Abstract
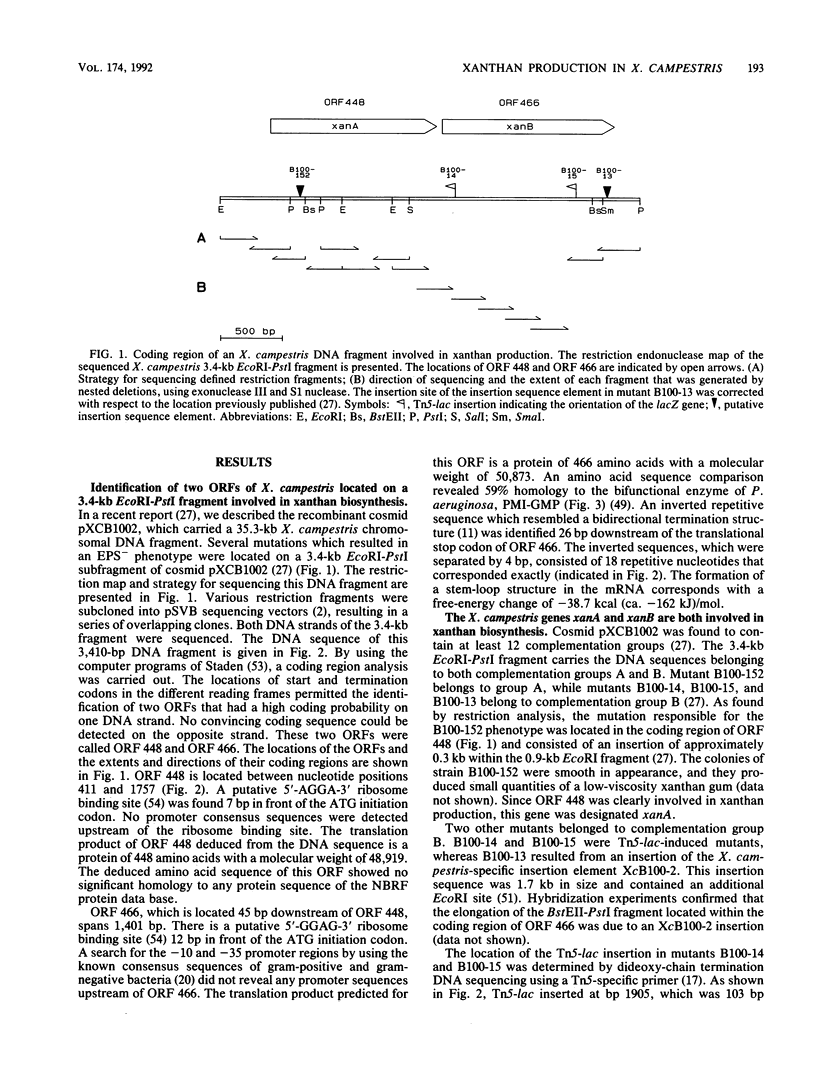
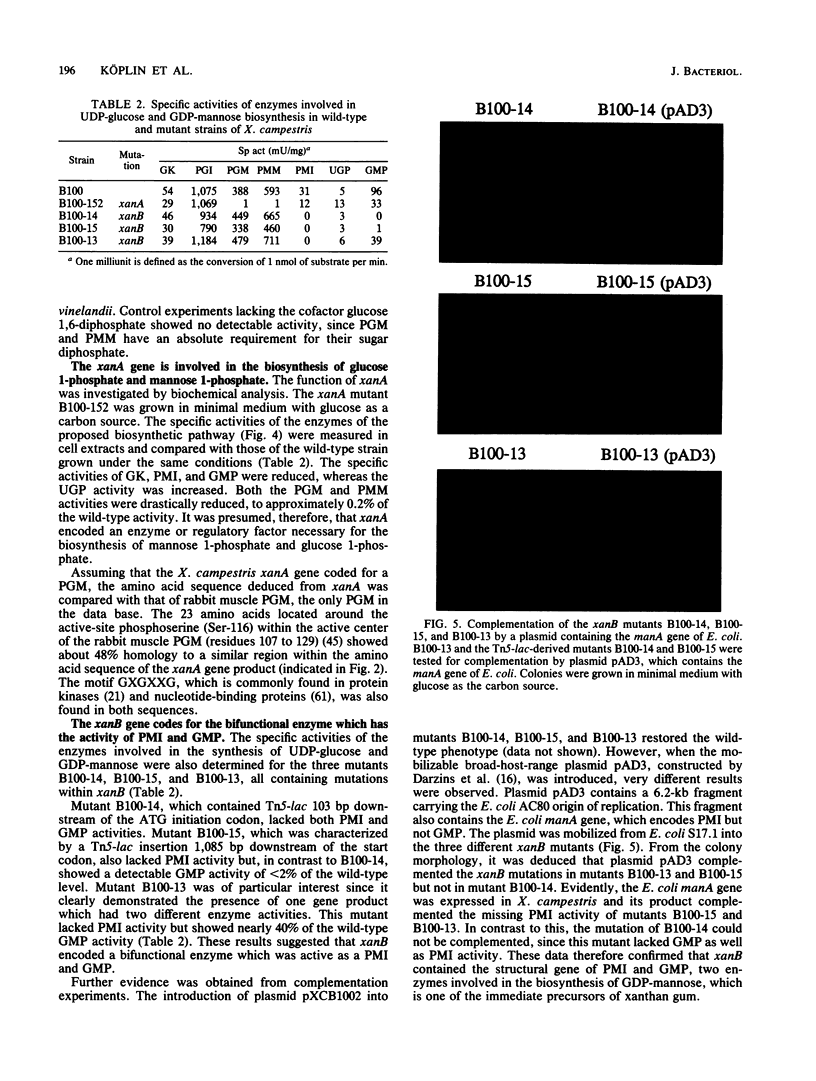
The nucleotide sequence of a 3.4-kb EcoRI-PstI DNA fragment of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris revealed two open reading frames, which were designated xanA and xanB. The genes xanA and xanB encode proteins of 448 amino acids (molecular weight of 48,919) and 466 amino acids (molecular weight of 50,873), respectively. These genes were identified by analyzing insertion mutants which were known to be involved in xanthan production. Specific tests for the activities of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of UDP-glucose and GDP-mannose indicated that the xanA gene product was involved in the biosynthesis of both glucose 1-phosphate and mannose 1-phosphate. The deduced amino acid sequence of xanB showed a significant degree of homology (59%) to the phosphomannose isomerase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of alginate. Moreover, biochemical analysis and complementation experiments with the Escherichia coli manA fragment revealed that xanB encoded a bifunctional enzyme, phosphomannose isomerase-GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Schwartz M. Phosphoglucomutase mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):621–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.621-626.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W., Pühler A. A family of high-copy-number plasmid vectors with single end-label sites for rapid nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W., Rump A., Klipp W., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of a 24,206-base-pair DNA fragment carrying the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):715–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
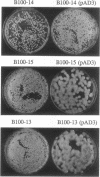
- Cadmus M. C., Rogovin S. P., Burton K. A., Pittsley J. E., Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. Colonial variation in Xanthomonas campestris NRRL B-1459 and characterization of the polysaccharide from a variant strain. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):942–948. doi: 10.1139/m76-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Riccio A., Bruni C. B. Convergently functional, Rho-independent terminator in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):362–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.362-368.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cava J. R., Elias P. M., Turowski D. A., Noel K. D. Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genetic regions encoding lipopolysaccharide structures essential for complete nodule development on bean plants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.8-15.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplin D. L., Cook D. Molecular genetics of extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis in vascular phytopathogenic bacteria. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):271–279. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Nixon L. L., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase genes and their expression in alginate-negative mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.249-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Fisher R. F., Jacobs T. W., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti 1021 nodulation genes: nodD is read divergently from nodABC. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):241–248. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracy R. W., Noltmann E. A. Studies on phosphomannose isomerase. II. Characterization as a zinc metalloenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4109–4116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding N. E., Cleary J. M., Cabañas D. K., Rosen I. G., Kang K. S. Genetic and physical analyses of a cluster of genes essential for xanthan gum biosynthesis in Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2854–2861. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2854-2861.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hötte B., Rath-Arnold I., Pühler A., Simon R. Cloning and analysis of a 35.3-kilobase DNA region involved in exopolysaccharide production by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2804–2807. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2804-2807.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ielpi L., Couso R. O., Dankert M. A. Pyruvic acid acetal residues are transferred from phosphoenolpyruvate to the pentasaccharide-P-P-lipid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 30;102(4):1400–1408. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ielpi L., Couso R., Dankert M. Lipid-linked intermediates in the biosynthesis of xanthan gum. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson P. E., Kenne L., Lindberg B. Structure of extracellular polysaccharide from Xanthomonas campestris. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Dec;45:275–282. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85885-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun S., Kado C. I. A plant-inducible gene of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris encodes an exocellular component required for growth in the host and hypersensitivity on nonhosts. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5165–5172. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5165-5172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Icho T., Iino T. Effects of galU mutation on flagellar formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):908–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.908-915.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Markovitz A. Depression of guanosine diphosphate-mannose pyrophosphorylase by mutations in two different regulator genes involved in capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.965-972.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Sydiskis R. J., Lieberman M. M. Genetic and biochemical studies on mannose-negative mutants that are deficient in phosphomannose isomerase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1492–1496. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1492-1496.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton L. D., Mindt L., Rees D. A., Sanderson G. R. Covalent structure of the extracellular polysaccharide from Xanthomonas campestris: evidence from partial hydrolysis studies. Carbohydr Res. 1976 Feb;46(2):245–257. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional start point of the phosphomannose isomerase gene (manA) of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindar D. F., Bucke C. The biosynthesis of alginic acid by Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):617–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1520617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray W. J., Jr, Hermodson M. A., Puvathingal J. M., Mahoney W. C. The complete amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle phosphoglucomutase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9166–9174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D., Berry A., May T. B., Rothmel R., Fialho A., Chakrabarty A. M. Purification and characterization of phosphomannose isomerase-guanosine diphospho-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase. A bifunctional enzyme in the alginate biosynthetic pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2080–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., Hötte B., Klauke B., Kosier B. Isolation and characterization of insertion sequence elements from gram-negative bacteria by using new broad-host-range, positive selection vectors. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1502–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1502-1508.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. The current status and portability of our sequence handling software. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):217–231. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G., Lee S. J., Romana L. K., Reeves P. R. The cps gene cluster of Salmonella strain LT2 includes a second mannose pathway: sequence of two genes and relationship to genes in the rfb gene cluster. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jun;227(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00259668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sá-Correia I., Darzins A., Wang S. K., Berry A., Chakrabarty A. M. Alginate biosynthetic enzymes in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: overproduction of phosphomannose isomerase, phosphomannomutase, and GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase by overexpression of the phosphomannose isomerase (pmi) gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3224–3231. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3224-3231.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne L., Tansey L., Pollock T. J. Clustering of mutations blocking synthesis of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3593–3600. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3593-3600.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verachtert H., Bass S. T., Seifert L. L., Hansen R. G. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of nucleoside triphosphates (pyrophosphorolysis of nucleoside diphosphate sugars). Anal Biochem. 1965 Nov;13(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A. Quantitative assay of polysaccharide components obtained from cell wall lipopolysaccharides of Xanthomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.980-982.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]