Abstract
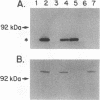
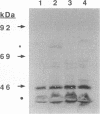
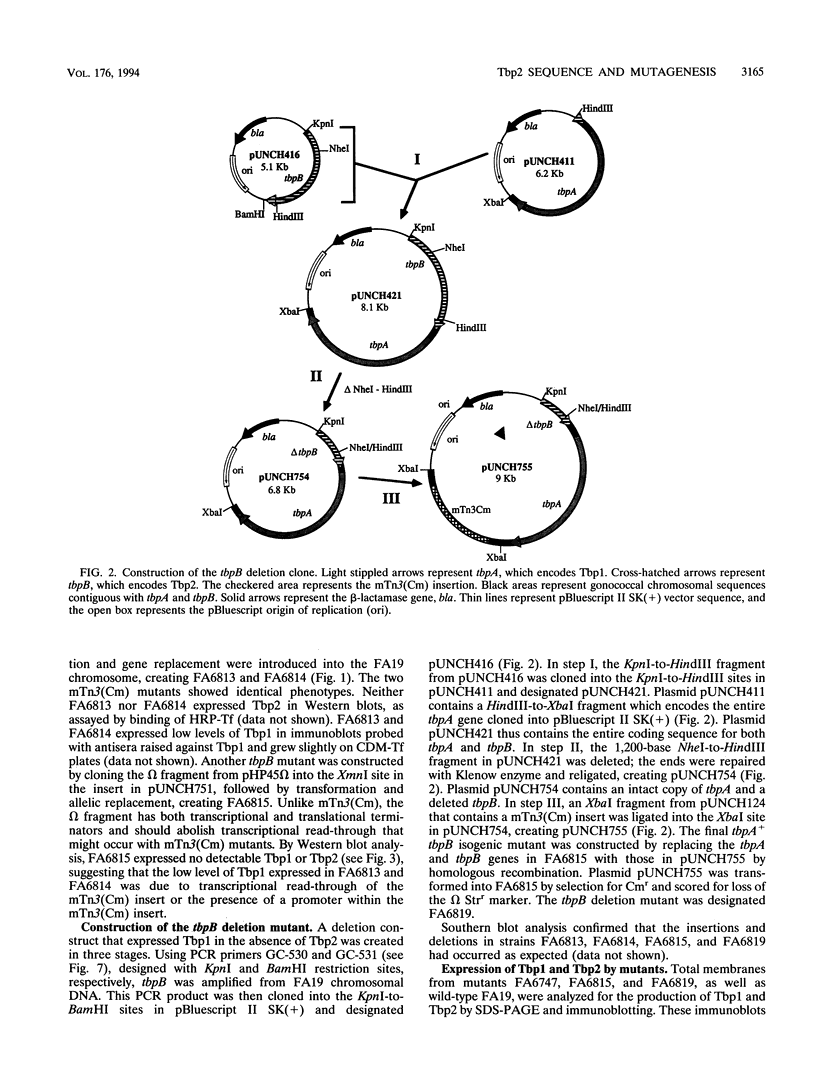
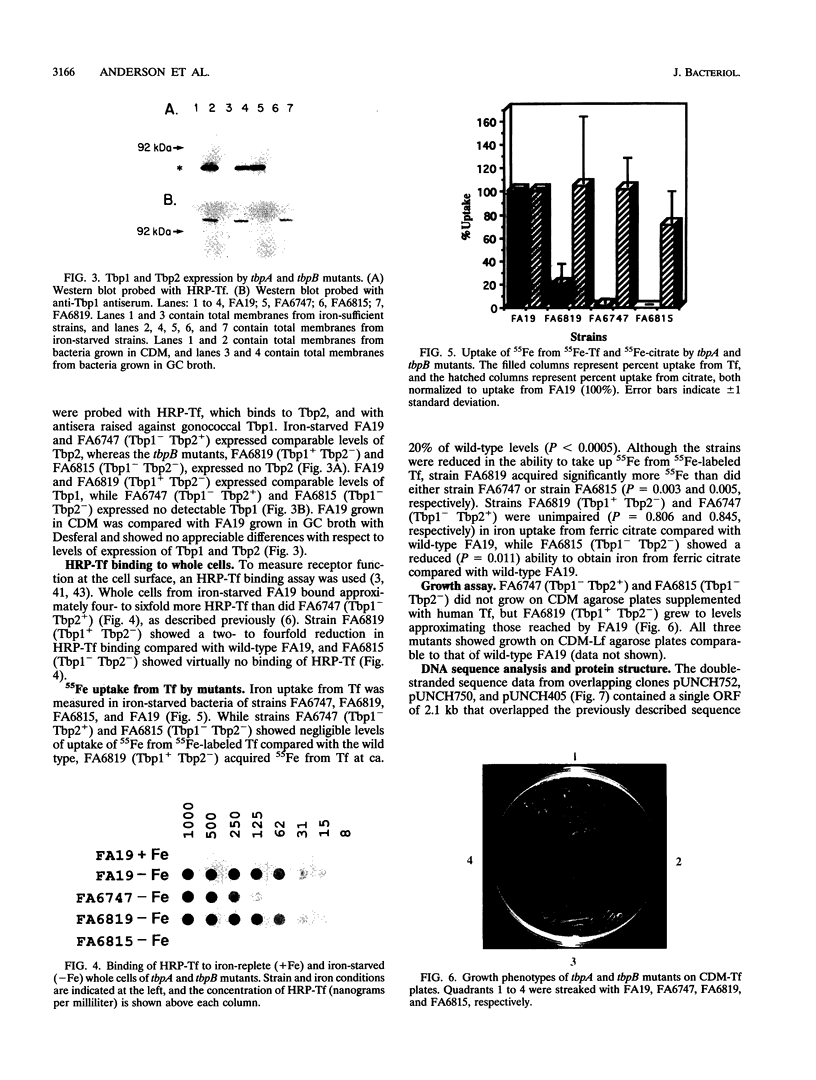
Pathogenic Neisseria species have been shown to scavenge iron from transferrin (Tf), although the mechanism is not yet fully understood. Two iron-repressible proteins that exhibit Tf-binding activity have been identified. This work describes the cloning and sequencing of tbpB, a 2.1-kb gene in N. gonorrhoeae that encodes Tbp2, an 85-kDa iron-repressible lipoprotein. Transcriptional interruption of tbpB had a strong polar effect on tbpA, the structural gene for Tbp1 that is located immediately downstream from tbpB. Such tbpB mutants did not express either Tbp2 or Tbp1, did not bind Tf to whole cells, did not grow on Tf plates, and did not take up iron from Tf. A mutant in which most of tbpB was deleted, presumably leaving tbpA under transcriptional control of the tbpB promoter, was constructed. This mutant did not express Tbp2 but expressed wild-type levels of Tbp1 and possessed the phenotype of reduced binding of Tf, decreased iron uptake from Tf, but normal growth on Tf plates. Mutants expressing Tbp2 and not Tbp1 bound less Tf, did not grow on Tf plates, and did not take up iron from Tf. These results suggest that tbpB and tbpA are polycistronic. Tbp2 apparently facilitates binding of Tf but is not essential for acquisition of iron from Tf under these in vitro conditions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton K. J., Biswas G. D., Tsai J., Adams J., Dyer D. W., Davis S. M., Koch G. G., Sen P. K., Sparling P. F. Genetic evidence that Neisseria gonorrhoeae produces specific receptors for transferrin and lactoferrin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5225–5235. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5225-5235.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Stewart P. W. Monoclonal antibody that recognizes an outer membrane antigen common to the pathogenic Neisseria species but not to most nonpathogenic Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.994-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen C. N., Biswas G. D., Sparling P. F. Expression of gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 1 causes Escherichia coli to bind human transferrin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2448–2450. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2448-2450.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen C. N., Biswas G. D., Tsai J., Paruchuri D. K., Thompson S. A., Sparling P. F. Gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 1 is required for transferrin utilization and is homologous to TonB-dependent outer membrane receptors. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5788–5797. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5788-5797.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., McKenna W., Woods J. P., Sparling P. F. Isolation by streptonigrin enrichment and characterization of a transferrin-specific iron uptake mutant of Neisseria meningitidis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins C., Thomas C. E., Seifert H. S., Sparling P. F. Species-specific uptake of DNA by gonococci is mediated by a 10-base-pair sequence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3911–3913. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3911-3913.