Abstract
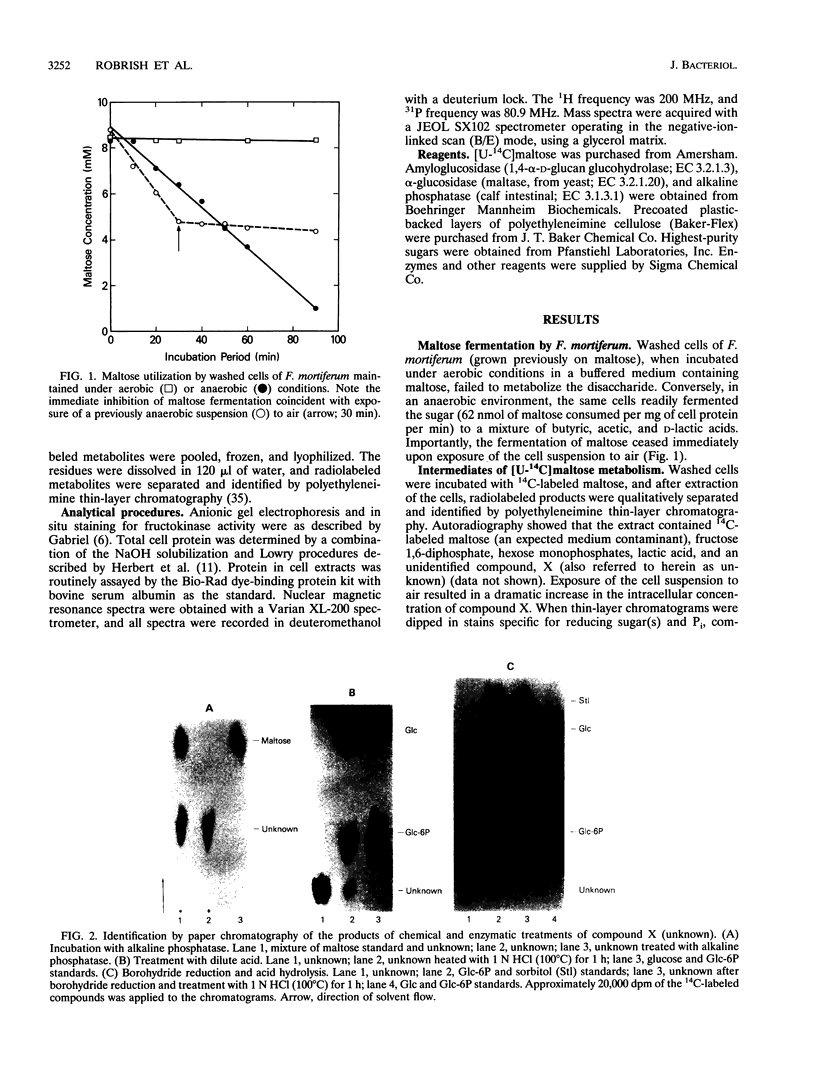
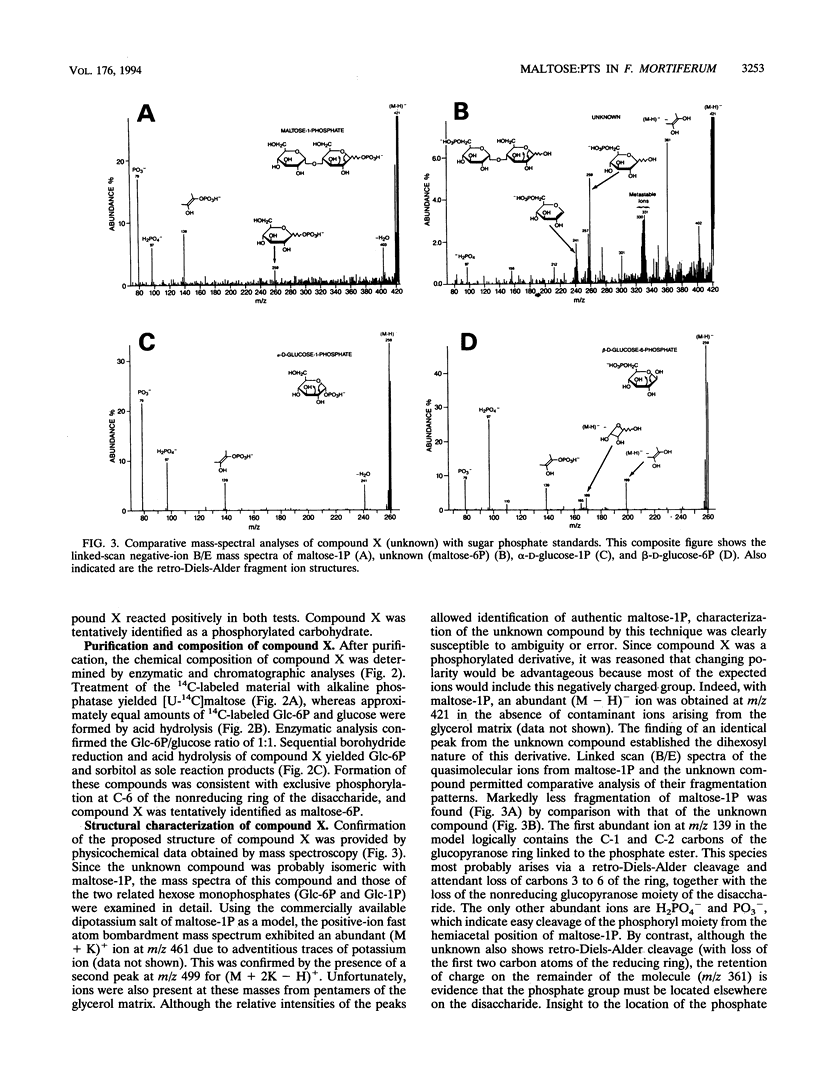
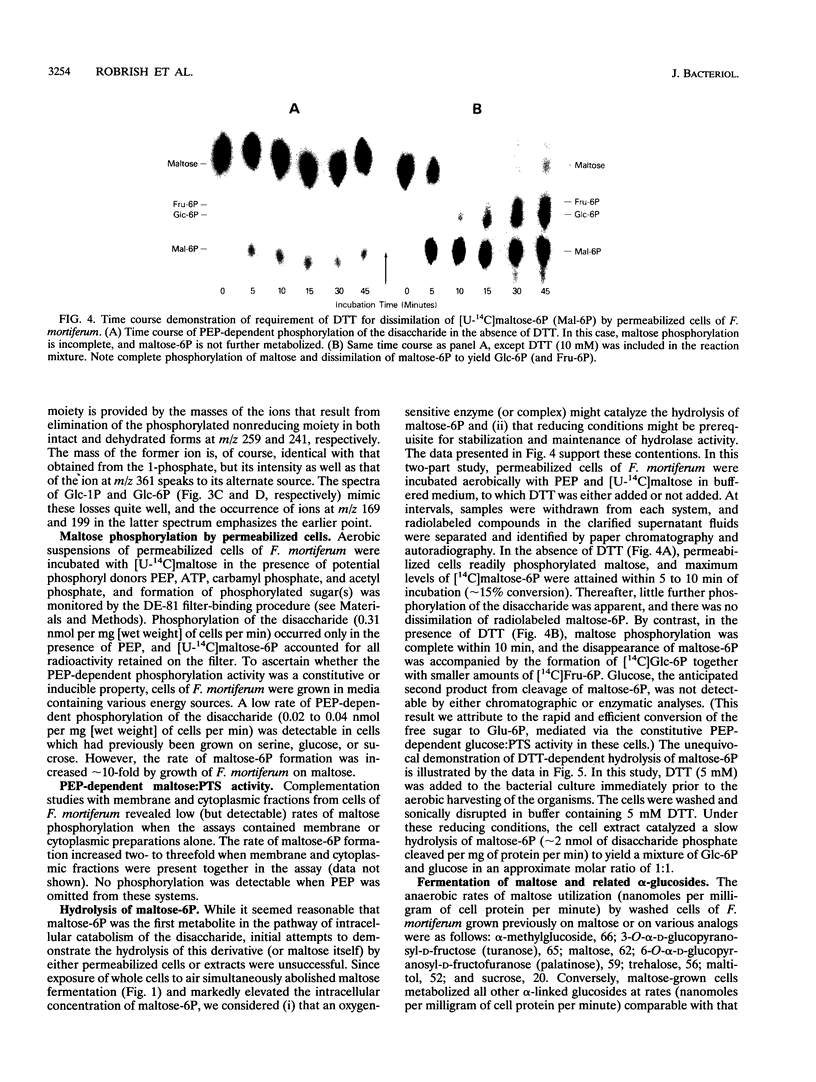
Phosphoenolypyruvate-dependent maltose:phosphotransferase activity was induced in cells of Fusobacterium mortiferum ATCC 25557 during growth on maltose. The disaccharide was rapidly metabolized by washed cells maintained under anaerobic conditions, but fermentation ceased immediately upon exposure of the cell suspension to air. Coincidentally, high levels of a phosphorylated derivative accumulated within the cells. Chemical and enzymatic analyses, in conjunction with data from 1H, 13C, and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, established the structure of the purified compound as 6-O-phosphoryl-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-D-glucose (maltose 6-phosphate). A method for the preparation of substrate amounts of this commercially unavailable disaccharide phosphate is described. Permeabilized cells of F. mortiferum catalyzed the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation of maltose under aerobic conditions. However, the hydrolysis of maltose 6-phosphate (to glucose 6-phosphate and glucose) by permeabilized cells or cell-free preparations required either an anaerobic environment or addition of dithiothreitol to aerobic reaction mixtures. The first step in dissimilation of the phosphorylated disaccharide appears to be catalyzed by an oxygen-sensitive maltose 6-phosphate hydrolase. Cells of F. mortiferum, grown previously on maltose, fermented a variety of alpha-linked glucosides, including maltose, turanose, palatinose, maltitol, alpha-methylglucoside, trehalose, and isomaltose. Conversely, cells grown on the separate alpha-glucosides also metabolized maltose. For this anaerobic pathogen, we suggest that the maltose:phosphotransferase and maltose 6-phosphate hydrolase catalyze the phosphorylative translocation and cleavage not only of maltose but also of structurally analogous alpha-linked glucosides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhumiratana A., Anderson R. L., Costilow R. N. Trehalose metabolism by Bacillus popilliae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.484-493.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas E. Biochemistry of oxygen toxicity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:79–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calmes R., Brown A. T. Regulation of lactose catabolism in Streptococcus mutans: purification and regulatory properties of phospho-beta-galactosidase. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):68–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.68-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Initial characterization of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans and its apparent identity with intracellular invertase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. VI. The nature of the derivatives accumulated. