Abstract
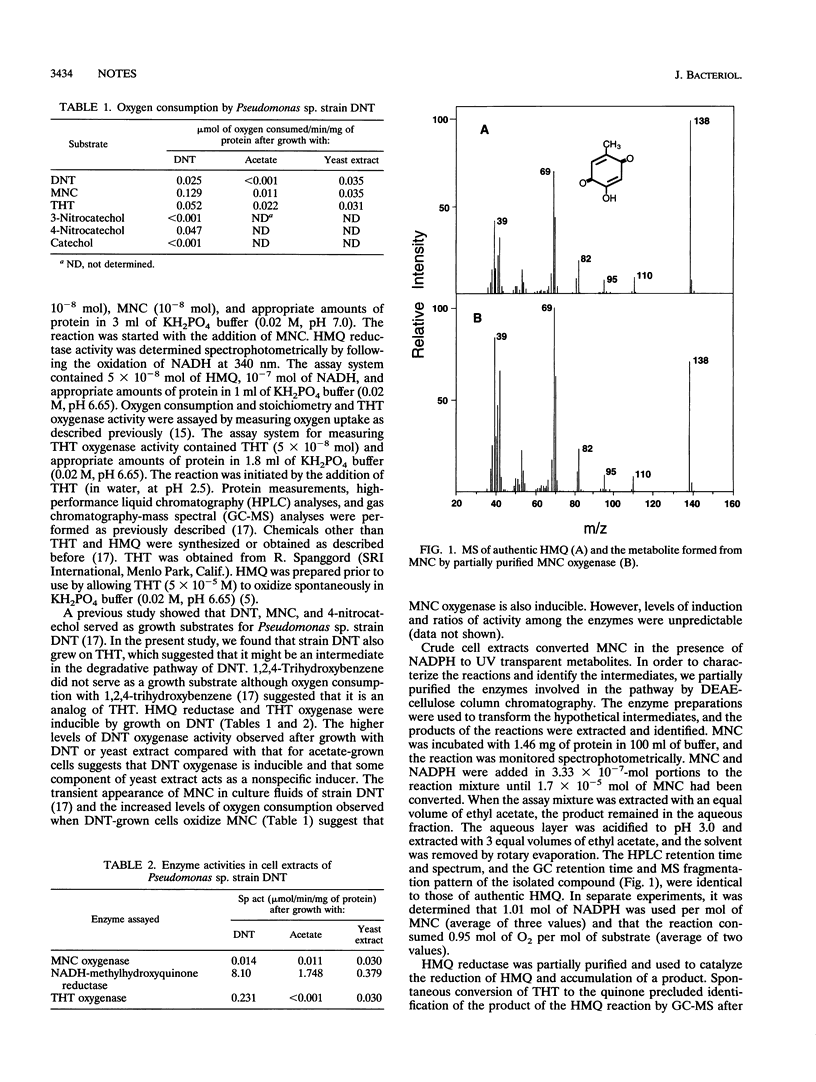
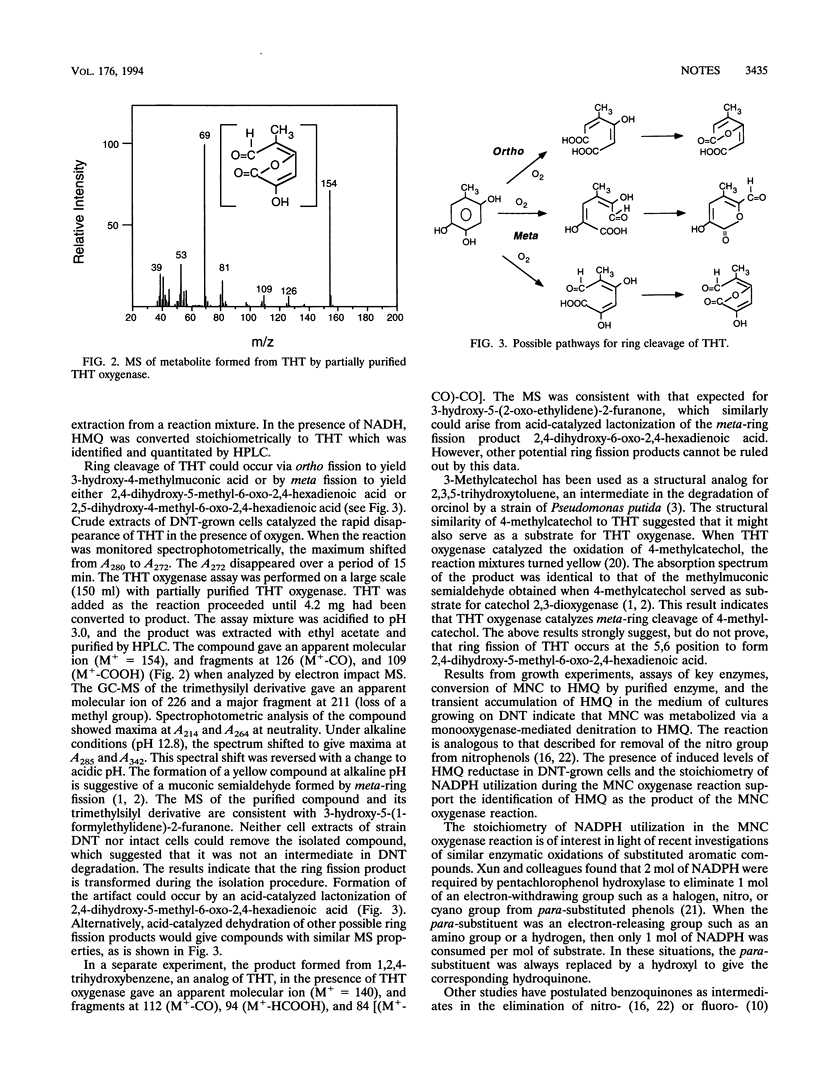
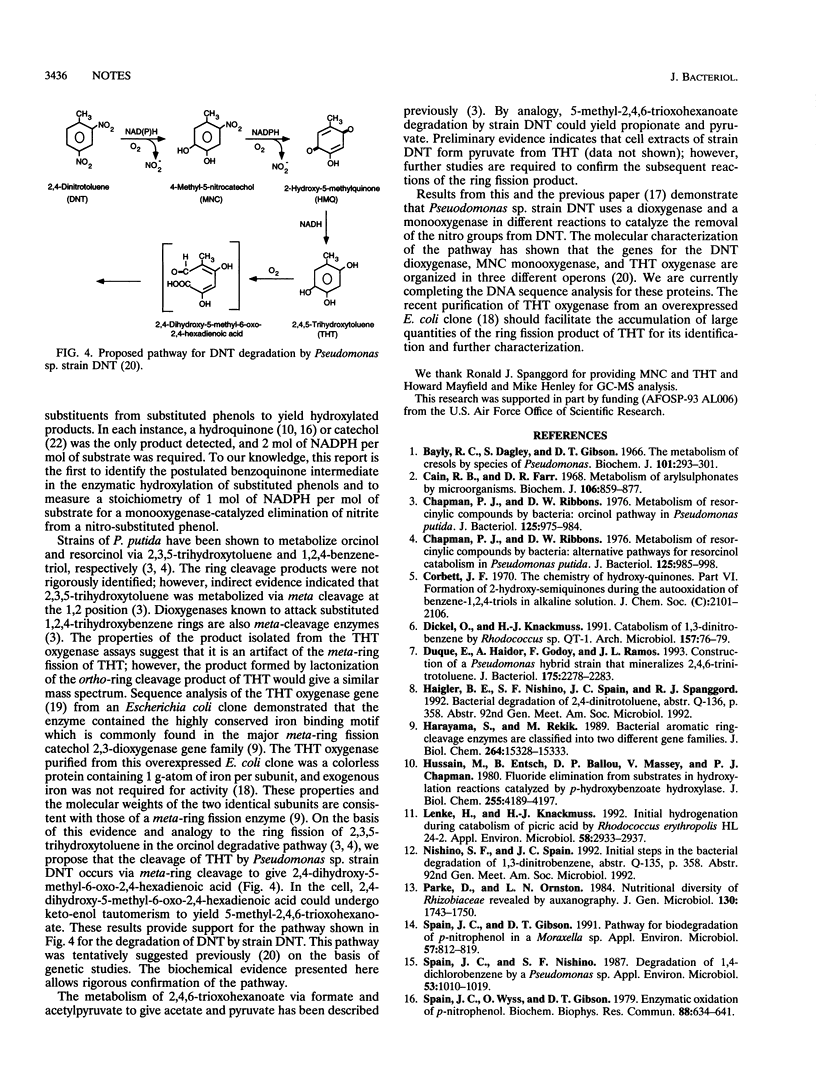
Pseudomonas sp. strain DNT degrades 2,4-dinitrotoluene (DNT) by a dioxygenase attack at the 4,5 position with concomitant removal of the nitro group to yield 4-methyl-5-nitrocatechol (MNC). Here we describe the mechanism of removal of the nitro group from MNC and subsequent reactions leading to ring fission. Washed suspensions of DNT-grown cells oxidized MNC and 2,4,5-trihydroxytoluene (THT). Extracts prepared from DNT-induced cells catalyzed the disappearance of MNC in the presence of oxygen and NADPH. Partially purified MNC oxygenase oxidized MNC in a reaction requiring 1 mol of NADPH and 1 mol of oxygen per mol of substrate. The enzyme converted MNC to 2-hydroxy-5-methylquinone (HMQ), which was identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. HMQ was also detected transiently in culture fluids of cells grown on DNT. A quinone reductase was partially purified and shown to convert HMQ to THT in a reaction requiring NADH. A partially purified THT oxygenase catalyzed ring fission of THT and accumulation of a compound tentatively identified as 3-hydroxy-5-(1-formylethylidene)-2-furanone. Preliminary results indicate that this compound is an artifact of the isolation procedure and suggest that 2,4-dihydroxy-5-methyl-6-oxo-2,4-hexadienoic acid is the actual ring fission product.