Abstract
The hip locus of Escherichia coli affects the frequency of persistence to the lethal consequences of selective inhibition of either DNA or peptidoglycan synthesis. Regulation of the hip operon, which consists of a regulatory region and two genes, hipB and hipA, was examined with strains containing a hip-lac transcriptional fusion placed in single copy at the lambda att site. Disruption of the hip locus increased activity from the fusion 16-fold. Repression was restored by supplying HipB in trans. HipB was overexpressed and purified. On the basis of gel filtration and cross-linking studies, HipB is a dimer in solution. Sequence analysis revealed that HipB is a Cro-like DNA-binding protein. The interaction of HipB with the hip regulatory region was examined by gel retardation, DNase I protection, and methylation protection studies. HipB binds with a Kapp (K apparent) of 40 pM to four operator sites with the conserved sequence TATCCN8GGATA (N represents any nucleotide). Binding to the operators is nearly simultaneous and appears to be cooperative. Analysis of the role of HipA in the regulation of the hip operon is complicated by the toxicity of HipA in the absence of HipB. Strains disrupted in hipB but not in hipA could not be recovered. Moreover, hipA-containing plasmids cannot be replicated in strains defective in or lacking hipB. HipA is found exclusively in a tight complex with HipB. Although disruption of hipA slightly increased expression from the hip-lac fusion, in vitro studies suggest that HipA does not bind to the hip regulatory region directly but indirectly via HipB.
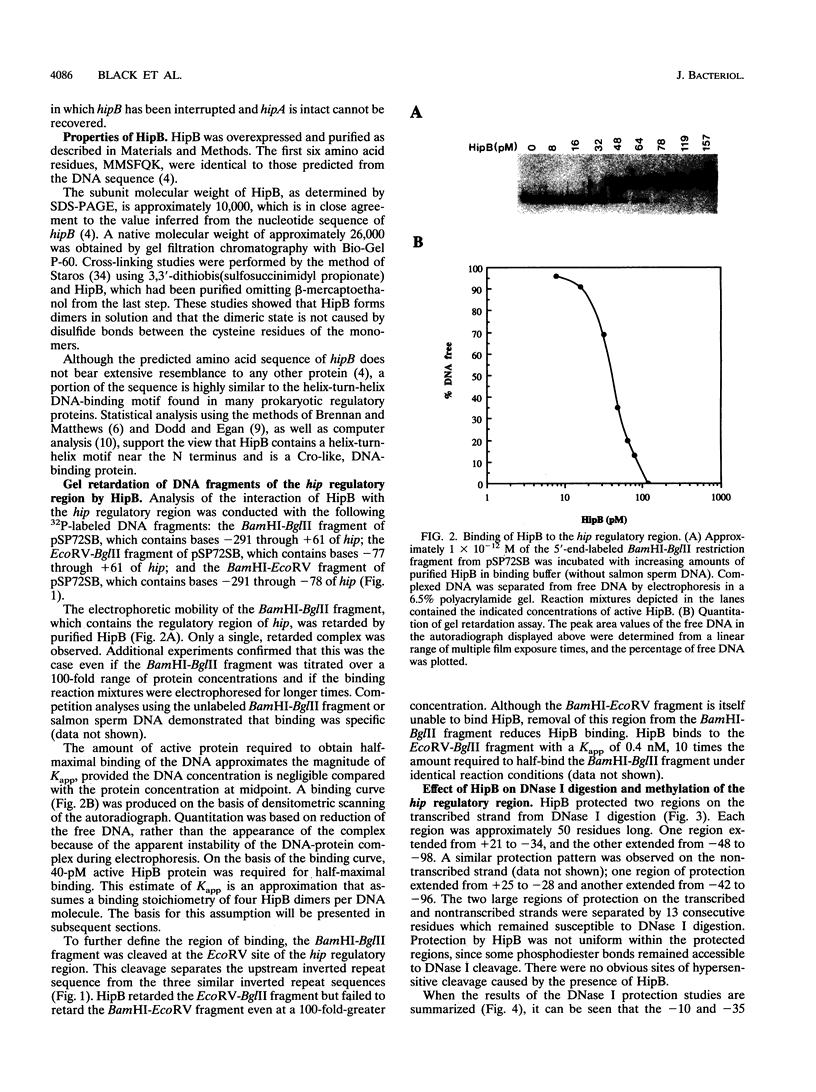
Full text
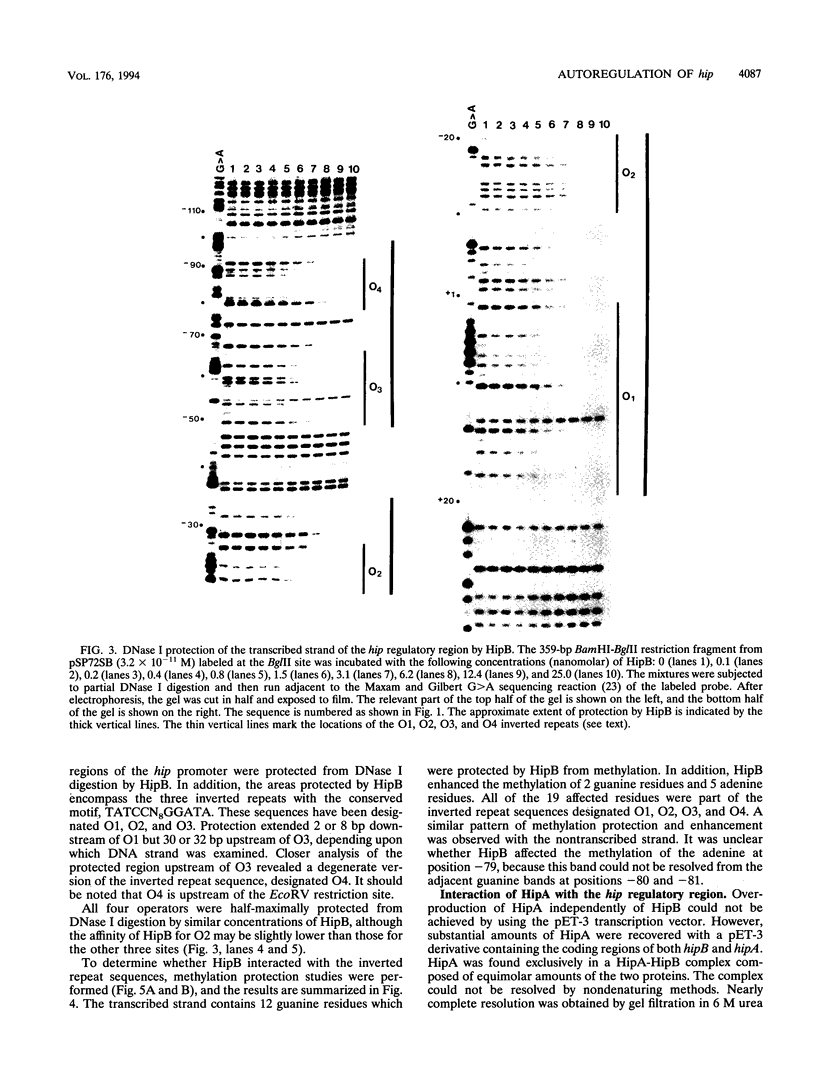
PDF


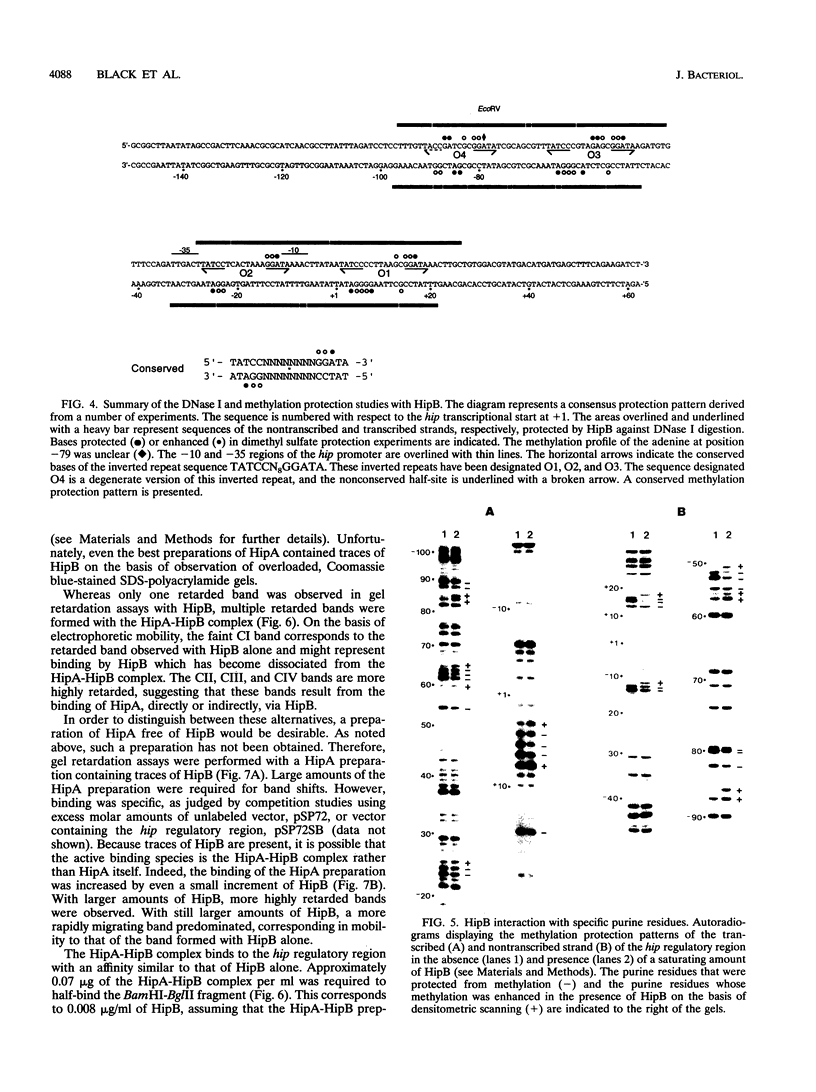


Images in this article