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1881–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Morse M. L. Purification of the staphylococcal 6-phospho-beta-D-- galactosidase. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Reiche B., Eisermann R., Fischer R., Kessler U., Tarrach A., De Vos W. M., Kalbitzer H. R., Glaser S. Structure and function of proteins involved in sugar transport by the PTS of gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb14098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., McDonald I. J. Beta-D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase from Streptococcus cremoris HP: purification and enzyme properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.667-674.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Pascal M., Lefesant J. A., Walle J., Dedonder R. Purification and some properties of an endocellular sucrase from a constitutive mutant of Bacillus subtilis Marburg 168. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Russell J. B. Transport and phosphorylation of disaccharides by the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2388–2393. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2388-2393.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal L. R. Transport and metabolism of trehalose in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Jan;137(1):70–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00425810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Fox D. K., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: glycose phosphotransferase system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:497–542. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Anderson R. L. Cellobiose metabolism in Aerobacter aerogenes. 3. Cleavage of cellobiose monophosphate by a phospho- -glucosidase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3420–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Anderson R. L. Cellobiose metabolism in Aerobacter aerogenes. II. Phosphorylation of cellobiose with adenosine 5'-triphosphate by a -glucoside kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3415–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W., Jacobson G. R. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):543–594. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.543-594.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidl J., Boos W. The malX malY operon of Escherichia coli encodes a novel enzyme II of the phosphotransferase system recognizing glucose and maltose and an enzyme abolishing the endogenous induction of the maltose system. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4862–4876. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4862-4876.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Saier M. H., Jr, Deutscher J., Grenier F., Thompson J., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: properties, mechanism, and regulation. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15(4):297–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Oliver C., Thompson J. Amino acid-dependent transport of sugars by Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3891-3897.