Abstract
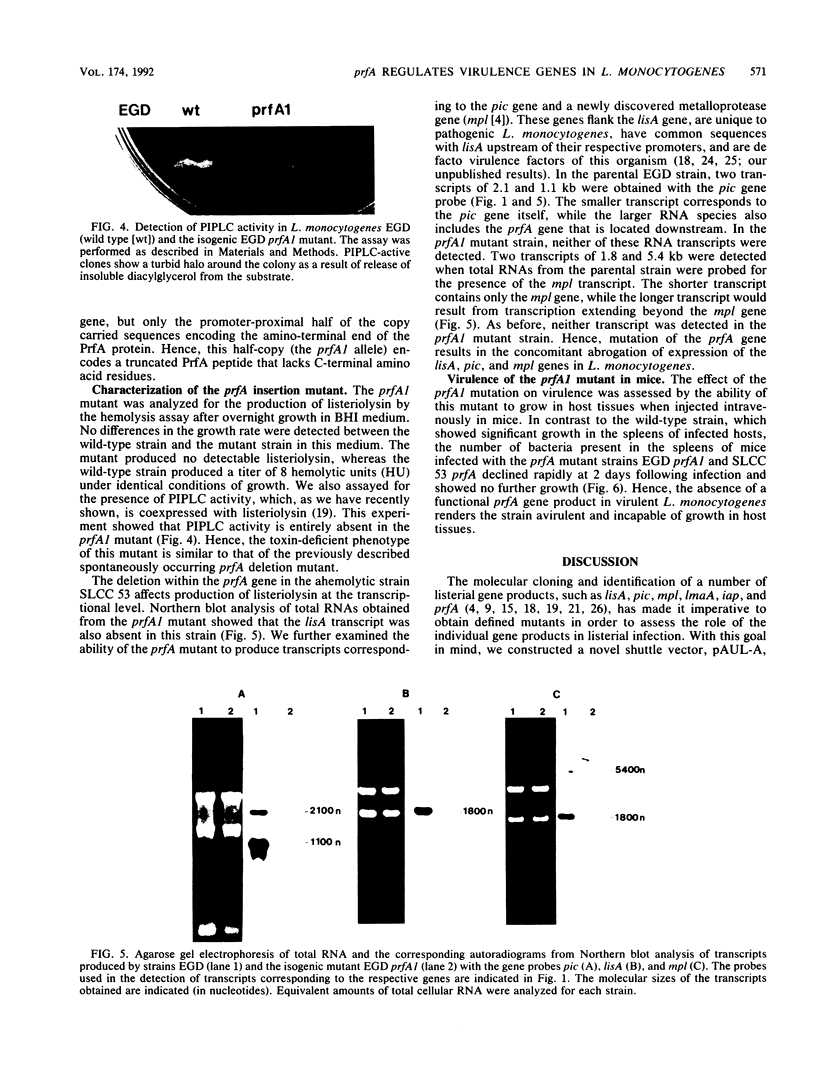
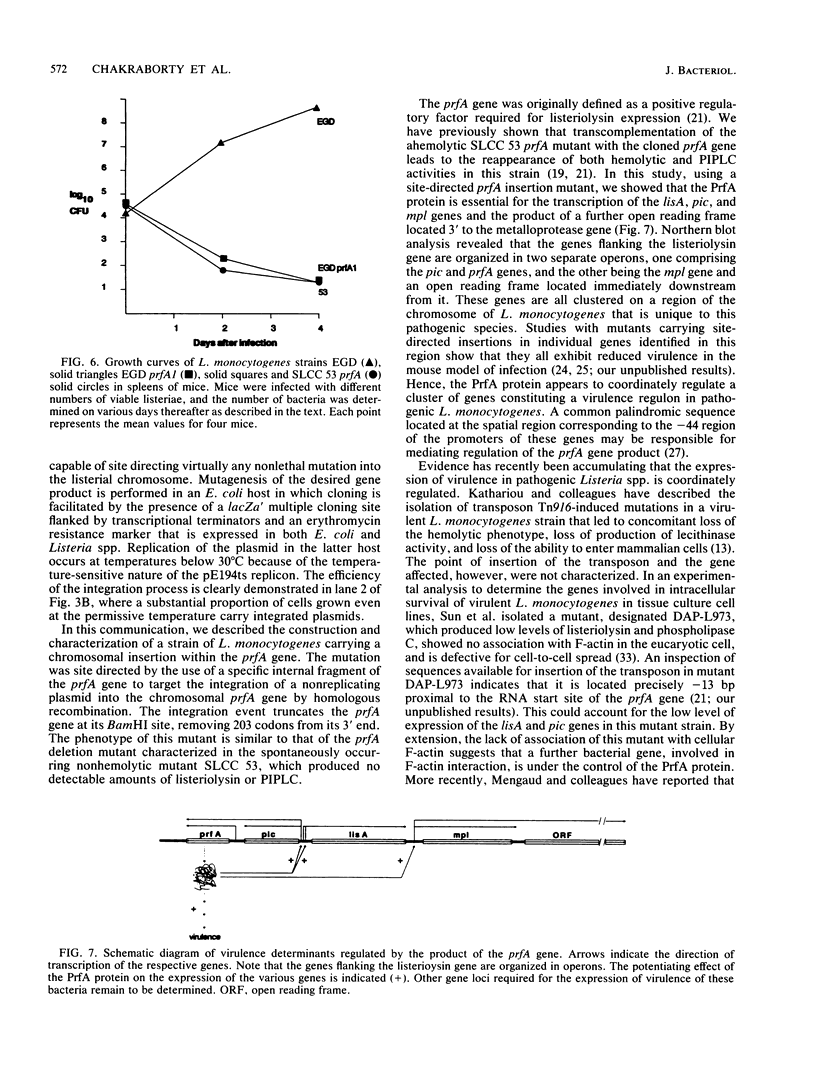
The prfA gene of Listeria monocytogenes encodes a protein that activates transcription of the listeriolysin gene (lisA). In order to explore the role of the prfA gene product in the pathogenesis of listerial infection, we constructed a site-directed insertion mutation in prfA by the chromosomal integration of a novel suicide vector containing a portion of the prfA coding region. This mutation not only transcriptionally silenced the listeriolysin (lisA) gene but also abrogated production of specific RNA transcripts corresponding to the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (pic) and metalloprotease (mpl) genes, two further virulence gene products expressed only by pathogenic Listeria strains. The strain was also found to be avirulent when tested in a mouse model of listerial infection. The concomitant loss of multiple characteristics such as production of LisA, Pic, Mpl, and loss of virulence in a mouse infection model is the result of a mutation in a single gene and demonstrates that the prfA gene product is a positive regulator of multiple virulence determinants in L. monocytogenes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Cloning of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments in Escherichia coli requires vectors protected by strong transcriptional terminators. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Chakraborty T. Nucleotide sequence of the listeriolysin gene from a Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a strain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6406–6406. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Leimeister-Wächter M., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and identification of a metalloprotease gene from Listeria monocytogenes that is species specific and physically linked to the listeriolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):65–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.65-72.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Hahn J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Replication and incompatibility properties of plasmid pE194 in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):722–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.722-735.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göhmann S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Schiltz E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Characterization of a Listeria monocytogenes-specific protein capable of inducing delayed hypersensitivity in Listeria-immune mice. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1091–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husslein V., Huhle B., Jarchau T., Lurz R., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the aerCaerA region of Aeromonas sobria encoding aerolysin and its regulatory region. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jul;2(4):507–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Pine L., George V., Carlone G. M., Holloway B. P. Nonhemolytic Listeria monocytogenes mutants that are also noninvasive for mammalian cells in culture: evidence for coordinate regulation of virulence. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3988–3995. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3988-3995.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Acquired resistance to facultative intracellular bacteria: relationship between persistence, cross-reactivity at the T-cell level, and capacity to stimulate cellular immunity of different Listeria strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.234-241.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Prévost M. C., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. A nonvirulent mutant of Listeria monocytogenes does not move intracellularly but still induces polymerization of actin. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3477–3486. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3477-3486.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T. Detection of listeriolysin, the thiol-dependent hemolysin in Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria ivanovii, and Listeria seeligeri. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2350–2357. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2350-2357.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Mutations affecting hemolysin production in Listeria monocytogenes located outside the listeriolysin gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnan M. J., Mascola L., Lou X. D., Goulet V., May S., Salminen C., Hird D. W., Yonekura M. L., Hayes P., Weaver R. Epidemic listeriosis associated with Mexican-style cheese. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 29;319(13):823–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809293191303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinverni R., Bille J., Perret C., Regli F., Tanner F., Glauser M. P. Listériose épidémique. Observation de 25 cas en 15 mois au Centre hospitalier universitaire vaudois. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1985 Jan 5;115(1):2–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Geoffroy C., Cossart P. Identification of a new operon involved in Listeria monocytogenes virulence: its first gene encodes a protein homologous to bacterial metalloproteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1043-1049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. N., Camilli A., Portnoy D. A. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes small-plaque mutants defective for intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P. J., Perkins J. B., Losick R. Genetic transposition and insertional mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis with Streptococcus faecalis transposon Tn917. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]