Abstract
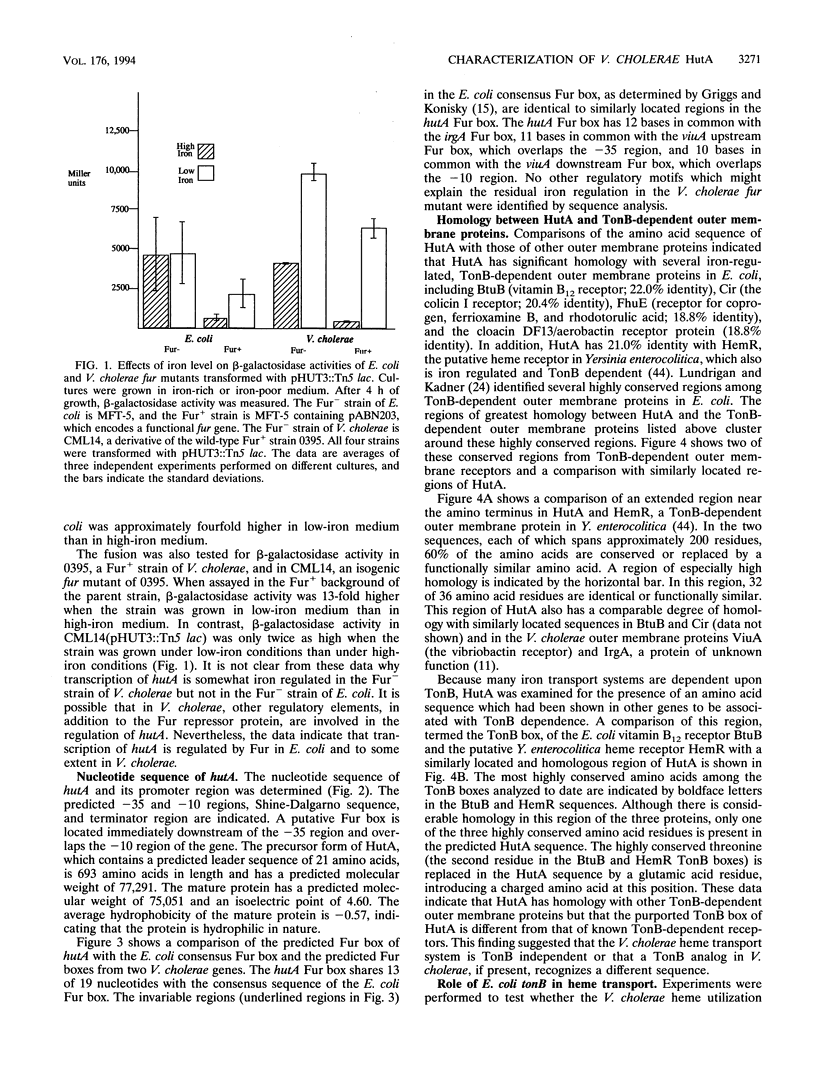
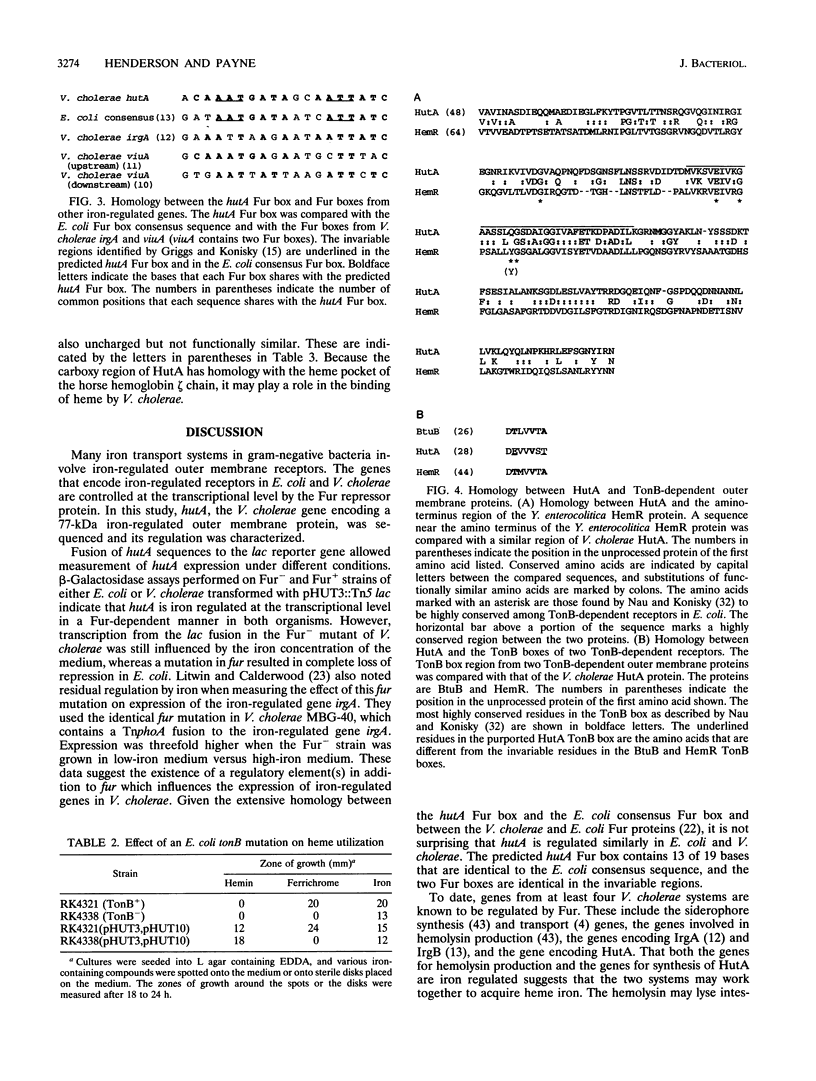
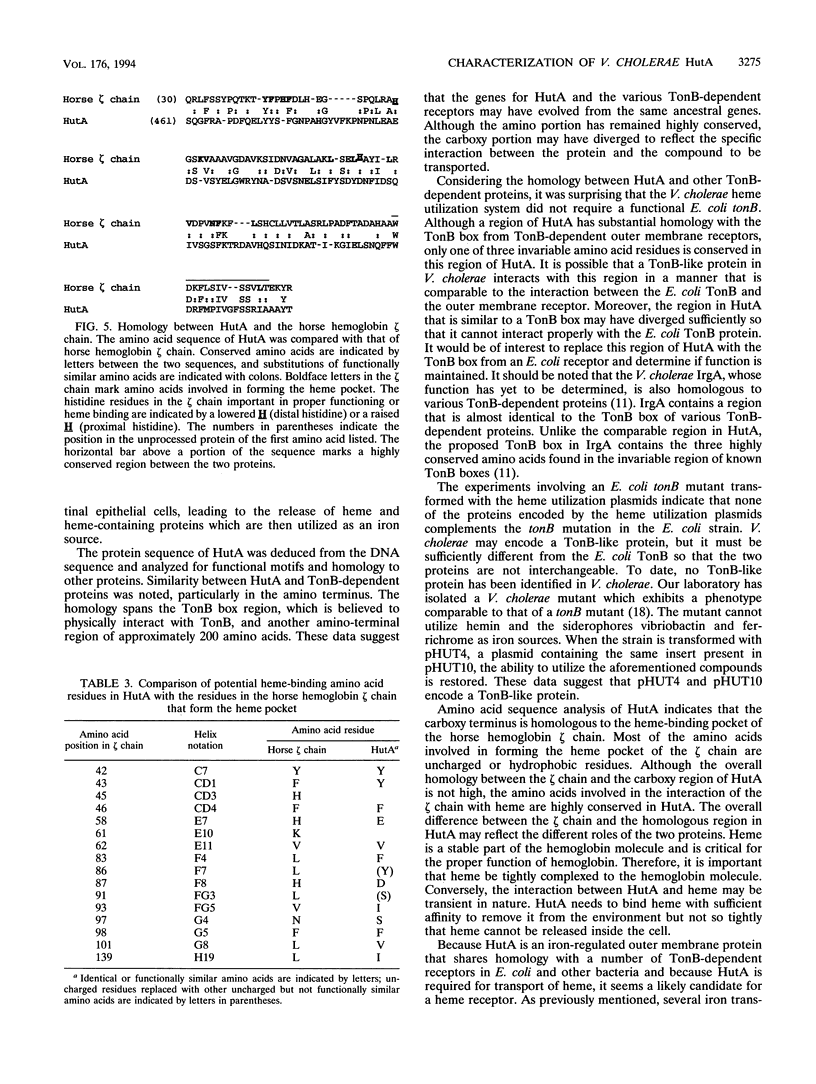
The regulation of hutA, the Vibrio cholerae gene encoding a 77-kDa iron-regulated outer membrane protein required for heme iron utilization, was characterized, and the DNA sequence of the gene was determined. A hutA::Tn5 lac fusion generated previously (D. P. Henderson and S. M. Payne, Mol. Microbiol. 7:461-469, 1993) was transformed into Fur- and Fur+ strains of Escherichia coli and V. cholerae. The results of beta-galactosidase assays on the transformed strains demonstrated that transcription of hutA is regulated by the Fur repressor protein in E. coli and at least partially regulated by Fur in V. cholerae. Analysis of the DNA sequence of hutA indicated that a sequence homologous to the E. coli consensus Fur box was present in the promoter region of hutA. The amino acid sequence of HutA is homologous to those of several TonB-dependent outer member proteins. However, when the V. cholerae heme utilization system, which requires one or more genes encoded by the recombinant plasmid pHUT10 in addition to hutA carried on a second vector, was transferred to a wild-type strain and an isogenic tonB mutant of E. coli, the tonB mutant could utilize heme iron as efficiently as the wild-type strain. These data indicate that the V. cholerae heme utilization system reconstituted in E. coli does not require a functional TonB protein. The tonB mutant transformed with the heme utilization plasmids could not utilize the siderophore ferrichrome as an iron source, indicating that none of the genes encoded on the heme utilization plasmids complements the tonB defect in E. coli. It is possible that a gene(s) encoded by the recombinant heme utilization plasmids encodes a protein serving a TonB-like function in V. cholerae. A region in the carboxy terminus of HutA is homologous to the horse hemoglobin gamma chain, and the amino acids involved in forming the heme pocket in the gamma chain are conserved in HutA. These data suggest that this region of HutA is involved in heme binding.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5471–5477. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Molecular mechanism of regulation of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):509–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.509-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Günter K., Hantke K. Transport of iron across the outer membrane. Biol Met. 1991;4(1):14–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01135552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterton J. R., Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M., Calderwood S. B. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of viuA, the gene encoding the ferric vibriobactin receptor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3729–3738. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3729-3738.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron uptake in Plesiomonas shigelloides: cloning of the genes for the heme-iron uptake system. