Abstract
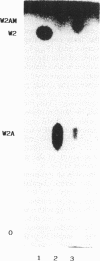
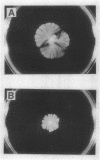
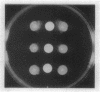
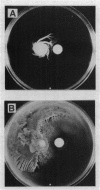
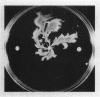
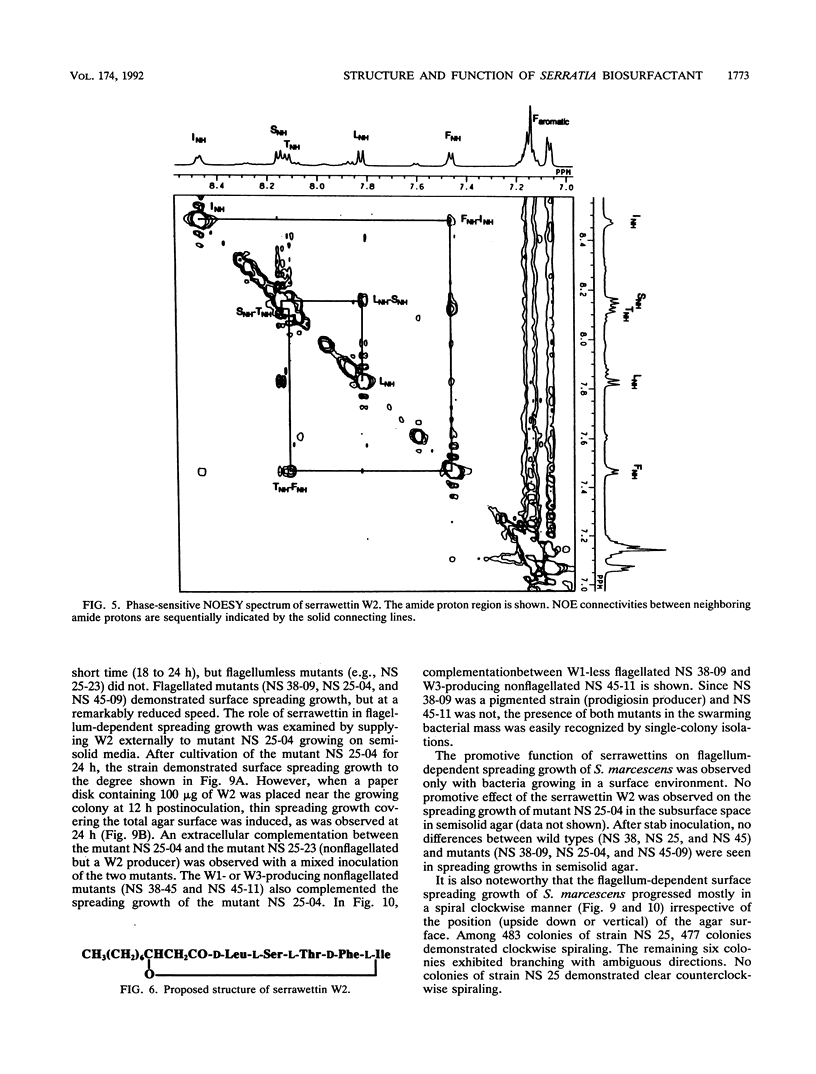
Serrawettin W2, a surface-active exolipid produced by nonpigmented Serratia marcescens NS 25, was examined for its chemical structure and physiological functions. The chemical structure was determined by degradation analyses, infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Serrawettin W2 was shown to be a novel cyclodepsipeptide containing a fatty acid (3-hydroxydecanoic acid) and five amino acids. The peptide was proposed to be D-leucine (N-bonded to the carboxylate of the fatty acid)-L-serine-L-threonine-D-phenylalanine-L-isoleucine (bonded to the 3-hydroxyl group). By examining the effects of isolated serrawettin W2 on serrawettinless mutants, this lipopeptide was shown to be active in the promotion of flagellum-independent spreading growth of the bacteria on a hard agar surface. The parent strain NS 25 formed a giant colony with a self-similar characteristic after incubation for a relatively long time (1 to 2 weeks), similar to other fractal colony-producing strains of S. marcescens (producers of the different serrawettins W1 and W3). On a semisolid medium that permitted flagellum-dependent spreading growth, an external supply of serrawettin W2 accelerated surface translocation of a serrawettinless mutant during a short period (12 h) of observation. In contrast, bacterial translocation in the subsurface space of the semisolid agar was not enhanced by serrawettins. Thus, the extracellular lipids seem to contribute specifically to the surface translocation of the bacteria by exhibiting surfactant activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Ness R., Avrahamy N., Matsuyama T., Rosenberg M. Increased cell surface hydrophobicity of a Serratia marcescens NS 38 mutant lacking wetting activity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4361–4364. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4361-4364.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunster L., Fokkema N. J., Schippers B. Effect of Surface-Active Pseudomonas spp. on Leaf Wettability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1340-1345.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Macdonald C. R., Duff S. J., Kosaric N. Enhanced Production of Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by Continuous Product Removal and Metal Cation Additions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):408–412. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.408-412.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Honda H., Tomita F., Suzuki T. Rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown on n-paraffin (mixture of C 12 , C 13 and C 14 fractions). J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Dec;24(12):855–859. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Inoue S. Sophorolipids from Torulopsis bombicola: possible relation to alkane uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1278-1283.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. K., Käppeli O., Fiechter A., Reiser J. Hydrocarbon assimilation and biosurfactant production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4212–4219. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4212-4219.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kaneda K., Ishizuka I., Toida T., Yano I. Surface-active novel glycolipid and linked 3-hydroxy fatty acids produced by Serratia rubidaea. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3015–3022. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3015-3022.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Sogawa M., Nakagawa Y. Fractal spreading growth of Serratia marcescens which produces surface active exolipids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Oct 15;52(3):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Sogawa M., Yano I. Direct Colony Thin-Layer Chromatography and Rapid Characterization of Serratia marcescens Mutants Defective in Production of Wetting Agents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1186–1188. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1186-1188.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Uetake H. Chromosomal locations of Salmonella conversion phages: mapping of prophages g 341, 15, and 34 in Salmonella anatum. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Marahiel M. A., Zuber P. Identification of a genetic locus required for biosynthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5662–5668. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5662-5668.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Zuber P. Cloning and characterization of srfB, a regulatory gene involved in surfactin production and competence in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5347–5353. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5347-5353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]