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach G. F., Klashinsky S., Anderson C., Potter A. A., Willson P. J. Characterization of two genes encoding distinct transferrin-binding proteins in different Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae isolates. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3253–3261. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3253-3261.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. C., Caamano D. L., Schryvers A. B. Identification and characterization of a porcine-specific transferrin receptor in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1173–1179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Scocca J. J. Identification and arrangement of the DNA sequence recognized in specific transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Hansen E. J. Molecular cloning, partial purification, and characterization of a haemin-binding lipoprotein from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Lipoproteins in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):451–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00763177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Sparling P. F. Haemophilus influenzae can use human transferrin as a sole source for required iron. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):248–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.248-251.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin S. W., Averil N., Cheng C. Y., Schryvers A. B. Preparation and analysis of isogenic mutants in the transferrin receptor protein genes, tbpA and tbpB, from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1125–1133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koebnik R., Braun V. Insertion derivatives containing segments of up to 16 amino acids identify surface- and periplasm-exposed regions of the FhuA outer membrane receptor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):826–839. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.826-839.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. C., Schryvers A. B. Specificity of the lactoferrin and transferrin receptors in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):827–829. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. R., Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F., Dyer D. W. Iron uptake from lactoferrin and transferrin by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.785-791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Williams P. Siderophore-independent acquisition of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):927–933. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. K., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Surface topology of the Escherichia coli K-12 ferric enterobactin receptor. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2736–2746. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2736-2746.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunnariwo J. A., Alcantara J., Schryvers A. B. Evidence for non-siderophore-mediated acquisition of transferrin-bound iron by Pasteurella multocida. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jul;11(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90093-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunnariwo J. A., Schryvers A. B. Iron acquisition in Pasteurella haemolytica: expression and identification of a bovine-specific transferrin receptor. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2091–2097. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2091-2097.