Abstract
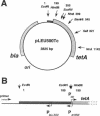
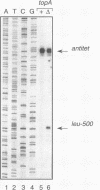
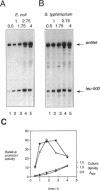
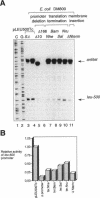
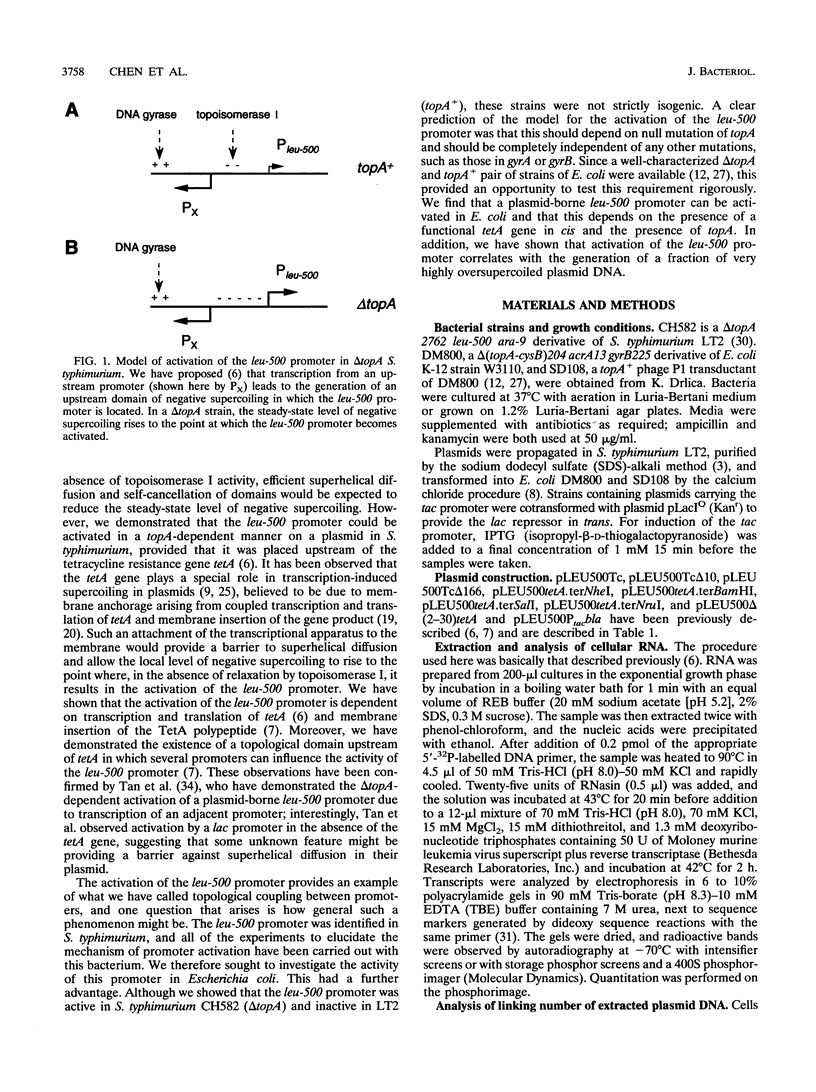
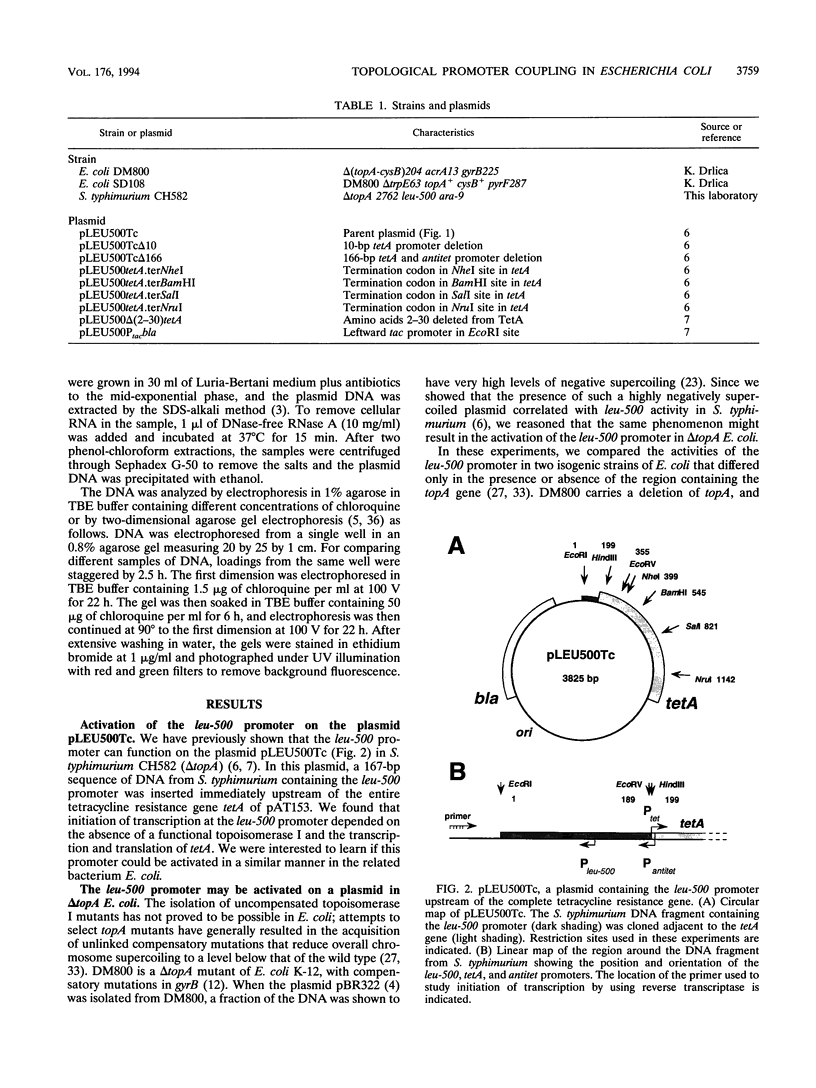
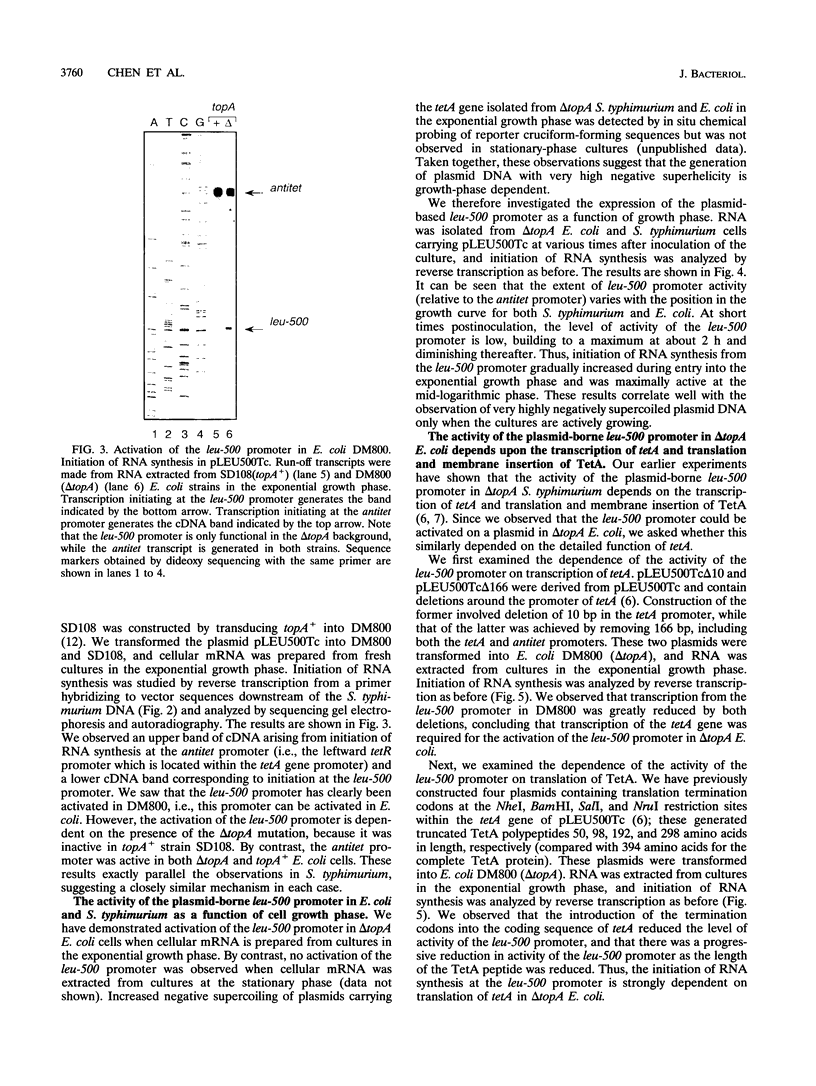
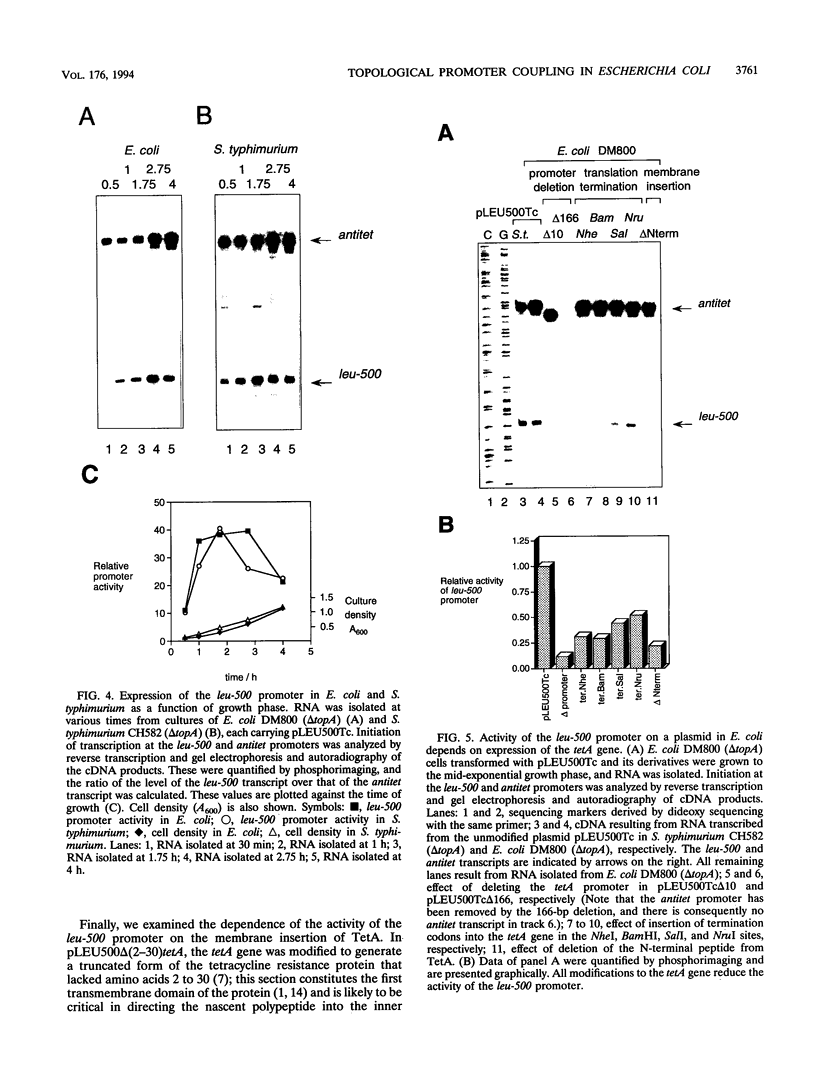
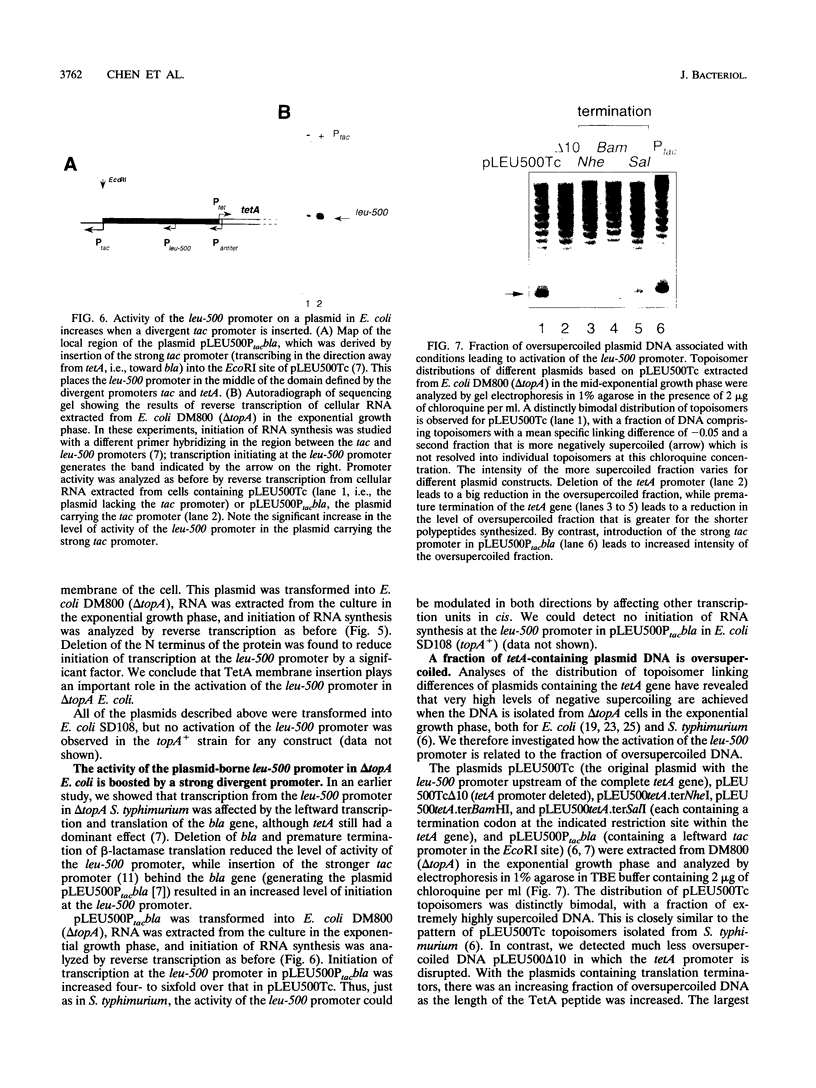
The leu-500 promoter of Salmonella typhimurium is activated in topA mutants. We have previously shown that this promoter can be activated on circular plasmids in a manner that depends on transcription and translation of the tetracycline resistance gene tetA and insertion of its product into the cell membrane. We have suggested that in the absence of enzymatic relaxation by topoisomerase I, the local domain of transcription-induced DNA supercoiling reaches a steady-state level that leads to the activation of the leu-500 promoter. In the present paper, we have shown that the leu-500 promoter may also be activated in Escherichia coli. Comparison of the closely related pair of E. coli strains DM800 (delta topA) and SD108 (topA+) shows that the activation is dependent on the presence of a null mutation in topA. We have also shown that activation of the plasmid-borne leu-500 promoter depends, as in S. typhimurium, on the function of an adjacent tetA gene, suggesting that membrane anchorage of the TetA peptide prevents dissipation of transcription-induced supercoiling by superhelical diffusion. The activity of the leu-500 promoter is boosted by placing a divergent tac promoter on the side opposite to tetA. The topoisomer distributions of these plasmids extracted from the cell have been analyzed. We find that when the parent plasmid pLEU500Tc, containing the leu-500 promoter upstream of the complete tetA gene, is extracted