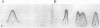Abstract
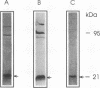
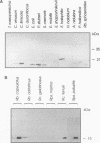
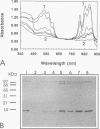
A rabbit antiserum was raised against the photoactive yellow protein (PYP) from Ectothiorhodospira halophila and purified by adsorption experiments to obtain a highly specific polyclonal antiserum. This antiserum was used to obtain the following results. (i) In E. halophila, PYP can be isolated from the fraction of soluble proteins. In the intact cell, however, PYP appeared to be associated with (intra)cytoplasmic membranes, as was concluded from analysis of immunogold-labelled thin sections of the organism. (ii) The regulation of expression of PYP was studied by using dot blot assays, Western blotting (immunoblotting), and rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Under all conditions investigated (light color, salt concentration, and growth phase), PYP was expressed constitutively in E. halophila. However, when Rhodospirillum salexigens was grown aerobically, the expression of PYP was suppressed. (iii) A large number of prokaryotic microorganisms contained a single protein, with an apparent size of approximately 15 kDa, that cross-reacted with the antiserum. Among the positively reacting organisms were both phototrophic and chemotrophic, as well as motile and nonmotile, organisms. After separation of cellular proteins into a membrane fraction and soluble proteins, it was established that organisms adapted to growth at higher salt concentrations tended to have the cross-reacting protein in the soluble fraction. In the cases of R. salexigens and Chromatium salexigens, we have shown that the cross-reacting protein involved is strongly homologous to PYP from E. halophila.
Full text
PDF

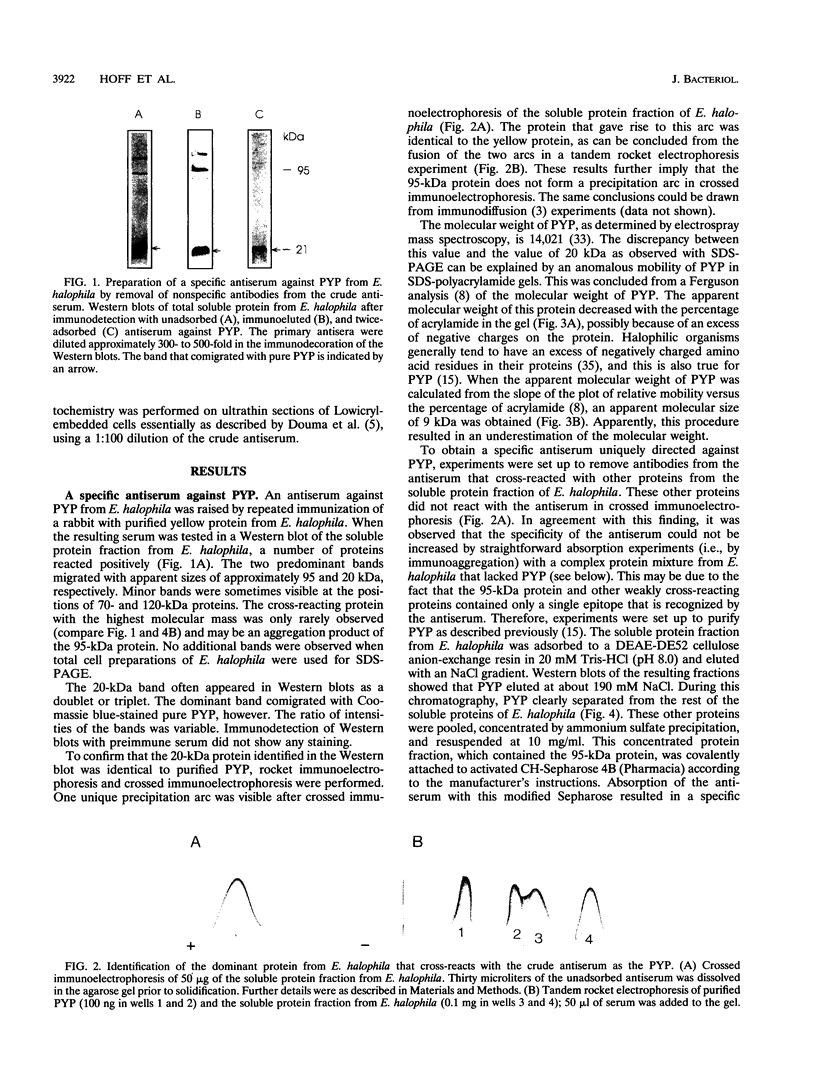
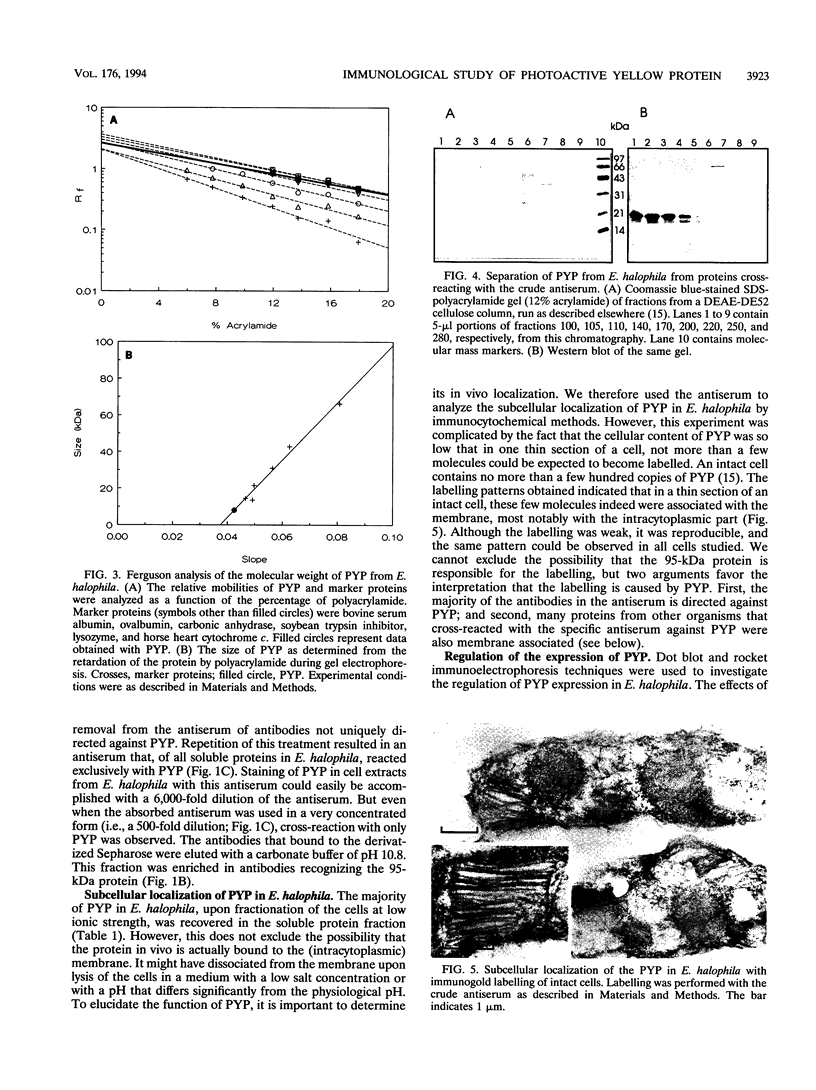
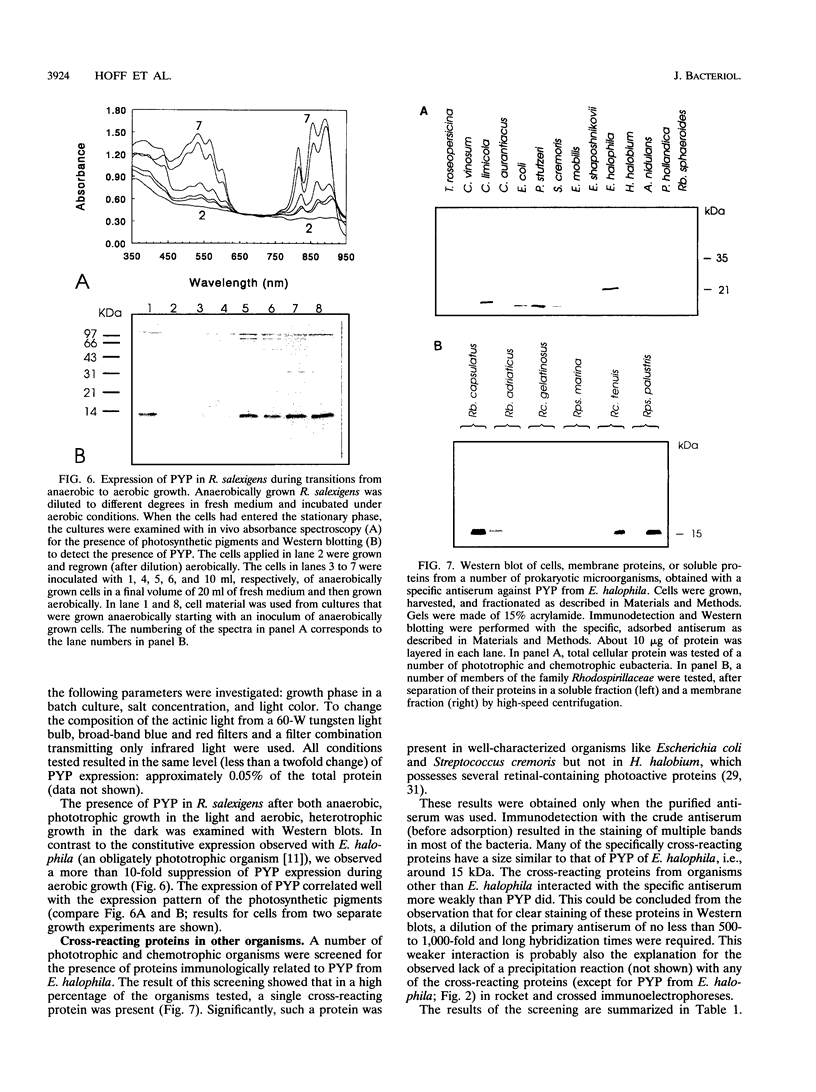



