Abstract
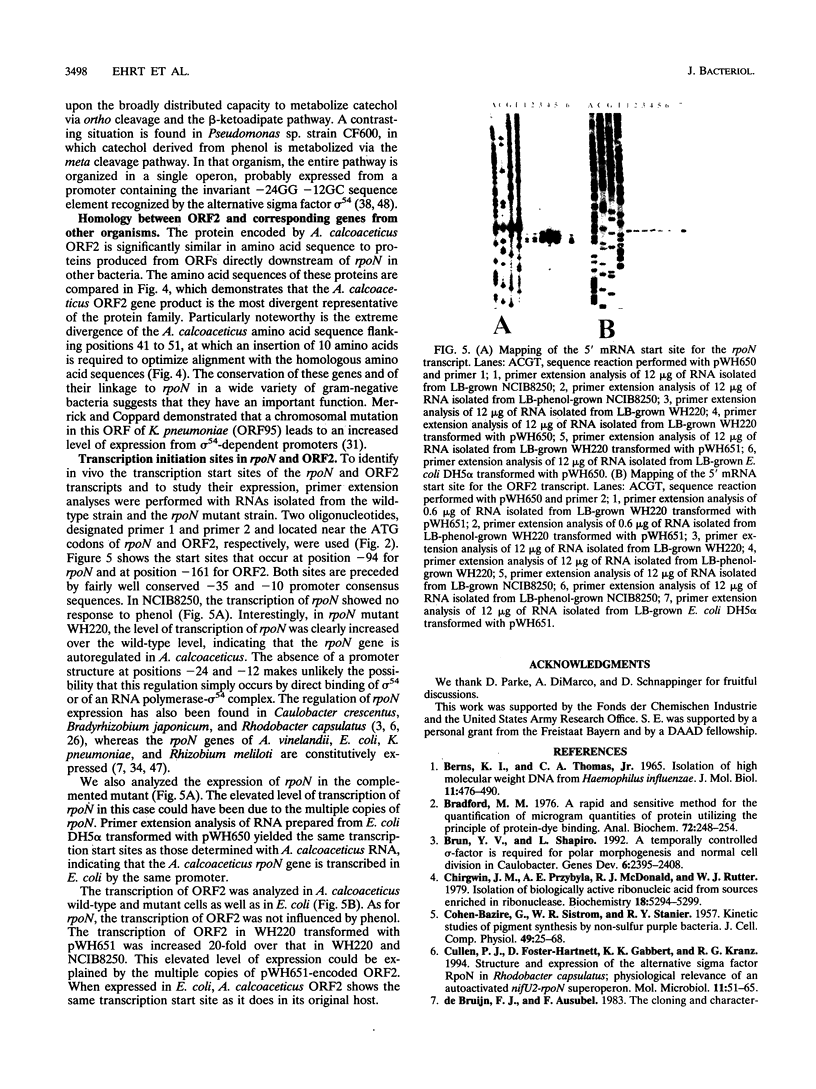
Members of the sigma 54 protein family, encoded by rpoN, are required for the transcription of genes associated with specialized metabolic functions. The ability to grow with phenol appears to be a specialized trait because it is expressed by few of the microorganisms that grow with catechol, the metabolic product of phenol monooxygenase. A mutation preventing the expression of phenol monooxygenase in the bacterial strain Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCIB8250 was complemented by wild-type DNA segments containing an open reading frame encoding a member of the sigma 54 protein family. DNA sequencing revealed a second open reading frame, designated ORF2, directly downstream of A. calcoaceticus rpoN. The locations of both ORF2 and the 113-residue amino acid sequence of its product are highly conserved in other bacteria. The mutation preventing the expression of rpoN results in an opal codon that terminates the translation of RpoN at a position corresponding to Trp-91 in the 483-residue amino acid sequence of the wild-type protein. Negative autoregulation of rpoN was suggested by the fact that the mutation inactivating RpoN enhanced the transcription of rpoN. Primer extension revealed independent transcription start sites for rpoN and ORF2.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNS K. I., THOMAS C. A., Jr ISOLATION OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT DNA FROM HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:476–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Shapiro L. A temporally controlled sigma-factor is required for polar morphogenesis and normal cell division in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2395–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. J., Foster-Hartnett D., Gabbert K. K., Kranz R. G. Structure and expression of the alternative sigma factor, RpoN, in Rhodobacter capsulatus; physiological relevance of an autoactivated nifU2-rpoN superoperon. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(1):51–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom B. R., Chapman P. J., Pritchard P. H. Phenol and trichloroethylene degradation by Pseudomonas cepacia G4: kinetics and interactions between substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1279-1285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardies S. C., Patient R. K., Klein R. D., Ho F., Reznikoff W. S., Wells R. D. Construction and mapping of recombinant plasmids used for the preparation of DNA fragments containing the Escherichia coli lactose operator and promoter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5527–5534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinteregger C., Leitner R., Loidl M., Ferschl A., Streichsbier F. Degradation of phenol and phenolic compounds by Pseudomonas putida EKII. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 May;37(2):252–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00178180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D., Gold L. Translation of the UGA triplet in vitro by tryptophan transfer RNA's. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. Tryptophan transfer RNA as the UGA suppressor. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):439–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunger M., Schmucker R., Kishan V., Hillen W. Analysis and nucleotide sequence of an origin of DNA replication in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and its use for Escherichia coli shuttle plasmids. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90494-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaishi H., Gomada M., Inouye S., Nakazawa A. Physical map location of the rpoN gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1550–1551. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1550-1551.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yamada M., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Cloning and sequence analysis of the ntrA (rpoN) gene of Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90474-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E. Genetics and physiology of Acinetobacter. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:349–371. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukor J. J., Olsen R. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of tbuD, the gene encoding phenol/cresol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas pickettii PKO1, and functional analysis of the encoded enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6518–6526. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6518-6526.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Fritsche S., Knobel H., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H., Fischer H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has two differentially regulated, functional homologs of the sigma 54 gene (rpoN). