Abstract
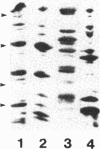
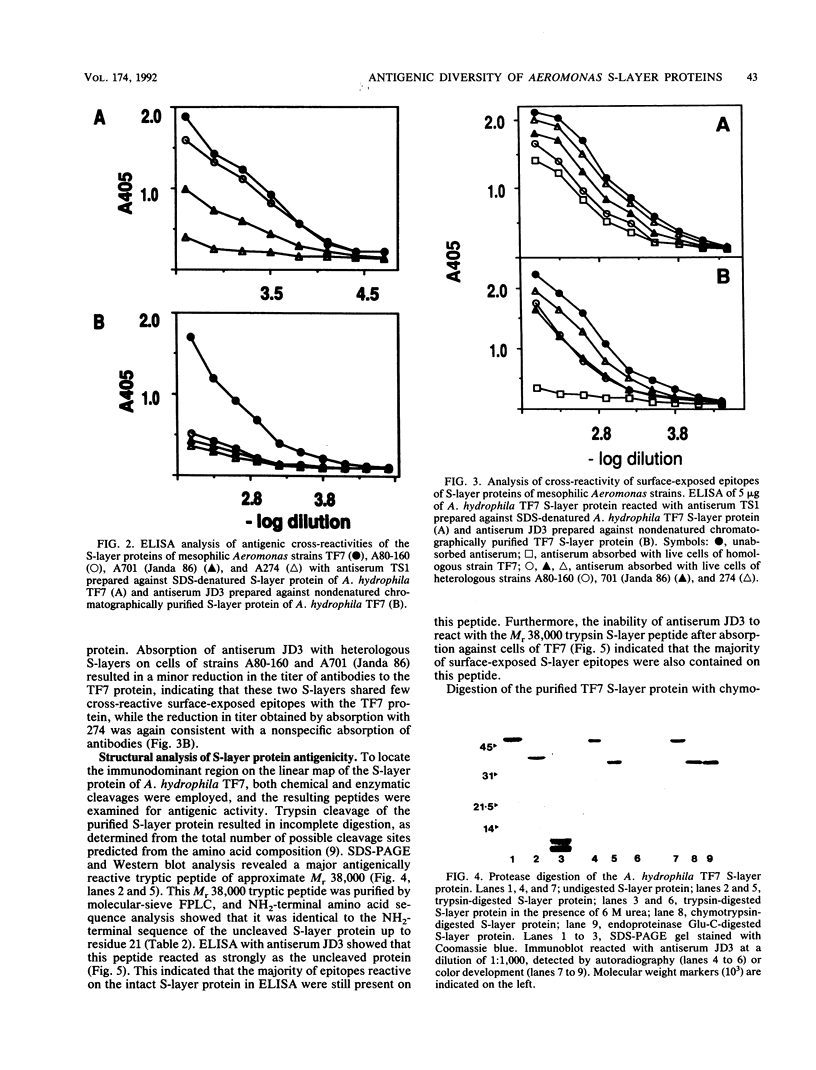
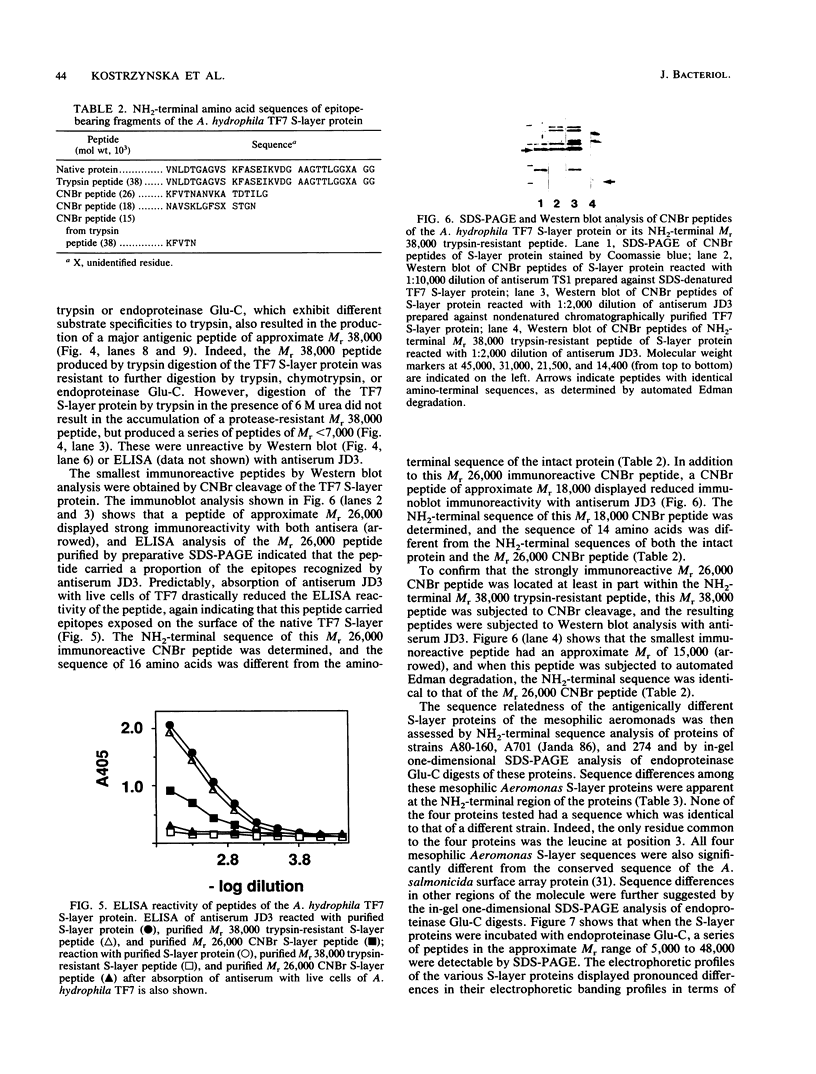
The antigenic relatedness of paracrystalline surface array proteins with subunit molecular weights of approximately 52,000 from isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas veronii biotype sobria belonging to a single heat-stable serogroup was examined. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting with two different polyclonal antisera against surface exposed and non-surface-exposed epitopes of the S-layer protein from A. hydrophila TF7 showed that the S-layer proteins of the mesophilic aeromonads were antigenically diverse. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of four antigenically different proteins showed that while the proteins were structurally related, they differed in primary sequence. Absorption experiments with heterologous live cells showed that cross-reactive epitopes were in non-surface-exposed regions of the S-layer proteins, while absorption with homologous live cells showed that the immunodominant epitopes of the S-layer protein of strain TF7 were strain specific and exposed on the surface of the native, tetragonal array produced by this strain. Proteolytic digestion of the TF7 S-layer protein with trypsin, chymotrypsin, or endoproteinase Glu-C produced an amino-terminal peptide of approximate Mr 38,000 which was refractile to further proteolytic cleavage under nondenaturing conditions. This peptide carried the immunodominant surface-exposed region of the protein, and chemical cleavage with cyanogen bromide further mapped the portion of these surface-exposed epitopes to a peptide of approximate Mr 26,000, part of which maps within the Mr 38,000 protease-resistant NH2-terminal peptide.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Karadaghi S., Wang D. N., Hovmöller S. Three-dimensional structure of the crystalline surface layer from Aeromonas hydrophila. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Oct;101(1):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Steigerwalt A. G., Altwegg-Bissig R., Lüthy-Hottenstein J., Brenner D. J. Biochemical identification of Aeromonas genospecies isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):258–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.258-264.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Cloning of the gene for the surface array protein of Aeromonas salmonicida and evidence linking loss of expression with genetic deletion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4086–4091. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4086-4091.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Repine J. E., Joiner K. A. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections. Failure of encapsulated Campylobacter fetus to bind C3b explains serum and phagocytosis resistance. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1434–1444. doi: 10.1172/JCI113474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S., Cavaignac S., Feutrier J., Phipps B. M., Kostrzynska M., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Structure of the tetragonal surface virulence array protein and gene of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15258–15265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Engelhardt H., Baumeister W., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Three-dimensional structure of an open form of the surface layer from the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.190-197.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Lallier R., Trust T. J. Surface antigens of virulent strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jun;12(1-4):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Trust T. J. Isolation and biochemical characterization of the S-layer protein from a pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila strain. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2631-2638.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Trust T. J. Surface protein composition of Aeromonas hydrophila strains virulent for fish: identification of a surface array protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):499–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.499-506.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Kostrzynska M., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Antigenic differences among Campylobacter fetus S-layer proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5035–5043. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5035-5043.