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2706–2711. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2706-2711.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. S., Levine B. A., Trayer I. P., Dorman C. J., Higgins C. F. Sequence-imposed structural constraints in the TonB protein of E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermi G. Three-dimensional fourier synthesis of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 2-5 A resolution: refinement of the atomic model. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Butterton J. R., Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M., Calderwood S. B. Characterization of a Vibrio cholerae virulence factor homologous to the family of TonB-dependent proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2407–2418. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Positive transcriptional regulation of an iron-regulated virulence gene in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1125–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Transcriptional regulation by iron of a Vibrio cholerae virulence gene and homology of the gene to the Escherichia coli fur system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6863–6870. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6863-6870.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. L., Sigel S. P., Payne S. M., Neilands J. B. Vibriobactin, a siderophore from Vibrio cholerae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):383–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. W., Konisky J. Mechanism for iron-regulated transcription of the Escherichia coli cir gene: metal-dependent binding of fur protein to the promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1048-1054.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K. J., Kadner R. J., Günther K. Suppression of the btuB451 mutation by mutations in the tonB gene suggests a direct interaction between TonB and TonB-dependent receptor proteins in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90488-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. P., Payne S. M. Cloning and characterization of the Vibrio cholerae genes encoding the utilization of iron from haemin and haemoglobin. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by metal-protein complexes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1621–1628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Sparling P. F. Haemophilus influenzae can use human transferrin as a sole source for required iron. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):248–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.248-251.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. Aerobactin-mediated utilization of transferrin iron. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6503–6508. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of the Vibrio cholerae fur gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1897–1903. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1897-1903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin C. M., Calderwood S. B. Cloning and genetic analysis of the Vibrio vulnificus fur gene and construction of a fur mutant by in vivo marker exchange. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):706–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.706-715.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundrigan M. D., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the ferrienterochelin receptor FepA in Escherichia coli. Homology among outer membrane receptors that interact with TonB. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10797–10801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. R., Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F., Dyer D. W. Iron uptake from lactoferrin and transferrin by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.785-791.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau C. D., Konisky J. Evolutionary relationship between the TonB-dependent outer membrane transport proteins: nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the Escherichia coli colicin I receptor gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1041-1047.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Iron absorption and transport in microorganisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:27–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidcock K. A., Wooten J. A., Daley B. A., Stull T. L. Iron acquisition by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.721-725.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K. TonB and the gram-negative dilemma. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2019–2025. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T., Chart H. Interaction of lactoferrin and transferrins with the outer membrane of Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):891–898. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J. T., Ahmer B. M., Seachord C. L., Darveau R. P., Postle K. Energy transduction between membranes. TonB, a cytoplasmic membrane protein, can be chemically cross-linked in vivo to the outer membrane receptor FepA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16302–16308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Butterton J. R., Calderwood S. B., Payne S. M. Identification of the vibriobactin receptor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3270–3274. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3270-3274.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron-regulated hemolysin production and utilization of heme and hemoglobin by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2891-2895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojiljkovic I., Hantke K. Hemin uptake system of Yersinia enterocolitica: similarities with other TonB-dependent systems in gram-negative bacteria. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4359–4367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



