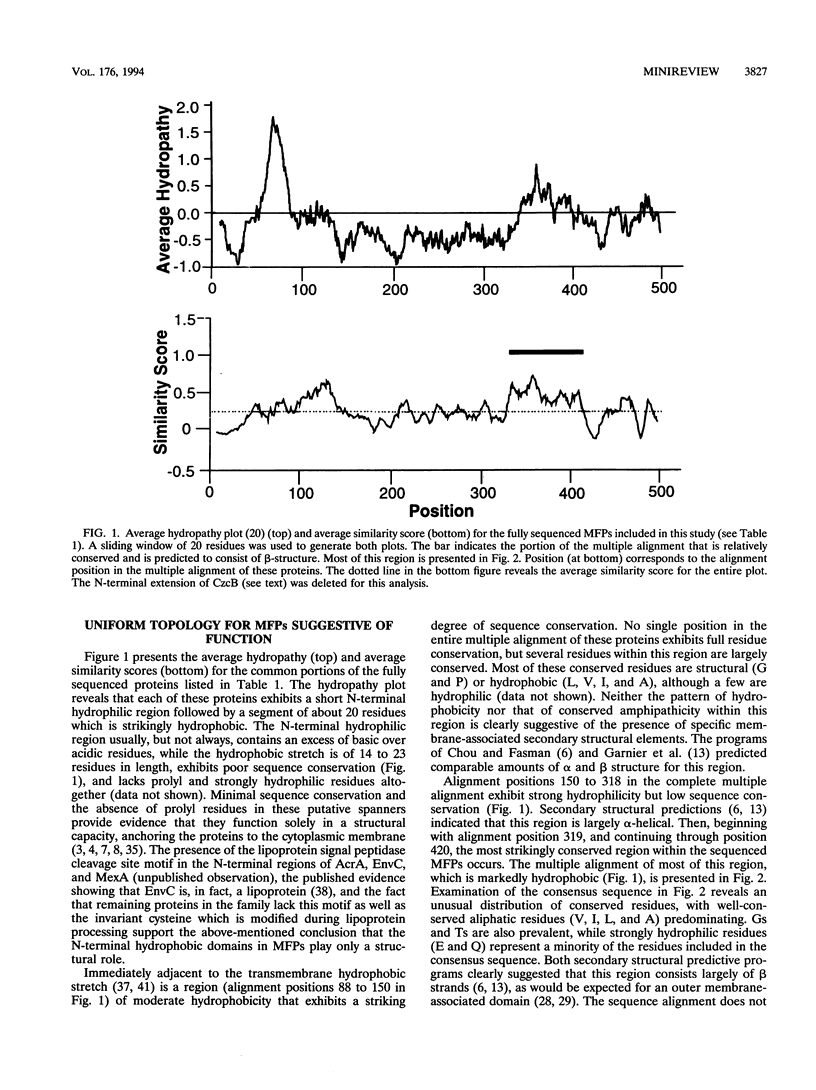
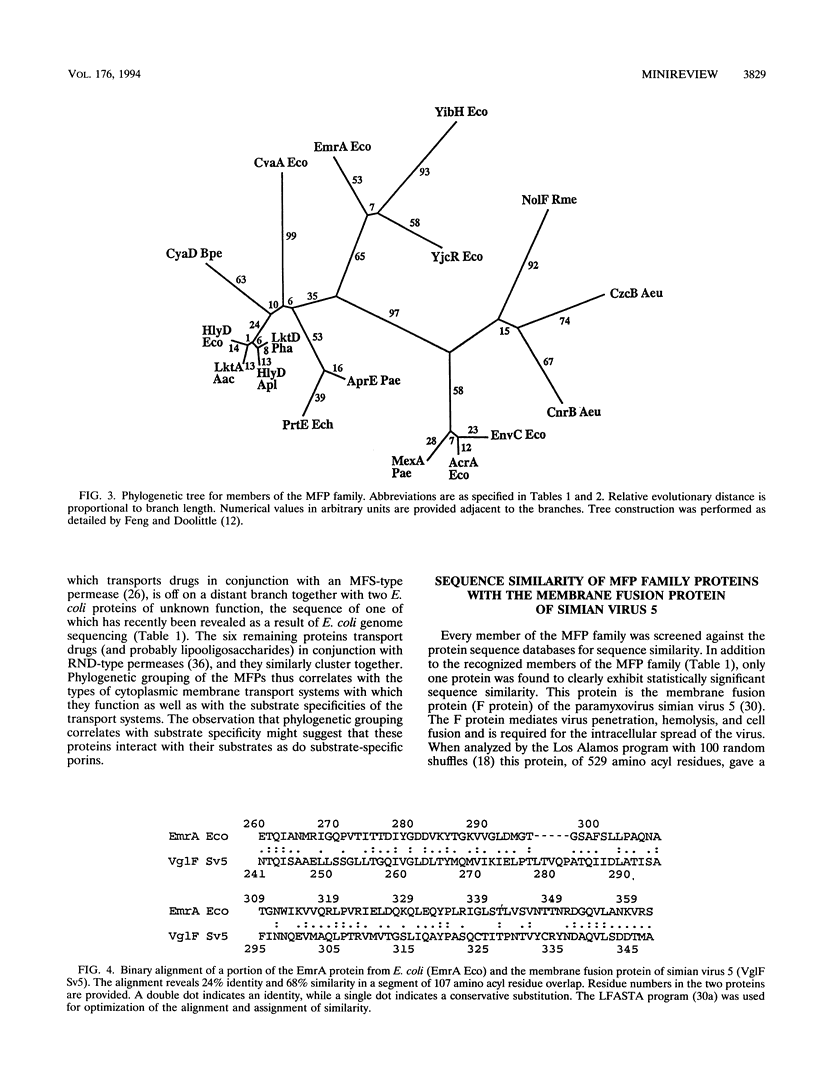
Abstract
Seventeen fully sequenced and two partially sequenced extracytoplasmic proteins of purple, gram-negative bacteria constitute a homologous family termed the putative membrane fusion protein (MFP) family. Each such protein apparently functions in conjunction with a cytoplasmic membrane transporter of the ATP-binding cassette family, major facilitator superfamily, or heavy metal resistance/nodulation/cell division family to facilitate transport of proteins, peptides, drugs, or carbohydrates across the two membranes of the gram-negative bacterial cell envelope. Evidence suggests that at least some of these transport systems also function in conjunction with a distinct outer membrane protein. We report here that the phylogenies of these proteins correlate with the types of transport systems with which they function as well as with the natures of the substrates transported. Characterization of the MFPs with respect to secondary structure, average hydropathy, and average similarity provides circumstantial evidence as to how they may allow localized fusion of the two gram-negative bacterial cell membranes. The membrane fusion protein of simian virus 5 is shown to exhibit significant sequence similarity to representative bacterial MFPs.
Full text
PDF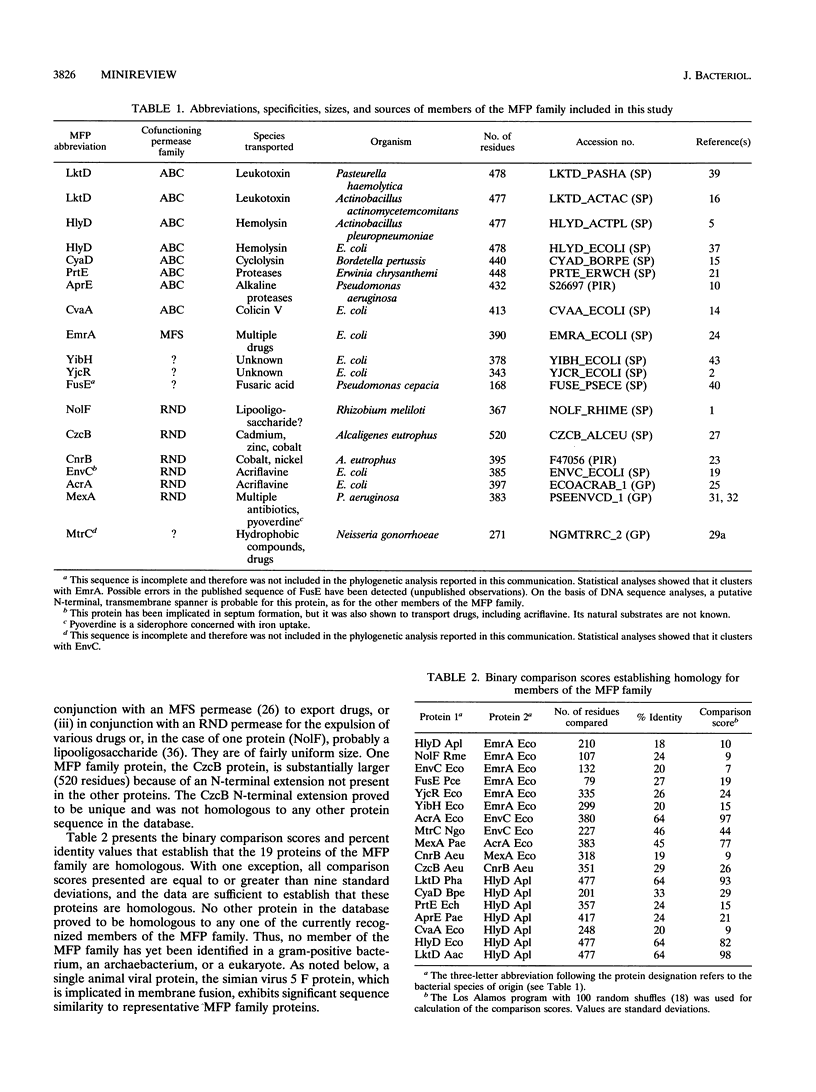




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baev N., Endre G., Petrovics G., Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Six nodulation genes of nod box locus 4 in Rhizobium meliloti are involved in nodulation signal production: nodM codes for D-glucosamine synthetase. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00282455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Burland V., Plunkett G., 3rd, Sofia H. J., Daniels D. L. Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome. IV. DNA sequence of the region from 89.2 to 92.8 minutes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5408–5417. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Deber C. M. Hypothesis about the function of membrane-buried proline residues in transport proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):917–921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Deber R. B., Hsu L. C., Woolley G. A., Young X. K., Deber C. M. Evidence for similar function of transmembrane segments in receptor and membrane-anchored proteins. Biopolymers. 1988 Jul;27(7):1171–1182. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. The Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hemolysin determinant: unlinked appCA and appBD loci flanked by pseudogenes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5151–5158. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5151-5158.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deber C. M., Brandl C. J., Deber R. B., Hsu L. C., Young X. K. Amino acid composition of the membrane and aqueous domains of integral membrane proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 15;251(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deber C. M., Glibowicka M., Woolley G. A. Conformations of proline residues in membrane environments. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):149–157. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong F., Lazdunski A., Cami B., Murgier M. Sequence of a cluster of genes controlling synthesis and secretion of alkaline protease in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: relationships to other secretory pathways. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90160-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath M. J., Skvirsky R. C., Kolter R. Functional complementation between bacterial MDR-like export systems: colicin V, alpha-hemolysin, and Erwinia protease. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7549–7556. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7549-7556.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson L., Mahanty H. K., Kolter R. Genetic analysis of an MDR-like export system: the secretion of colicin V. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3875–3884. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthmiller J. M., Kraig E., Cagle M. P., Kolodrubetz D. Sequence of the lktD gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5292–5292. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M. I. Los Alamos sequence analysis package for nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):183–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R., Henrich B., Plapp R. Molecular analysis and nucleotide sequence of the envCD operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00290673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis K. Multidrug resistance pumps in bacteria: variations on a theme. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya O., Lewis K. Emr, an Escherichia coli locus for multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8938–8942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi: the specific secretion functions are analogous to those of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D., Cook D. N., Alberti M., Pon N. G., Nikaido H., Hearst J. E. Molecular cloning and characterization of acrA and acrE genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(19):6299–6313. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.19.6299-6313.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marger M. D., Saier M. H., Jr A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90081-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H., Nies A., Chu L., Silver S. Expression and nucleotide sequence of a plasmid-determined divalent cation efflux system from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Porins and specific channels of bacterial outer membranes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Saier M. H., Jr Transport proteins in bacteria: common themes in their design. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):936–942. doi: 10.1126/science.1279804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Fusion protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of mRNA predicts a highly hydrophobic glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Heinrichs D. E., Neshat S. Cloning and sequence analysis of an EnvCD homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: regulation by iron and possible involvement in the secretion of the siderophore pyoverdine. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):529–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Krebes K., McNally C., Neshat S. Multiple antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence for involvement of an efflux operon. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7363–7372. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7363-7372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr A new subfamily of bacterial ABC-type transport systems catalyzing export of drugs and carbohydrates. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1326–1332. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Computer-aided analyses of transport protein sequences: gleaning evidence concerning function, structure, biogenesis, and evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):71–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.71-93.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Tam R., Reizer A., Reizer J. Two novel families of bacterial membrane proteins concerned with nodulation, cell division and transport. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(5):841–847. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schülein R., Gentschev I., Mollenkopf H. J., Goebel W. A topological model for the haemolysin translocator protein HlyD. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jul;234(1):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00272357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffer D., Klein J. R., Plapp R. EnvC, a new lipoprotein of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Mar 1;107(2-3):175–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Yagi T., Katayama S., Katsuragi K., Tachibana K., Toyoda H., Ouchi S., Obata K., Shibano Y., Noda M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the fusaric acid-resistance gene from Pseudomonas cepacia. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Jul;55(7):1913–1918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. C., Seror S. J., Blight M., Pratt J. M., Broome-Smith J. K., Holland I. B. Analysis of the membrane organization of an Escherichia coli protein translocator, HlyB, a member of a large family of prokaryote and eukaryote surface transport proteins. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90748-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao S., Sandt C. H., Feulner G., Vlazny D. A., Gray J. A., Hill C. W. Rhs elements of Escherichia coli K-12: complex composites of shared and unique components that have different evolutionary histories. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):2799–2808. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2799-2808.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


