the choline-binding domain of pneumococcal murein hydrolases. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington D. F., Crimmins D. L., Voellinger D. C., Yother J., Briles D. E. A 43-kilodalton pneumococcal surface protein, PspA: isolation, protective abilities, and structural analysis of the amino-terminal sequence. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1285–1289. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1285-1289.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington D. F., Voellinger D. C., McDaniel L. S., Briles D. E. Analysis of pneumococcal PspA microheterogeneity in SDS polyacrylamide gels and the association of PspA with the cell membrane. Microb Pathog. 1992 Nov;13(5):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Choline in the cell wall of a bacterium: novel type of polymer-linked choline in Pneumococcus. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Complete sequence of the staphylococcal gene encoding protein A. A gene evolved through multiple duplications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1695–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltman W. D., McDaniel L. S., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Variation in the molecular weight of PspA (pneumococcal surface protein A) among Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90008-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Briles D. E. Structural properties and evolutionary relationships of PspA, a surface protein of Streptococcus pneumoniae, as revealed by sequence analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):601–609. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.601-609.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Forman C., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Protection of mice from infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae by anti-phosphocholine antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):184–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.184-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Handsome G. L., Briles D. E. Truncated forms of PspA that are secreted from Streptococcus pneumoniae and their use in functional studies and cloning of the pspA gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):610–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.610-618.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., McDaniel L. S., Briles D. E. Transformation of encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1463–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1463-1465.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]