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Farr D. R. Metabolism of arylsulphonates by micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):859–877. doi: 10.1042/bj1060859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: alternative pathways for resorcinol catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.985-998.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: orcinol pathway in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):975–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.975-984.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickel O., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of 1,3-dinitrobenzene by Rhodococcus sp. QT-1. Arch Microbiol. 1991;157(1):76–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00245339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duque E., Haidour A., Godoy F., Ramos J. L. Construction of a Pseudomonas hybrid strain that mineralizes 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2278–2283. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2278-2283.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M. Bacterial aromatic ring-cleavage enzymes are classified into two different gene families. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15328–15333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Entsch B., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Chapman P. J. Fluoride elimination from substrates in hydroxylation reactions catalyzed by p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4189–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenke H., Knackmuss H. J. Initial hydrogenation during catabolism of picric acid by Rhodococcus erythropolis HL 24-2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):2933–2937. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.2933-2937.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Gibson D. T. Pathway for Biodegradation of p-Nitrophenol in a Moraxella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):812–819. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.812-819.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanggord R. J., Spain J. C., Nishino S. F., Mortelmans K. E. Biodegradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3200–3205. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3200-3205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suen W. C., Spain J. C. Cloning and characterization of Pseudomonas sp. strain DNT genes for 2,4-dinitrotoluene degradation. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1831–1837. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1831-1837.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Topp E., Orser C. S. Diverse substrate range of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol hydroxylase and reaction stoichiometries. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2898–2902. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2898-2902.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kocher H. P. Purification and characterization of a bacterial nitrophenol oxygenase which converts ortho-nitrophenol to catechol and nitrite. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1789–1794. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1789-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