from E. coli DM800 (delta topA), the distribution of linking numbers is bimodal. There is a fraction with a lower level of supercoiling (mean linking difference approximately -0.05) that is constant for all plasmids extracted from either delta topA or topA+ cells. In addition, we observe a second fraction with highly negatively supercoiled DNA (mean linking difference approximately -0.09) only in DNA extracted from delta topA cells. The proportion of the oversupercoiled fraction correlates with the activity of the leu-500 promoter: it is strongly reduced when the tetA promoter is deleted or when translation of TetA is prematurely terminated, while it is increased when the strong tac promoter is present in cis. We suggest that this oversupercoiled fraction represents the proportion of plasmid molecules active in tetA transcription and that it is this supercoiling that activates the leu-500 promoter.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard J. D., Bertrand K. P. Membrane topology of the pBR322 tetracycline resistance protein. TetA-PhoA gene fusions and implications for the mechanism of TetA membrane insertion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17809–17819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amouyal M., Buc H. Topological unwinding of strong and weak promoters by RNA polymerase. A comparison between the lac wild-type and the UV5 sites of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):795–808. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowater R., Aboul-Ela F., Lilley D. M. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of circular DNA topoisomers. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:105–120. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D., Bowater R. P., Lilley D. M. Activation of the leu-500 promoter: a topological domain generated by divergent transcription in a plasmid. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13162–13170. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D., Bowater R., Dorman C. J., Lilley D. M. Activity of a plasmid-borne leu-500 promoter depends on the transcription and translation of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. N., Ma D., Pon N. G., Hearst J. E. Dynamics of DNA supercoiling by transcription in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10603–10607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayn A., Malkhosyan S., Mirkin S. M. Transcriptionally driven cruciform formation in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5991–5997. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P., Nordheim A. Transcription-induced conformational change in a topologically closed DNA domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2941–2946. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert B., Beck C. F. Topology of the transposon Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistance protein within the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11663–11670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Tripp M., Friedman S. B., Calvo J. M. Promoter mutation causing catabolite repression of the Salmonella typhimurium leucine operon. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):948–953. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.948-953.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Higgins C. F. Local DNA topology and gene expression: the case of the leu-500 promoter. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):779–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Positively supercoiled plasmid DNA is produced by treatment of Escherichia coli with DNA gyrase inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2999–3017. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. K., Kazic T., Berg D. E. Formation of supercoiling domains in plasmid pBR322. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2181–2187. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2181-2187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch A. S., Wang J. C. Anchoring of DNA to the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane through cotranscriptional synthesis of polypeptides encoding membrane proteins or proteins for export: a mechanism of plasmid hypernegative supercoiling in mutants deficient in DNA topoisomerase I. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1645-1655.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin P., Zumstein L., Sternglanz R., Wang J. C. The Escherichia coli supX locus is topA, the structural gene for DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5437–5441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai F. H., Margolin P. ANALYSIS OF UNLINKED SUPPRESSORS OF AN O degrees MUTATION IN SALMONELLA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50(1):140–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J. DNA topoisomerase I mutants. Increased heterogeneity in linking number and other replicon-dependent changes in DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and suppression of the leu-500 promoter mutation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):947–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.947-949.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. Topoisomerase I mutants: the gene on pBR322 that encodes resistance to tetracycline affects plasmid DNA supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8952–8956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Manes S. H., Drlica K. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants: increased supercoiling is corrected by mutations near gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A. R., Wells R. D. Direct evidence for the effect of transcription on local DNA supercoiling in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90721-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. M., Higgins C. F., Lilley D. M. DNA supercoiling and the leu-500 promoter mutation of Salmonella typhimurium. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1863–1869. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. M., Higgins C. F., Lilley D. M. The genetic control of DNA supercoiling in Salmonella typhimurium. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1745–1752. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. DNA supercoiling: another level for regulating gene expression. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R., DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Becherer K., Zumstein L., Wang J. C. Mutations in the gene coding for Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I affect transcription and transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J., Shu L., Wu H. Y. Activation of the leu-500 promoter by adjacent transcription. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1077-1086.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. I., Ohmori H., Bird R. E. Origin of replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. P., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Peck L. J., Becherer K. DNA supercoiling and its effects on DNA structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):85–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]