Abstract
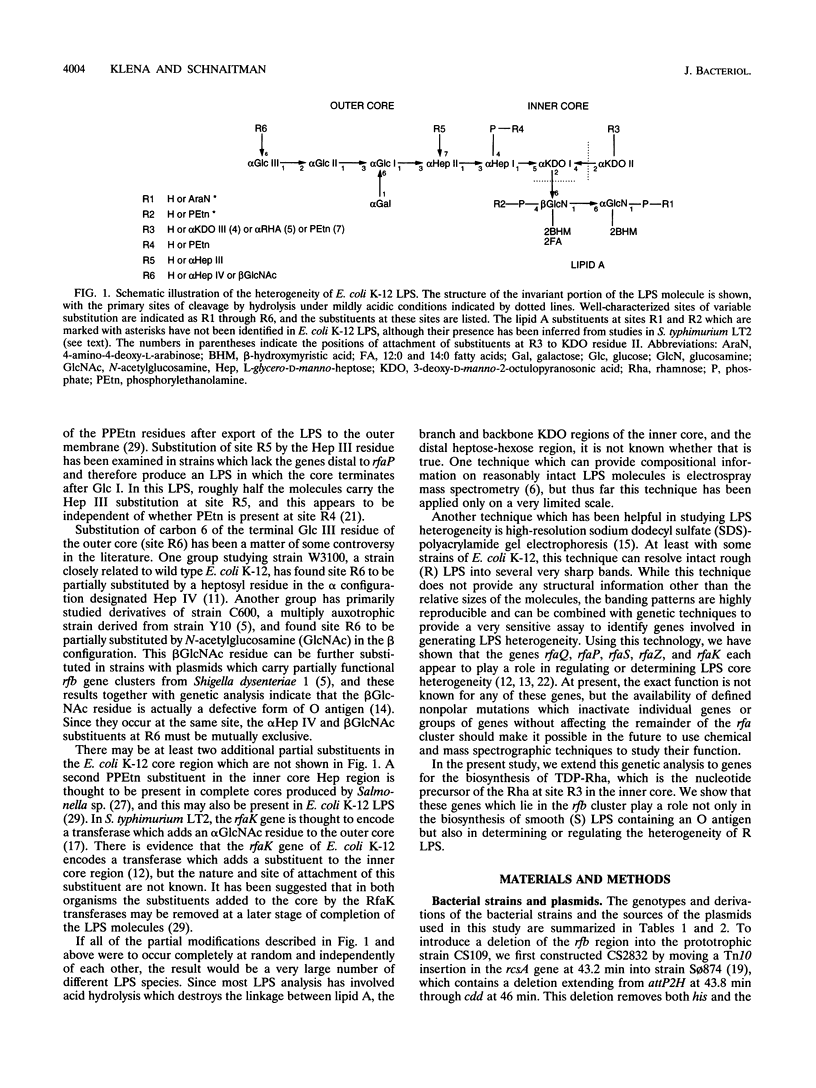
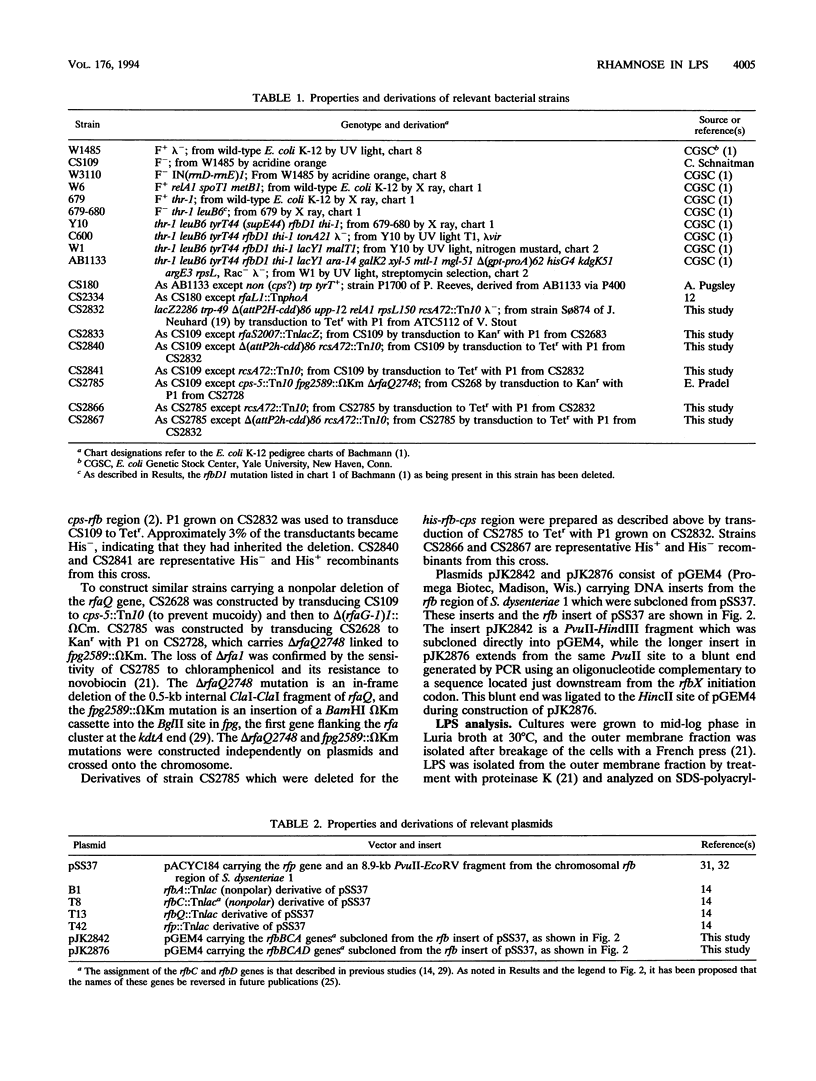
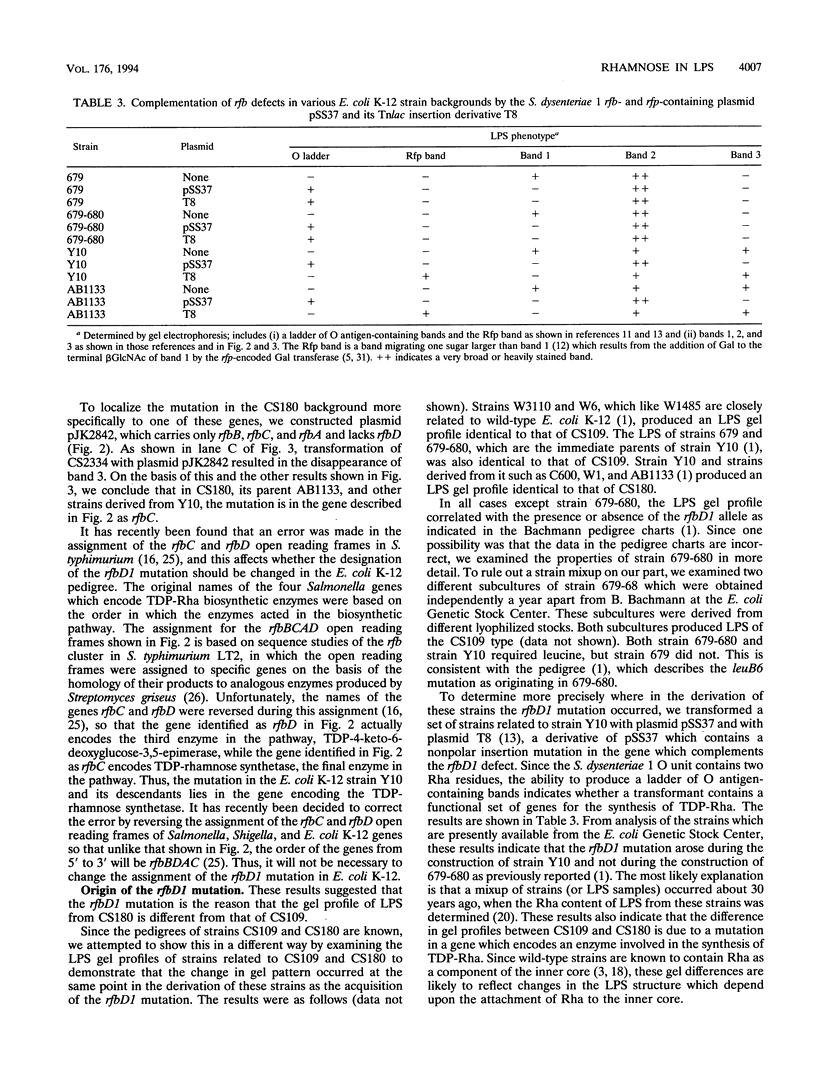
The rough lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of commonly used strains of Escherichia coli K-12 has two distinctly different band patterns when analyzed by high-resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The LPS of ancestral strains such as W1485F- consists primarily of a single broad gel band. In contrast, the LPS of strains derived from strain Y10 such as AB1133 or C600 gives three sharp gel bands. Complementation studies using DNA fragments from the rfb gene cluster of Shigella dysenteriae 1 indicated that the difference between the two gel patterns is due to a mutation in the gene encoding the TDP-rhamnose synthetase, the final enzyme involved in TDP-rhamnose biosynthesis. This mutation arose during the construction of strain Y10, and not in strain 679-680 as previously thought. The requirement for the rfaS gene for synthesis of the broad major band seen in W1485F- LPS and the shift in gel migration of a component of this band when an rfaQ mutation was introduced indicated that this broad band contained the unique form of rough E. coli LPS which has been termed lipooligosaccharide. This finding indicates that lipooligosaccharide is likely to contain rhamnose and suggests a model in which one of the functions of partial substituents such as rhamnose may be to direct core synthesis into different pathways to produce alternative forms of LPS.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Monner D. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):455–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.455-464.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementz T. The gene coding for 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonic acid transferase and the rfaQ gene are transcribed from divergently arranged promoters in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7750–7756. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7750-7756.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fält I. C., Schweda E. K., Weintraub A., Sturm S., Timmis K. N., Lindberg A. A. Expression of the Shigella dysenteriae type-1 lipopolysaccharide repeating unit in Escherichia coli K12/Shigella dysenteriae type-1 hybrids. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):573–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson B. W., Melaugh W., Phillips N. J., Apicella M. A., Campagnari A. A., Griffiss J. M. Investigation of the structural heterogeneity of lipooligosaccharides from pathogenic Haemophilus and Neisseria species and of R-type lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella typhimurium by electrospray mass spectrometry. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2702–2712. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2702-2712.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander I. M., Kilpeläinen I., Vaara M. Increased substitution of phosphate groups in lipopolysaccharides and lipid A of the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: a 31P-NMR study. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(3):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst O., Brade H. Isolation and identification of 3-deoxy-5-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-D-manno-2-octulopyranosonate from the inner core region of the lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli K-12. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Oct 25;207(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst O., Röhrscheidt-Andrzejewski E., Brade H. Isolation and characterisation of 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulopyranosonate 7-(2-aminoethyl phosphate) from the inner core region of Escherichia coli K-12 and Salmonella minnesota lipopolysaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Sep 5;204:93–102. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84024-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst O., Zähringer U., Brade H., Zamojski A. Structural analysis of the heptose/hexose region of the lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-12 strain W3100. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Aug 20;215(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(91)84031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klena J. D., Ashford R. S., 2nd, Schnaitman C. A. Role of Escherichia coli K-12 rfa genes and the rfp gene of Shigella dysenteriae 1 in generation of lipopolysaccharide core heterogeneity and attachment of O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7297–7307. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7297-7307.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klena J. D., Pradel E., Schnaitman C. A. The rfaS gene, which is involved in production of a rough form of lipopolysaccharide core in Escherichia coli K-12, is not present in the rfa cluster of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1524–1527. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1524-1527.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klena J. D., Schnaitman C. A. Function of the rfb gene cluster and the rfe gene in the synthesis of O antigen by Shigella dysenteriae 1. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesse A. J., Campagnari A. A., Bittner W. E., Apicella M. A. Increased resolution of lipopolysaccharides and lipooligosaccharides utilizing tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jan 24;126(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90018-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson D. F., Manning P. A., Morona R. Characterization of the dTDP-rhamnose biosynthetic genes encoded in the rfb locus of Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):281–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer H., Rapin A. M., Schmidt G., Boman H. G. Immunochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides from wild-type and mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):357–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhard J., Thomassen E. Altered deoxyribonucleotide pools in P2 eductants of Escherichia coli K-12 due to deletion of the dcd gene. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):999–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.999-1001.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nikaido K., Rapin A. M. Biosynthesis of thymidine diphosphate L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. T., Kloser A. W., Schnaitman C. A., Stein M. A., Gottesman S., Gibson B. W. Role of the rfaG and rfaP genes in determining the lipopolysaccharide core structure and cell surface properties of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2525–2538. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2525-2538.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Parker C. T., Schnaitman C. A. Structures of the rfaB, rfaI, rfaJ, and rfaS genes of Escherichia coli K-12 and their roles in assembly of the lipopolysaccharide core. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4736–4745. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4736-4745.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Schnaitman C. A. Effect of rfaH (sfrB) and temperature on expression of rfa genes of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6428–6431. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6428-6431.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves P. Evolution of Salmonella O antigen variation by interspecific gene transfer on a large scale. Trends Genet. 1993 Jan;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90067-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland K. L., Martin L. E., Esther C. R., Spitznagel J. K. Spontaneous pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 define a new two-component regulatory system with a possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4154–4164. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4154-4164.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A., Klena J. D. Genetics of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in enteric bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):655–682. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.655-682.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Armitage I. M., Anderson L., Takayama K., Qureshi N., Raetz C. R. Location of polar substituents and fatty acyl chains on lipid A precursors from a 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid-deficient mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Studies by 1H, 13C, and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16089–16098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm S., Jann B., Jann K., Fortnagel P., Timmis K. N. Genetic and biochemical analysis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 O antigen polysaccharide biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12: structure and functions of the rfb gene cluster. Microb Pathog. 1986 Jun;1(3):307–324. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm S., Timmis K. N. Cloning of the rfb gene region of Shigella dysenteriae 1 and construction of an rfb-rfp gene cassette for the development of lipopolysaccharide-based live anti-dysentery vaccines. Microb Pathog. 1986 Jun;1(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