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padda J. S., Schryvers A. B. N-linked oligosaccharides of human transferrin are not required for binding to bacterial transferrin receptors. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2972–2976. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2972-2976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauptit R. A., Schirmer T., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P., Parker M. W., Tucker A. D., Tsernoglou D., Weiss M. S., Schultz G. E. A common channel-forming motif in evolutionarily distant porins. J Struct Biol. 1991 Oct;107(2):136–145. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(91)90017-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T., Chart H. Interaction of lactoferrin and transferrins with the outer membrane of Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):891–898. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Campos A., Anderson C., Gerlach G. F., Klashinsky S., Potter A. A., Willson P. J. Immunization of pigs against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae with two recombinant protein preparations. Vaccine. 1992;10(8):512–518. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90349-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutz J. M., Abdullah T., Singh S. P., Kalve V. I., Klebba P. E. Evolution of the ferric enterobactin receptor in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5964–5974. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5964-5974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Hantke K. Iron-hydroxamate uptake systems in Bacillus subtilis: identification of a lipoprotein as part of a binding protein-dependent transport system. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):111–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Lee B. C. Comparative analysis of the transferrin and lactoferrin binding proteins in the family Neisseriaceae. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Mar;35(3):409–415. doi: 10.1139/m89-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Nickel P., Meyer T. F., So M. Opacity determinants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: gene expression and chromosomal linkage to the gonococcal pilus gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyvé M., Moons M., Tommassen J. Carboxy-terminal phenylalanine is essential for the correct assembly of a bacterial outer membrane protein. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90880-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Loss of transferrin receptor activity in Neisseria meningitidis correlates with inability to use transferrin as an iron source. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3132–3138. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3132-3138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Aerobactin utilization by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and cloning of a genomic DNA fragment that complements Escherichia coli fhuB mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3414–3421. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3414-3421.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Warner P. J. ColV plasmid-mediated, colicin V-independent iron uptake system of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):411–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.411-416.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]