Abstract
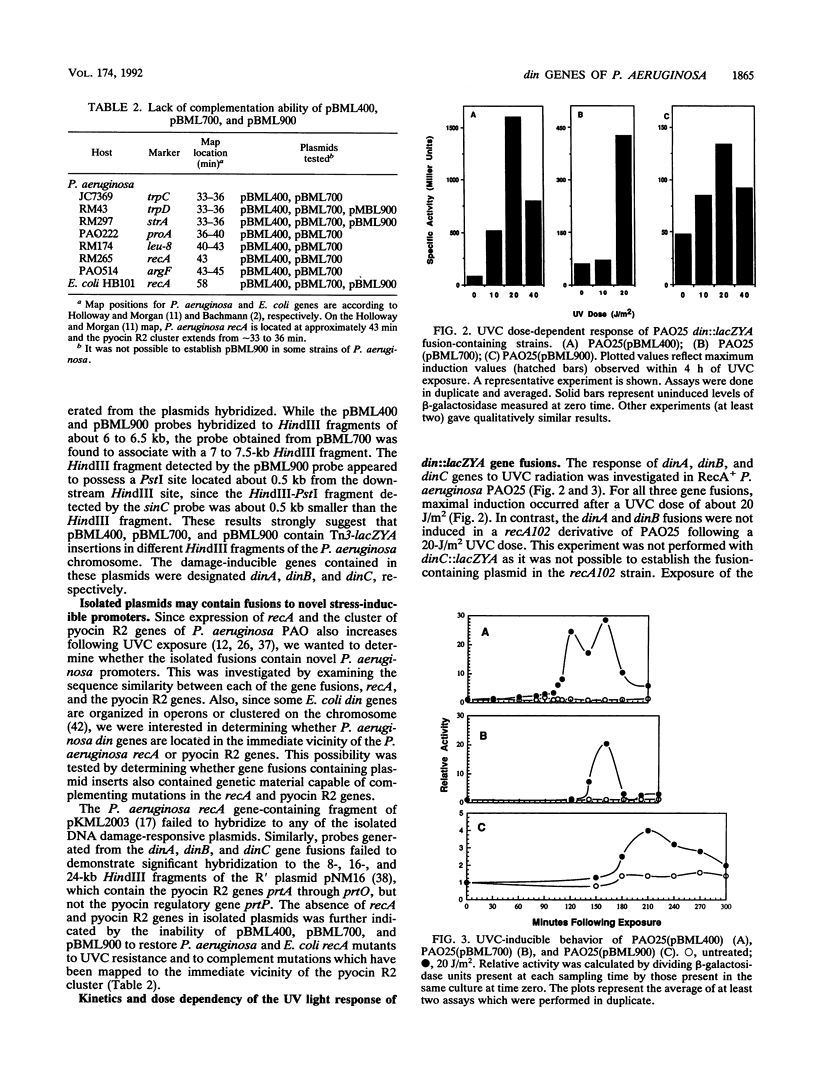
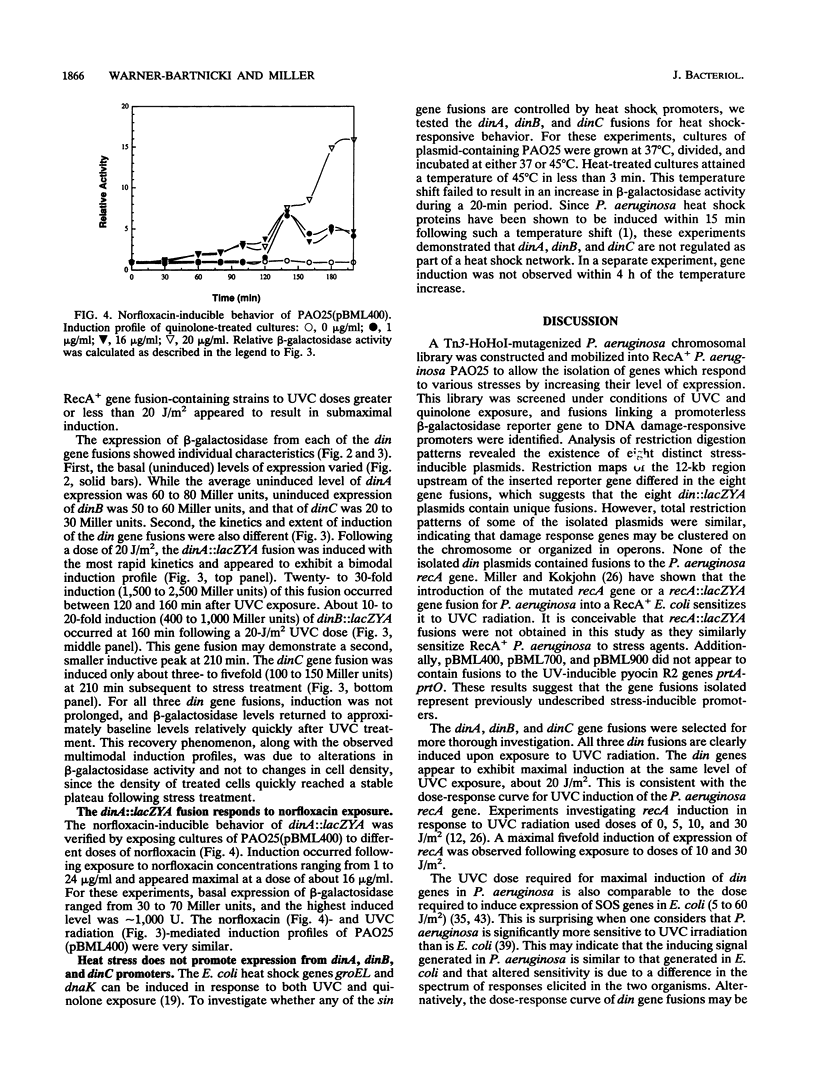
Although the pervasive soil and water microorganism Pseudomonas aeruginosa demonstrates heightened sensitivity to UV radiation, this species possesses a recA gene that, based on structural and functional properties, could mediate a DNA damage-responsive regulon similar to the SOS regulon of Escherichia coli. To determine whether P. aeruginosa encodes such stress-inducible genes, the response of P. aeruginosa to DNA-damaging agents including far-UV radiation (UVC) and the quinolone antimicrobial agent norfloxacin was investigated by monitoring the expression of fusions linking P. aeruginosa promoters to a beta-galactosidase reporter gene. These fusions were obtained by Tn3-HoHoI insertional mutagenesis of a P. aeruginosa genomic library. Eight different damage-inducible (din) gene fusions were isolated which lack homology to the P. aeruginosa recA gene. Expression of the three gene fusions studied, dinA::lacZYA, dinB::lacZYA, and dinC::lacZYA, increased following UVC and quinolone exposure but not following heat shock. Similar to E. coli SOS genes, the din genes were induced to different extents and with dissimilar kinetics following UVC irradiation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan B., Linseman M., MacDonald L. A., Lam J. S., Kropinski A. M. Heat shock response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3668–3674. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3668-3674.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Miller R. V. Effects of norfloxacin on DNA metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Feary T. W. Transductional analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa methionineless auxotrophs. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.210-216.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D. Genetic aspects of biodegradation by pseudomonads. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF01990357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Morgan A. F. Genome organization in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:79–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. M., Ohman D. E. Autogenous regulation and kinetics of induction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa recA transcription as analyzed with operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4699–4705. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4699-4705.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khidhir M. A., Casaregola S., Holland I. B. Mechanism of transient inhibition of DNA synthesis in ultraviolet-irradiated E. coli: inhibition is independent of recA whilst recovery requires RecA protein itself and an additional, inducible SOS function. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00327522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa recA gene: the Les- phenotype. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):578–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.578-582.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Molecular cloning and characterization of the recA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):568–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.568-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. groEL and dnaK genes of Escherichia coli are induced by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in an htpR+-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Autodigestion of lexA and phage lambda repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Walker G. C. New phenotypes associated with mucAB: alteration of a MucA sequence homologous to the LexA cleavage site. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1818–1823. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1818-1823.