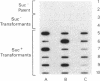
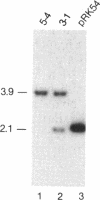
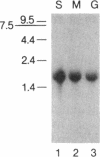
Abstract
A sucrose-inducible alpha-glucosidase activity that hydrolyzes sucrose in Candida albicans has been demonstrated previously. The enzyme is assayable in whole cells and was inhibited by both sucrose and maltose. A C. albicans gene (CASUC1) that affects sucrose utilization and alpha-glucosidase activity was cloned by expression in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae suc2 mutant (2102) devoid of invertase genes. CASUC1 enabled the S. cerevisiae mutant to utilize both sucrose and maltose. DNA sequence analysis revealed that CASUC1 encodes a putative zinc finger-containing protein with 28% identity to a maltose-regulatory gene (MAL63) of S. cerevisiae. The gene products of CASUC1 and MAL63 are approximately the same size (501 and 470 amino acids, respectively), and each contains a single zinc finger located at the N terminus. The zinc fingers of CASUC1 and MAL63 comprise six conserved cysteines (C6 zinc finger) and are of the general form Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa6-Cys-Xaavariable-Cys-Xaa2-Cys-+ ++Xaa6-Cys (where Xaan indicates a stretch of the indicated number of any amino acids). Both contain five amino acids in the variable region. CASUC1 also complemented the maltose utilization defect of an S. cerevisiae mutant (TCY-137) containing a defined mutation in a maltose-regulatory gene. The sucrose utilization defect of type II Candida stellatoidea, a sucrase-negative mutant of C. albicans, was corrected by CASUC1. Determinations of alpha-glucosidase activity in whole cells revealed that activity was restored in transformants cultivated on either sucrose or maltose. To our knowledge, this is the first zinc finger-encoding gene, as well as the first putative regulatory gene, to be identified in C. albicans.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzi E., Chen W., Ulaszewski S., Capieaux E., Goffeau A. The multidrug resistance gene PDR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16871–16879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. A., Geever R., Giles N. H. Expression of qa-1F activator protein: identification of upstream binding sites in the qa gene cluster and localization of the DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1256–1266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beri R. K., Whittington H., Roberts C. F., Hawkins A. R. Isolation and characterization of the positively acting regulatory gene QUTA from Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7991–8001. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T. H., Sollitti P., Marmur J. Structure of the multigene family of MAL loci in Saccharomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):60–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00330943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. D., Goldenthal M. J., Chow T., Buchferer B., Marmur J. Organization of the MAL loci of Saccharomyces. Physical identification and functional characterization of three genes at the MAL6 locus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00383304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Schekman R., Flessel M. C., Thorner J. An MF alpha 1-SUC2 (alpha-factor-invertase) gene fusion for study of protein localization and gene expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7080–7084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P., Schimmel P. LEU3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a factor for control of RNA levels of a group of leucine-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2708–2717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Tsay E. Y., Kirsch D. R. Isolation of the Candida albicans gene for orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase by complementation of S. cerevisiae ura3 and E. coli pyrF mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00328721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenthal M. J., Vanoni M., Buchferer B., Marmur J. Regulation of MAL gene expression in yeast: gene dosage effects. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):508–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00331157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Positive regulation in the general amino acid control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5374–5378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. H., Marmur J. Primary structure of the maltase gene of the MAL6 locus of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1986;41(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. H., Marmur J. Upstream regulatory regions controlling the expression of the yeast maltase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2477–2483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Blackmer K., Racioppi J. V. A salivary gland-specific, maltase-like gene of the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Kurtz M. B., Kirsch D. R. Directed mutagenesis in Candida albicans: one-step gene disruption to isolate ura3 mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Lai M. H., Kirsch D. R. Cloning and characterization of the 2,3-oxidosqualene cyclase-coding gene of Candida albicans. Gene. 1990 Mar 15;87(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. A., Eaton N. R. Purification and characterization of maltase and alpha-methyl glucosidase from yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. A., Zimmermann F. K., Eaton N. R. Genetic and biochemical evidence of sucrose fermentation by maltase in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;123(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00282987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Michels C. A. The MAL63 gene of Saccharomyces encodes a cysteine-zinc finger protein. Curr Genet. 1988 Oct;14(4):319–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00419988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopetzki E., Buckel P., Schumacher G. Cloning and characterization of baker's yeast alpha-glucosidase: over-expression in a yeast strain devoid of vacuolar proteinases. Yeast. 1989 Jan-Feb;5(1):11–24. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. L., Campbell J. L. Cloning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA replication genes: isolation of the CDC8 gene and two genes that compensate for the cdc8-1 mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Hicks J. B., Lipke P. N. Evidence that Candida stellatoidea type II is a mutant of Candida albicans that does not express sucrose-inhibitable alpha-glucosidase. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2804–2808. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2804-2808.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Riggsby W. S., Uphoff R. A., Hicks J. B., Whelan W. L., Reiss E., Magee B. B., Wickes B. L. Genetic differences between type I and type II Candida stellatoidea. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.527-532.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Merz W. G. Association of electrophoretic karyotype of Candida stellatoidea with virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1814–1819. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1814-1819.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Whelan W. L. Ploidy and DNA content of Candida stellatoidea cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3207–3208. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3207-3208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messenguy F., Dubois E., Descamps F. Nucleotide sequence of the ARGRII regulatory gene and amino acid sequence homologies between ARGRII PPRI and GAL4 regulatory proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Langevin G. L., Singer R. H., Garcea R. L., Hereford L. M. Amino acid sequences that determine the nuclear localization of yeast histone 2B. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4048–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni B. F., Needleman R. B. Identification of the upstream activating sequence of MAL and the binding sites for the MAL63 activator of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3797–3800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Kim K. S., Kogan S., Guarente L. Functional dissection and sequence of yeast HAP1 activator. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. M., Eaton N. R. Functional blocks of the ad-1 and ad-2 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 7;34(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90831-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollitti P., Marmur J. Primary structure of the regulatory gene from the MAL6 locus of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):56–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00333398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B. Regional distant sequence homology between amylases, alpha-glucosidases and transglucanosylases. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80644-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Carlson M. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast SUC2 gene for invertase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1943–1954. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanoni M., Sollitti P., Goldenthal M., Marmur J. Structure and regulation of the multigene family controlling maltose fermentation in budding yeast. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;37:281–322. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickes B. L., Golin J. E., Kwon-Chung K. J. Chromosomal rearrangement in Candida stellatoidea results in a positive effect on phenotype. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1762–1771. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1762-1771.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Witte M. M., Dickson R. C., Riley M. I. Characterization of a positive regulatory gene, LAC9, that controls induction of the lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis: structural and functional relationships to GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao B., Sollitti P., Marmur J. Primary structure of the maltose-permease-encoding gene of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann F. K., Eaton N. R. Genetics of induction and catabolite repression of Maltese synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;134(3):261–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00267720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]