Abstract
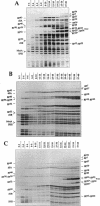
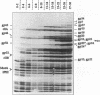
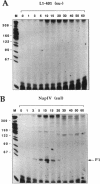
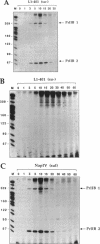
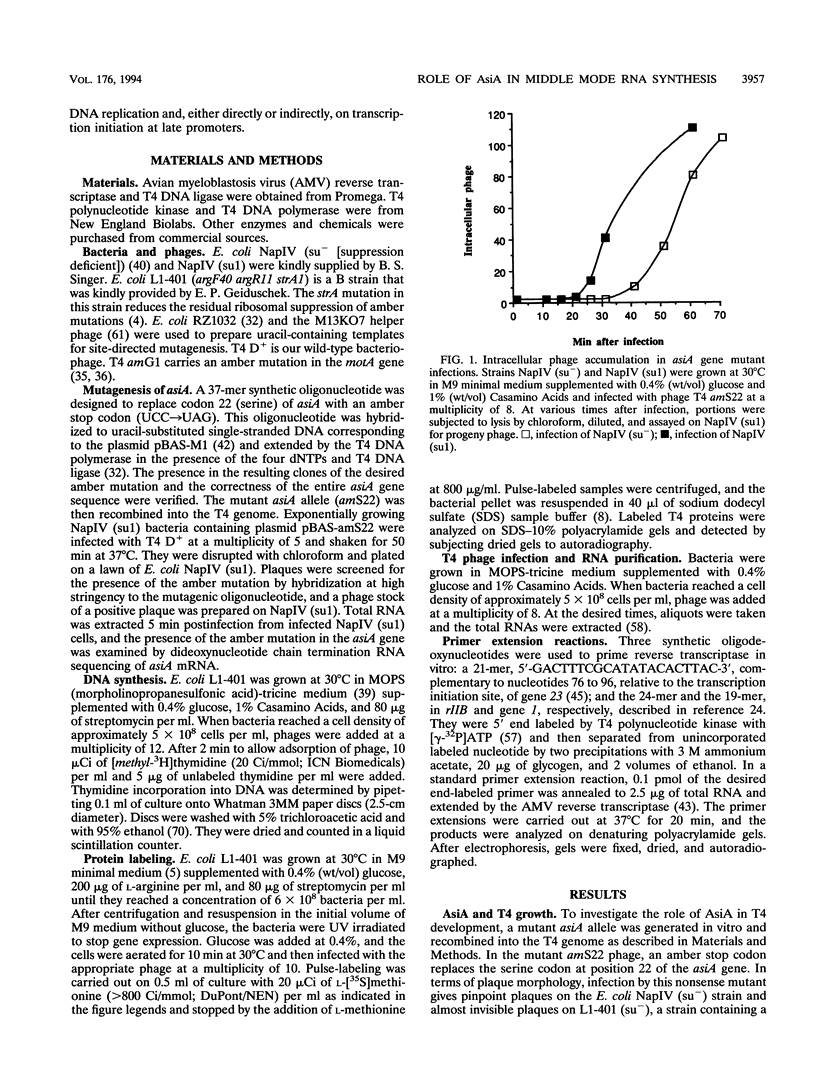
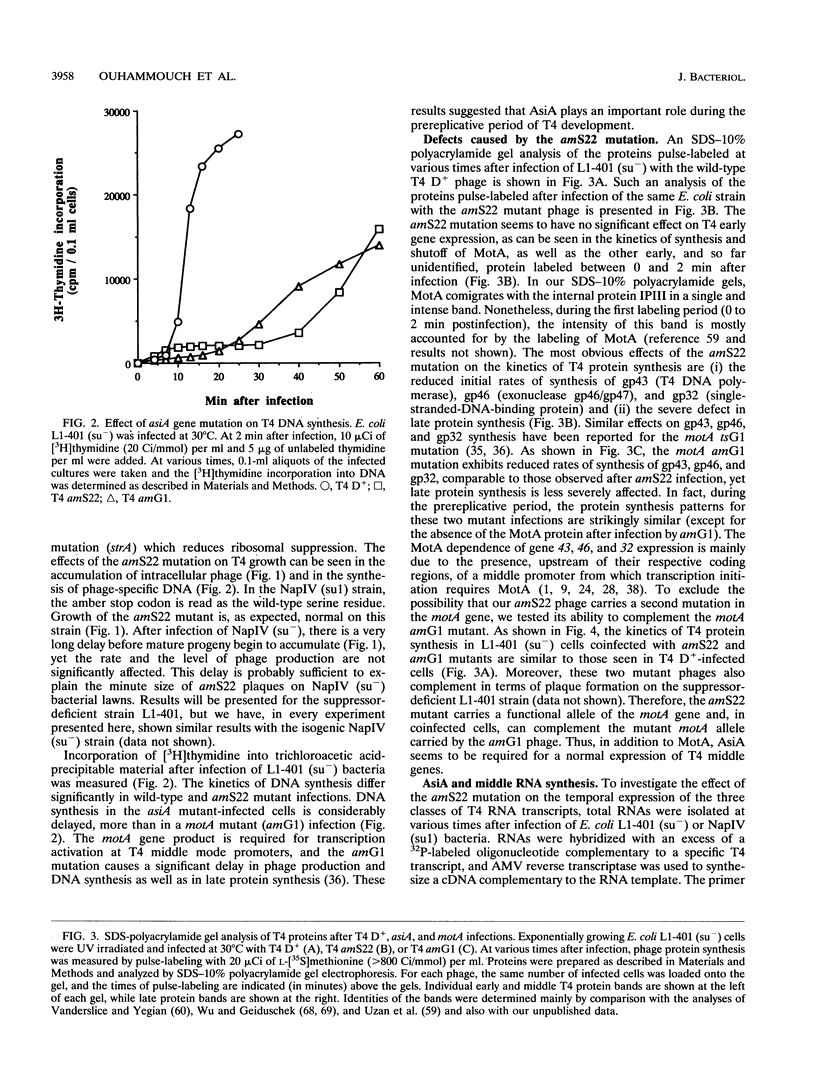
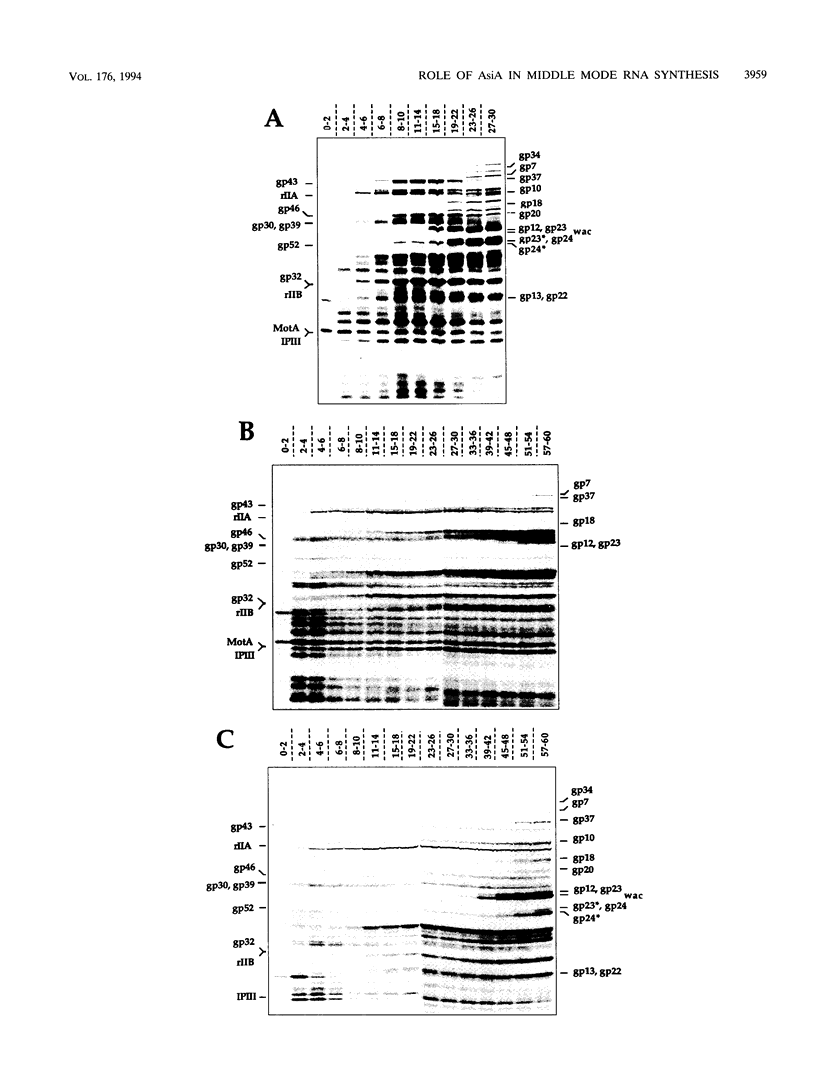
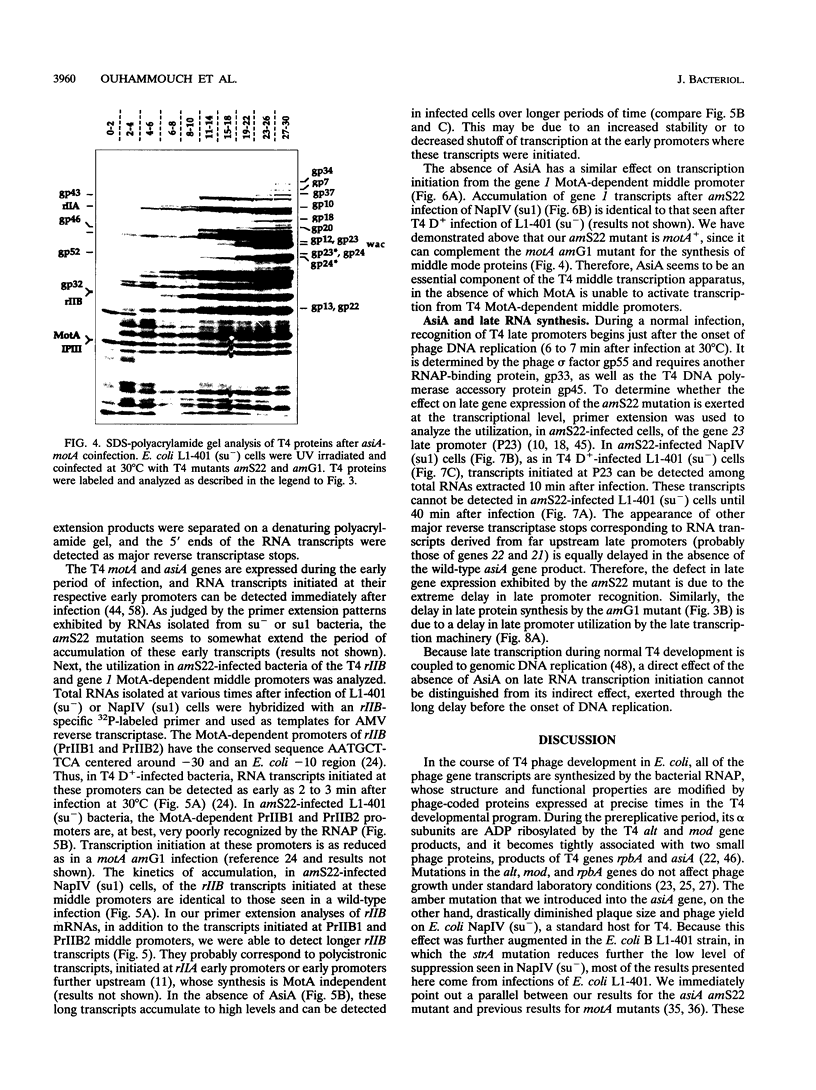
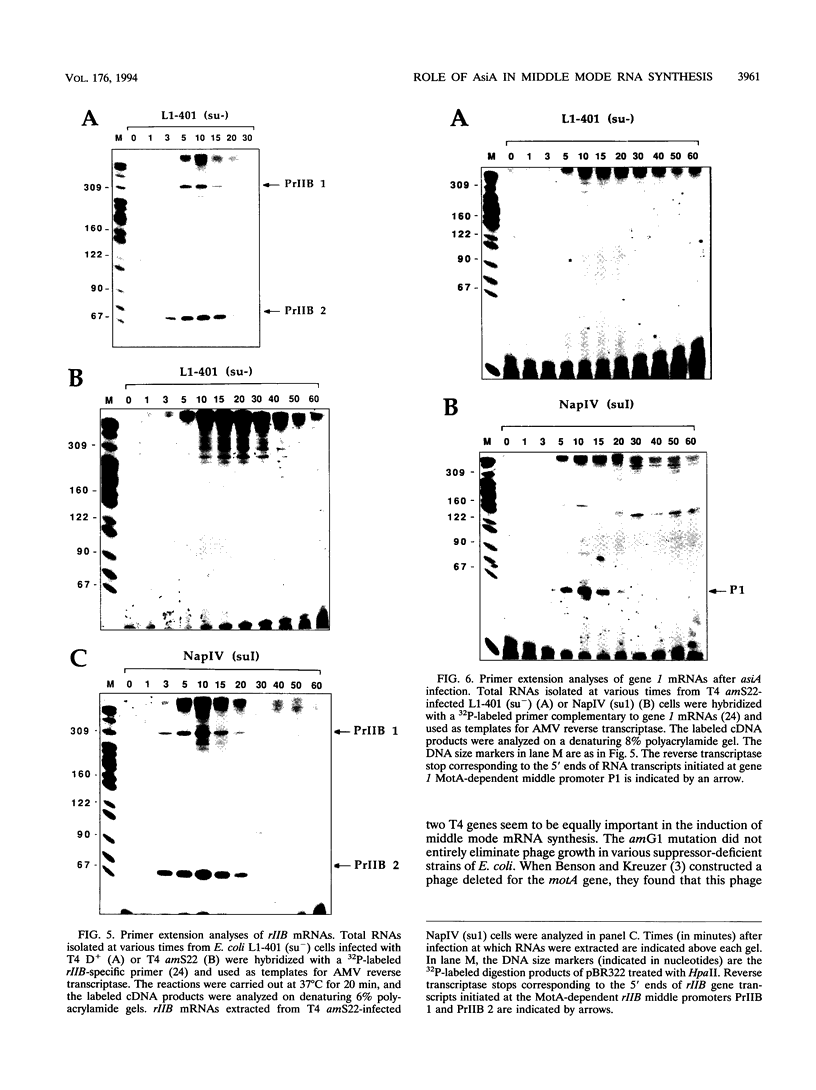
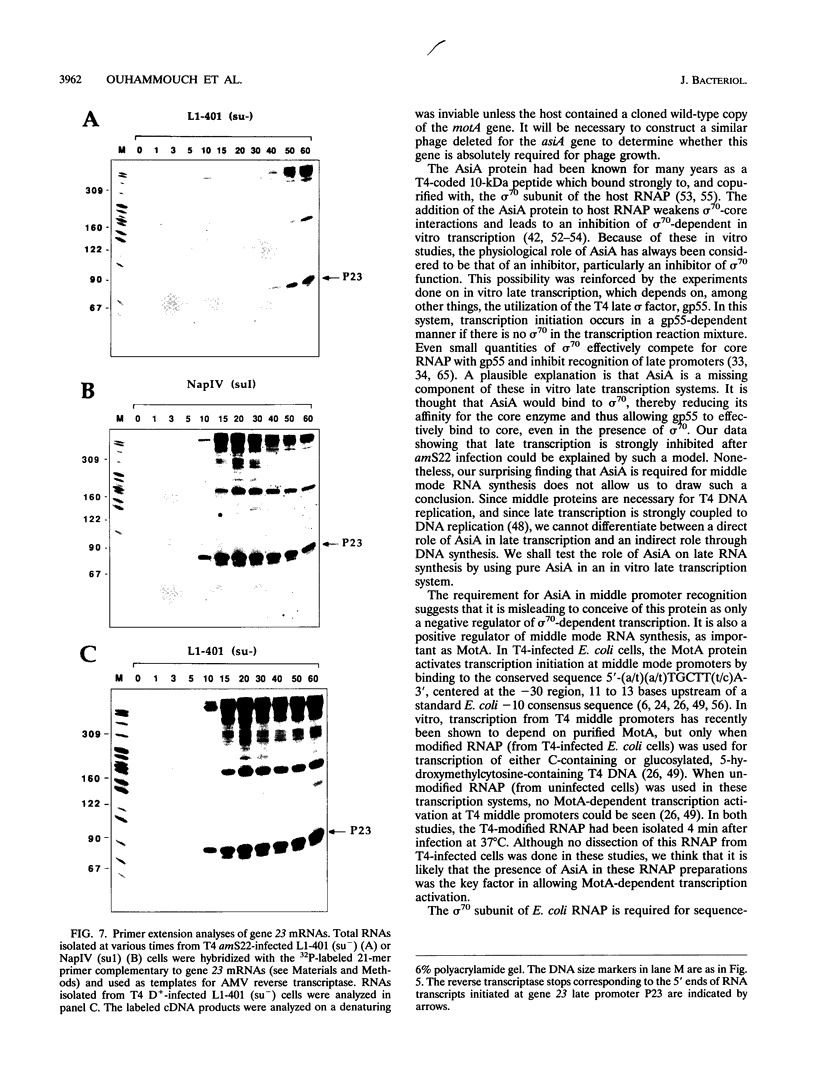
The asiA gene of bacteriophage T4 encodes a 10-kDa peptide which binds strongly in vitro to the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, thereby weakening sigma 70-core interactions and inhibiting sigma 70-dependent transcription. To assess the physiological role of this protein, we have introduced an amber mutation into the proximal portion of the asiA gene. On suppressor-deficient hosts, this mutant phage (amS22) produces minute plaques and exhibits a pronounced delay in phage production. During these mutant infections, T4 DNA synthesis is strongly delayed, suggesting that the AsiA protein plays an important role during the prereplicative period of phage T4 development. The kinetics of protein synthesis show clearly that while T4 early proteins are synthesized normally, those expressed primarily via the middle mode exhibit a marked inhibition. In fact, the pattern of protein synthesis after amS22 infection resembles greatly that seen after infection by amG1, an amber mutant in motA, a T4 gene whose product is known to control middle mode RNA synthesis. The amber mutations in the motA and asiA genes complement, both for phage growth and for normal kinetics of middle mode protein synthesis. Furthermore, primer extension analyses show that three different MotA-dependent T4 middle promoters are not recognized after infection by the asiA mutant phage. Thus, in conjunction with the MotA protein, the AsiA protein is required for transcription activation at T4 middle mode promoters.
Full text
PDF