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Kokjohn T. A. Expression of the recA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO is inducible by DNA-damaging agents. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2385–2387. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2385-2387.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Kokjohn T. A. General microbiology of recA: environmental and evolutionary significance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peak M. J., Peak J. G. Solar-ultraviolet-induced damage to DNA. Photodermatol. 1989 Feb;6(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Culebras E., Moreno F., Baquero F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):631–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Haas D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO to nalidixic acid and low levels of beta-lactam antibiotics: mapping of chromosomal genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):242–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. The sequence and function of the recA gene and its protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):412–419. doi: 10.1007/BF00328132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel P. F., Fogliano M., Strausbaugh L. D. Regulation of the Escherichia coli K-12 uvrB operon. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.676-685.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Kohlbrenner W. E., Weigl D., Baranowski J. Mechanism of quinolone inhibition of DNA gyrase. Appearance of unique norfloxacin binding sites in enzyme-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Shiga S., Kageyama M. Genetic determinant of pyocin R2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. I. Localization of the pyocin R2 gene cluster between the trpCD and trpE genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):375–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00325898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Shiga S., Kikuchi A., Kageyama M. Genetic determinant of pyocin R2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. II. Physical characterization of pyocin R2 genes using R-prime plasmids constructed from R68.45. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):382–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00325899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C. S., Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Inducible UV repair potential of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jul;136(7):1241–1249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-7-1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., An G., Flores C., Nester E. W. A Tn3 lacZ transposon for the random generation of beta-galactosidase gene fusions: application to the analysis of gene expression in Agrobacterium. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):891–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N. S., Clark A. J., Low B. Genetic location of certain mutations conferring recombination deficiency in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.244-249.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M., Roegner-Maniscalco V., Sweasy J. B., McCall J. O. Recovery from ultraviolet light-induced inhibition of DNA synthesis requires umuDC gene products in recA718 mutant strains but not in recA+ strains of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6805–6809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Zuber P., Perkins J. B., Sandman K., Igo M., Losick R. New ways to study developmental genes in spore-forming bacteria. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):285–291. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4697.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