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Oliver C., Thompson J. Sugar metabolism by fusobacteria: regulation of transport, phosphorylation, and polymer formation by Fusobacterium mortiferum ATCC 25557. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4547–4554. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4547-4554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Thompson J. Regulation of fructose metabolism and polymer synthesis by Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 10953. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5714–5723. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5714-5723.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman S. Sialic acid, serendipity, and sugar transport: discovery of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Reizer J. Proposed uniform nomenclature for the proteins and protein domains of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1433–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1433-1438.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Regulation and function of sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):487–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.487-491.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis: phosphorylation of galactose and glucose moieties in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):774–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.774-785.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Nguyen N. Y., Robrish S. A. Sucrose fermentation by Fusobacterium mortiferum ATCC 25557: transport, catabolism, and products. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3227–3235. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3227-3235.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Nguyen N. Y., Sackett D. L., Donkersloot J. A. Transposon-encoded sucrose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Purification of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase and genetic linkage to N5-(L-1-carboxyethyl)-L-ornithine synthase in strain K1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14573–14579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Torchia D. A. Use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 14C fluorography in studies of glycolysis and regulation of pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.791-800.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G., Fox C. F. The beta-glucoside system of Escherichia coli. IV. Purification and properties of phospho-beta-glucosidases A and B. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5586–5598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Würsch P., Koellreutter B. Maltotriitol inhibition of maltose metabolism in Streptococcus mutans via maltose transport, amylomaltase and phospho-alpha-glucosidase activities. Caries Res. 1985;19(5):439–449. doi: 10.1159/000260879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