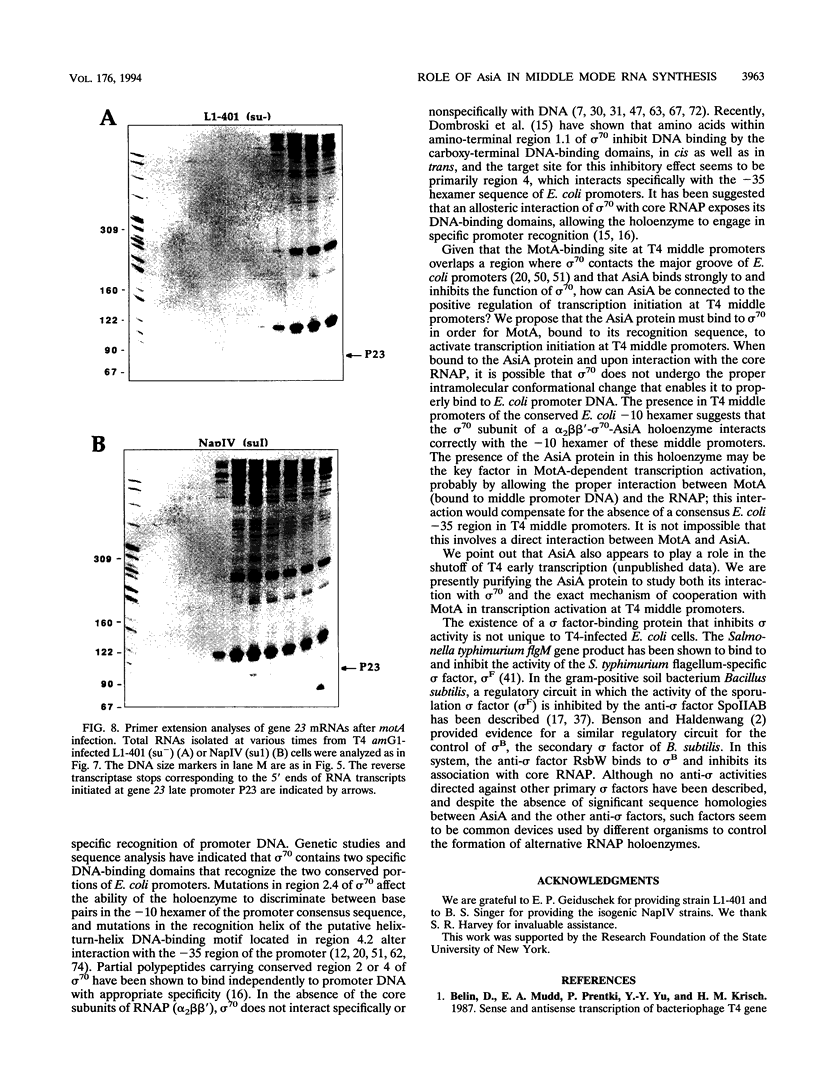


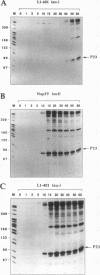
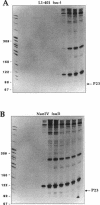
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma B is regulated by a binding protein (RsbW) that blocks its association with core RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson K. H., Kreuzer K. N. Role of MotA transcription factor in bacteriophage T4 DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolle A., Epstein R. H., Salser W., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: synthesis and relative stability of early and late RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):325–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardillo T. S., Landry E. F., Wiberg J. S. regA protein of bacteriophage T4D: identification, schedule of synthesis, and autogenous regulation. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):905–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.905-916.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Mudd E. A., Krisch H. M. Transcription and messenger RNA processing upstream of bacteriophage T4 gene 32. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):39–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00261155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Young E. T. T4 late transcripts are initiated near a conserved DNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):369–371. doi: 10.1038/299369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daegelen P., Brody E. The rIIA gene of bacteriophage T4. II. Regulation of its messenger RNA synthesis. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):249–260. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D., Zuber P., Losick R. Two amino acids in an RNA polymerase sigma factor involved in the recognition of adjacent base pairs in the -10 region of a cognate promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Amino-terminal amino acids modulate sigma-factor DNA-binding activity. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2446–2455. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Walter W. A., Record M. T., Jr, Siegele D. A., Gross C. A. Polypeptides containing highly conserved regions of transcription initiation factor sigma 70 exhibit specificity of binding to promoter DNA. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90174-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan L., Losick R. SpoIIAB is an anti-sigma factor that binds to and inhibits transcription by regulatory protein sigma F from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P. Regulation of expression of the late genes of bacteriophage T4. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:437–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G., Setzer J. ADP ribosylation of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase is nonessential for bacteriophage T4 development. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):547–549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.547-549.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild N., Gayle M., Sweeney R., Hollingsworth T., Modeer T., Gold L. Transcriptional activation of bacteriophage T4 middle promoters by the motA protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen D. R., Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. An RNA polymerase-binding protein that is required for communication between an enhancer and a promoter. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):573–578. doi: 10.1126/science.2185541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M. Transcription from a bacteriophage T4 middle promoter using T4 motA protein and phage-modified RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18034–18044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz H. R. Bacteriophage T4 mutants deficient in alteration and modification of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T., Karam J. D. Transcriptional mapping of a DNA replication gene cluster in bacteriophage T4. Sites for initiation, termination, and mRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5303–5316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch H. M., Van Houwe G., Belin D., Gibbs W., Epstein R. H. Regulation of the expression of bacteriophage T4 genes 32 and 43. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Doi R. H. Free sigma factor of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase can bind to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9778–9781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Jaffe D., Doi R. H. Free sigma subunit of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase binds to DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):63–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00339006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Goldfarb A. Late sigma factor of bacteriophage T4. Formation and properties of RNA polymerase-promoter complexes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1174–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Zalenskaya K., Goldfarb A. Competition between sigma factors for core RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8521–8530. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Richardson J., Goodin D. Mutant of bacteriophage T4D affecting expression of many early genes. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):48–50. doi: 10.1038/250048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Van Houwe G., Epstein R. H. Isolation and characterization of conditional lethal mutations in the mot gene of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):551–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. T., Hilditch C. M., Diederich B., Errington J., Yudkin M. D. Sigma F, the first compartment-specific transcription factor of B. subtilis, is regulated by an anti-sigma factor that is also a protein kinase. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90520-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd E. A., Prentki P., Belin D., Krisch H. M. Processing of unstable bacteriophage T4 gene 32 mRNAs into a stable species requires Escherichia coli ribonuclease E. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3601–3607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Kutsukake K., Suzuki H., Lino T. A novel transcriptional regulation mechanism in the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium: an antisigma factor inhibits the activity of the flagellum-specific sigma factor, sigma F. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3149–3157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsini G., Ouhammouch M., Le Caer J. P., Brody E. N. The asiA gene of bacteriophage T4 codes for the anti-sigma 70 protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.85-93.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouhammouch M., Brody E. N. Temperature-dependent template switching during in vitro cDNA synthesis by the AMV-reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5443–5450. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. L., Christensen A. C., Boosman A., Stockard J., Young E. T., Doermann A. H. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T4 gene 23 and the amino acid sequence of its product. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh U., Meares C. F. Footprint of the sigma protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91629-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Coupling of late transcription to viral replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. P., Kreuzer K. N. Purified MotA protein binds the -30 region of a bacteriophage T4 middle-mode promoter and activates transcription in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11399–11407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Inhibition of DNA-enzyme binding by an RNA polymerase inhibitor from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Rhoton J. C. Characterization of an inhibitor causing potassium chloride sensitivity of an RNA polymerase from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5074–5079. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Favre R., Brody E. A nuclease that cuts specifically in the ribosome binding site of some T4 mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8895–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Leautey J., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Brody E. Identification and biosynthesis of the bacteriophage T4 mot regulatory protein. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1207–1212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderslice R. W., Yegian C. D. The identification of late bacteriophage T4 proteins on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldburger C., Gardella T., Wong R., Susskind M. M. Changes in conserved region 2 of Escherichia coli sigma 70 affecting promoter recognition. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellman A., Meares C. F. Footprint of the sigma protein: a re-examination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91959-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Interactions of the bacteriophage T4 gene 55 product with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Competition with Escherichia coli sigma 70 and release from late T4 transcription complexes following initiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12365–12371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Yarbrough L. R., Hillel Z., Wu F. Y. Sigma cycle during in vitro transcription: demonstration by nanosecond fluorescence depolarization spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3019–3023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Geiduschek E. P. The role of replication proteins in the regulation of bacteriophage T4 transcription. I. Gene 45 and hydroxymethyl-C-containing DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):513–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Geiduschek E. P. The role of replication proteins in the regulation of bacteriophage T4 transcription. II. Gene 45 and late transcription uncoupled from replication. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):539–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Yeh Y. C. DNA arrested mutants of gene 59 of bacteriophage T4. II. Replicative intermediates. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):108–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. T., Menard R. C. Sizes of bacteriophage T4 early mRNA's separated by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and identified by in vitro translation and by hybridization to recombinant T4 plasmids. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):772–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.772-789.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zograff Y. N. On the role of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigma factor in T4 phage development. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):557–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00268782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Healy J., Carter H. L., 3rd, Cutting S., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Mutation changing the specificity of an RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franciscis V., Brody E. In vitro system for middle T4 RNA. I. Studies with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4087–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franciscis V., Favre R., Uzan M., Leautey J., Brody E. In vitro system for middle T4 RNA. II. Studies with T4-modified RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4097–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]