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Logan S. M., Cubbage S., Eidhin D. N., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Beveridge T. J., Ferris F. G., Trust T. J. Structural and biochemical analyses of a surface array protein of Campylobacter fetus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4165–4173. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4165-4173.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R. D., Jr, Joste N., McDonald G. A. Cloning, expression and sequence analysis of the gene encoding the 120 kD surface-exposed protein of Rickettsia rickettsii. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1579–1586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Oshiro L. S., Abbott S. L., Duffey P. S. Virulence markers of mesophilic aeromonads: association of the autoagglutination phenomenon with mouse pathogenicity and the presence of a peripheral cell-associated layer. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3070–3077. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3070-3077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Olafson R. W., Trust T. J. Surface layer virulence A-proteins from Aeromonas salmonicida strains. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1064–1071. doi: 10.1139/o84-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Porphyrin binding by the surface array virulence protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1332-1336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokka R. P., Janda J. M., Oshiro L. S., Altwegg M., Shimada T., Sakazaki R., Brenner D. J. Biochemical and genetic characterization of autoagglutinating phenotypes of Aeromonas species associated with invasive and noninvasive disease. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):890–894. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokka R. P., Vedros N. A., Janda J. M. Electrophoretic analysis of the surface components of autoagglutinating surface array protein-positive and surface array protein-negative Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2240–2247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2240-2247.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N., Matsudaira P. Direct protein microsequencing from Immobilon-P Transfer Membrane. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Brander E. Crystalline cell surface layer of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5756–5758. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5756-5758.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Lalonde G., Leblanc D., Olivier G., Lallier R. Aeromonas hydrophila in rainbow trout: relation between virulence and surface characteristics. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1501–1503. doi: 10.1139/m80-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn C. B., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Role of surface components in serum resistance of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1069–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1069-1075.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. G., Dooley J. S., Whippey P. W., Trust T. J. Structure of an S layer on a pathogenic strain of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2625-2630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Kay W. W. Immunoglobulin binding by the regular surface array of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9298–9303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Trust T. J., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W. Purification and characterization of the cell surface virulent A protein from Aeromonas salmonicida. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2934–2939. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Shimada T. O-serogrouping scheme for mesophilic Aeromonas strains. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1984 Oct-Dec;37(5-6):247–255. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.37.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeoka A., Takumi K., Koga T., Kawata T. Purification and characterization of S layer proteins from Clostridium difficile GAI 0714. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Feb;137(2):261–267. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. V., Gross R. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Extended serogrouping scheme for motile, mesophilic Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):980–984. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.980-984.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]