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1125–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1125-1138.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Cayrol J. M., Ramos J. L., Harayama S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of the RpoN sigma-factor of Pseudomonas putida. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10125–10125. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Mulbry W., Noguchi N., Rogers E. J. UGA can be decoded as tryptophan at low efficiency in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1810–1812. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1810-1812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Coppard J. R. Mutations in genes downstream of the rpoN gene (encoding sigma 54) of Klebsiella pneumoniae affect expression from sigma 54-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1765–1775. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Gibbins J. R. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrogen-regulation gene ntrA of Klebsiella pneumoniae and comparison with conserved features in bacterial RNA polymerase sigma factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7607–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Stewart W. D. Studies on the regulation and function of the Klebsiella pneumoniae ntrA gene. Gene. 1985;35(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Chambers S. The helix-turn-helix motif of sigma 54 is involved in recognition of the -13 promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7221–7226. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7221-7226.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Gibbins J., Toukdarian A. The nucleotide sequence of the sigma factor gene ntrA (rpoN) of Azotobacter vinelandii: analysis of conserved sequences in NtrA proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00325701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle E. L., Ornston L. N. Benzoate and muconate, structurally dissimilar metabolites, induce expression of catA in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):414–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.414-415.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle E. L., Shapiro M. K., Ornston L. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus genes for benzoate degradation. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5496–5503. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5496-5503.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund I., Powlowski J., Shingler V. Complete nucleotide sequence and polypeptide analysis of multicomponent phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6826–6833. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6826-6833.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. K., Klose K. E., Stedman K. M., Kustu S. Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4267–4273. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4267-4273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurk A., Kasak L., Kivisaar M. Sequence of the gene (pheA) encoding phenol monooxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. EST1001: expression in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90531-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. Purification of the alternative sigma factor, sigma 54, from Salmonella typhimurium and characterization of sigma 54-holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19510–19518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powlowski J., Shingler V. In vitro analysis of polypeptide requirements of multicomponent phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6834–6840. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6834-6840.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Role of eukaryotic-type functional domains found in the prokaryotic enhancer receptor factor sigma 54. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90269-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Powlowski J., Marklund U. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the complete phenol/3,4-dimethylphenol catabolic pathway of Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):711–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.711-724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Metzke M., Timmis K. N. An upstream XylR- and IHF-induced nucleoprotein complex regulates the sigma 54-dependent Pu promoter of TOL plasmid. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1159–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Slooten J. C., Cervantes E., Broughton W. J., Wong C. H., Stanley J. Sequence and analysis of the rpoN sigma factor gene of rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, a primary coregulator of symbiosis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5563–5574. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5563-5574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