Selected References
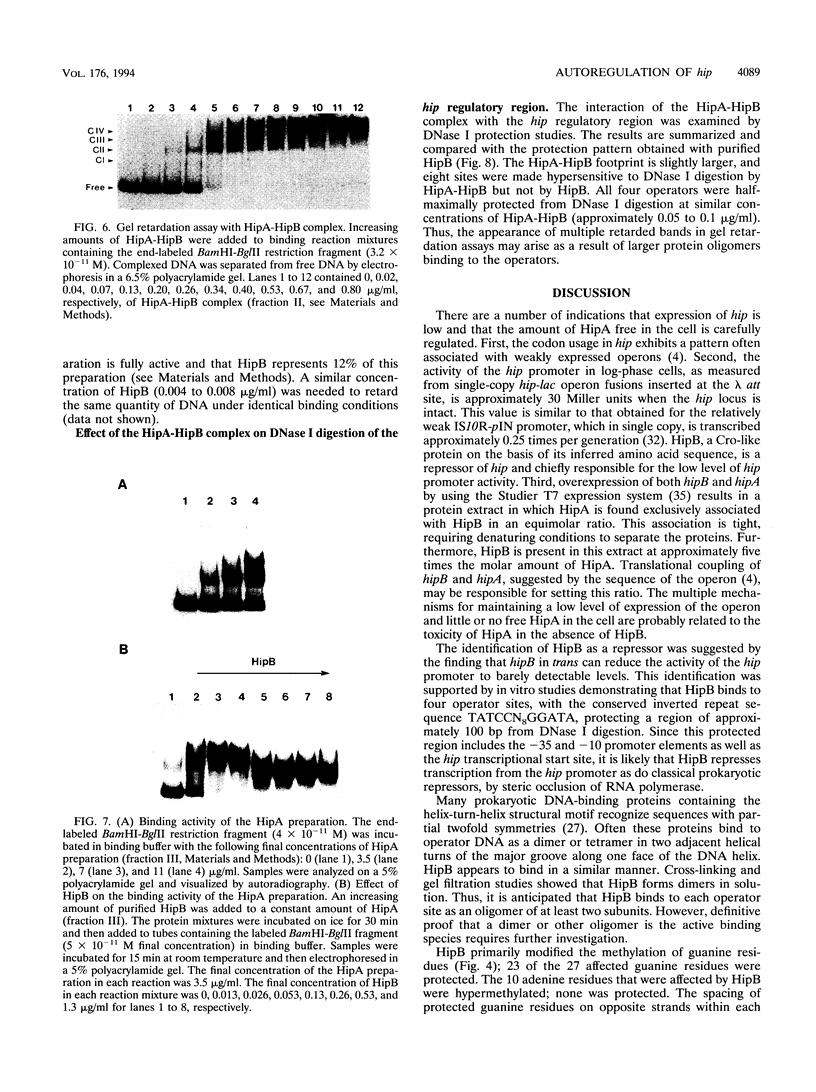
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. S., Kelly A. J., Mardis M. J., Moyed H. S. Structure and organization of hip, an operon that affects lethality due to inhibition of peptidoglycan or DNA synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5732–5739. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5732-5739.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Electron microscope study of septum formation in Escherichia coli strains B and B-r during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1039–1056. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1039-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Nomura M. Translational regulation is responsible for growth-rate-dependent and stringent control of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins L11 and L1 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich M., Ramani N., Mathew E., Sirko A., Tsui P. The role of integration host factor in gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2557–2563. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterson N. I., Koshland D. E., Jr Replacement and amplification of bacterial genes with sequences altered in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4894–4898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka M., Akiyama M., Horiuchi T. A consensus sequence of three DNA replication terminus sites on the E. coli chromosome is highly homologous to the terR sites of the R6K plasmid. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Pelletier A. J., Tecklenburg M. L., Kuempel P. L. Identification of the DNA sequence from the E. coli terminus region that halts replication forks. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Messer W., Schwarz U. Regulation of polar cap formation in the life cycle of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Interactions between DNA-bound repressors govern regulation by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyed H. S., Bertrand K. P. hipA, a newly recognized gene of Escherichia coli K-12 that affects frequency of persistence after inhibition of murein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.768-775.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyed H. S., Broderick S. H. Molecular cloning and expression of hipA, a gene of Escherichia coli K-12 that affects frequency of persistence after inhibition of murein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):399–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.399-403.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer R., Moyed H. S. Conditional impairment of cell division and altered lethality in hipA mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3321–3326. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3321-3326.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V. N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide active esters: bis(N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) esters of two dicarboxylic acids are hydrophilic, membrane-impermeant, protein cross-linkers. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3950–3955. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., McHugh G. L., Bozza M. A., Swartz M. N. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 exhibiting reduced killing by both quinolone and beta-lactam antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1938–1943. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]