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. L., McIntosh L. Light-activated heterotrophic growth of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803: a blue-light-requiring process. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2761–2767. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2761-2767.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Seÿen H. G., Konings W. N. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles and chromatophoresis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. N., Rodbard D. Precision of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis for the molecular weight estimation of a membrane glycoprotein: studies on bovine rhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRee D. E., Tainer J. A., Meyer T. E., Van Beeumen J., Cusanovich M. A., Getzoff E. D. Crystallographic structure of a photoreceptor protein at 2.4 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6533–6537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Fitch J. C., Bartsch R. G., Tollin G., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochromes and a photoactive yellow protein isolated from the moderately halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodospirillum salexigens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Fitch J. C., Bartsch R. G., Tollin G., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochromes and a photoactive yellow protein isolated from the moderately halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodospirillum salexigens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E. Isolation and characterization of soluble cytochromes, ferredoxins and other chromophoric proteins from the halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 23;806(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Causgrove T. P., Cheng P., Blankenship R. E. Picosecond decay kinetics and quantum yield of fluorescence of the photoactive yellow protein from the halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):988–991. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82313-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Hazzard J. H., Cusanovich M. A. Photoactive yellow protein from the purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Quantum yield of photobleaching and effects of temperature, alcohols, glycerol, and sucrose on kinetics of photobleaching and recovery. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):559–564. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82703-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Yakali E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Properties of a water-soluble, yellow protein isolated from a halophilic phototrophic bacterium that has photochemical activity analogous to sensory rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):418–423. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otomo J., Marwan W., Oesterhelt D., Desel H., Uhl R. Biosynthesis of the two halobacterial light sensors P480 and sensory rhodopsin and variation in gain of their signal transduction chains. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2155–2159. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2155-2159.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sganga M. W., Bauer C. E. Regulatory factors controlling photosynthetic reaction center and light-harvesting gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90037-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyk A., Schyns G., Tandeau de Marsac N., Houmard J. Transduction of the light signal during complementary chromatic adaptation in the cyanobacterium Calothrix sp. PCC 7601: DNA-binding proteins and modulation by phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger W. W., Hoff W. D., Armitage J. P., Hellingwerf K. J. The eubacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila is negatively phototactic, with a wavelength dependence that fits the absorption spectrum of the photoactive yellow protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3096–3104. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3096-3104.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Sensory rhodopsins of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:193–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beeumen J. J., Devreese B. V., Van Bun S. M., Hoff W. D., Hellingwerf K. J., Meyer T. E., McRee D. E., Cusanovich M. A. Primary structure of a photoactive yellow protein from the phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila, with evidence for the mass and the binding site of the chromophore. Protein Sci. 1993 Jul;2(7):1114–1125. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]