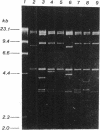
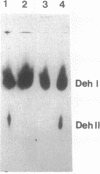
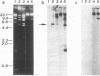
Abstract
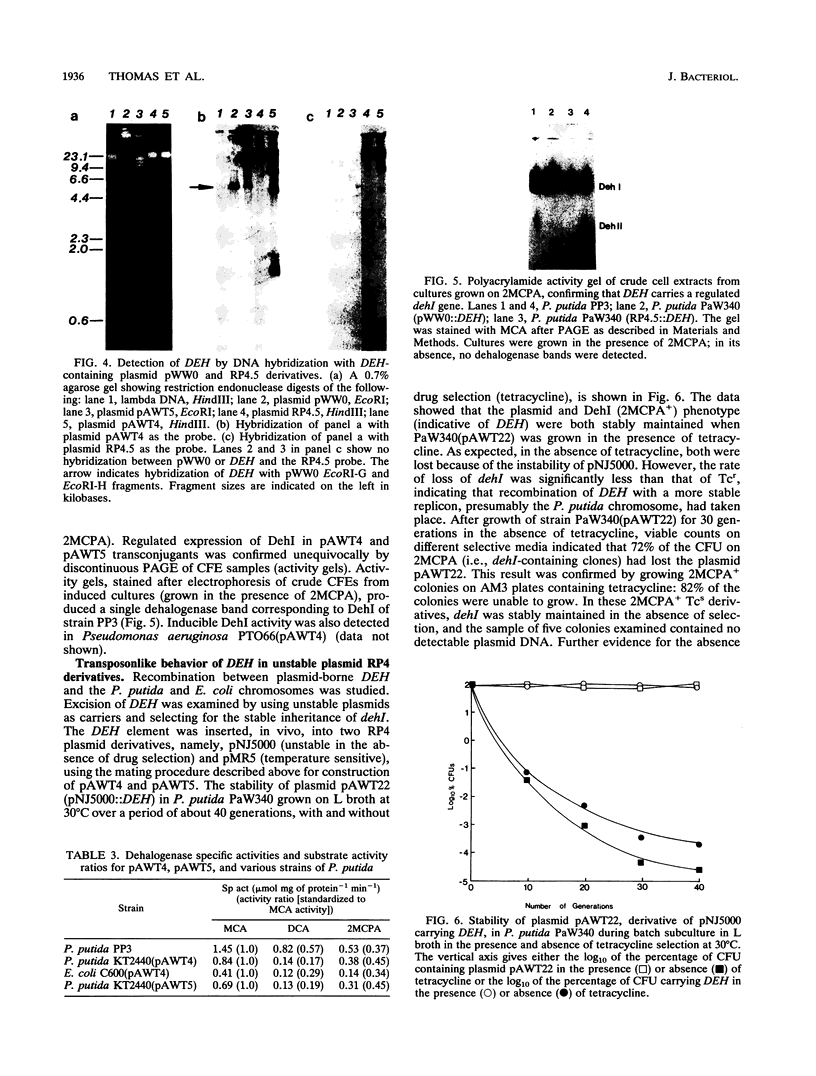
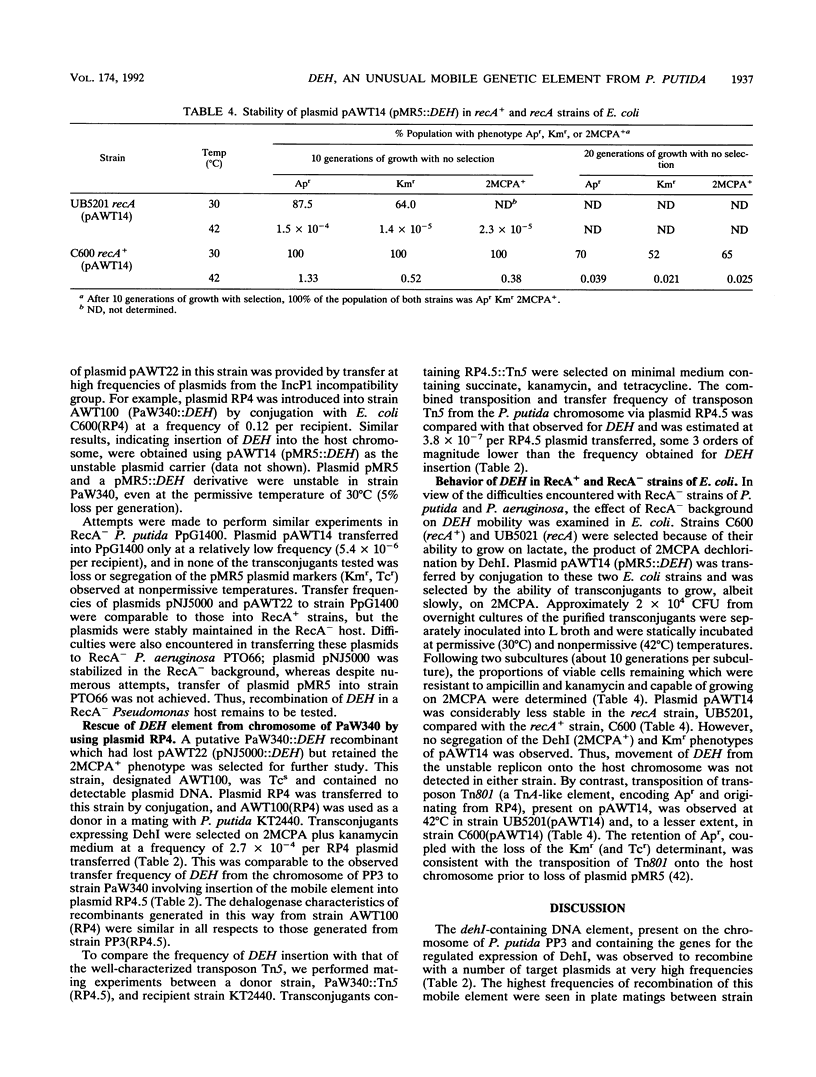
As a result of the production of two dehalogenases (DehI and DehII), Pseudomonas putida PP3 utilized halogenated alkanoic acids, such as 2-monochloropropionic acid (2MCPA), as sole sources of carbon and energy. The DehI gene (dehI) was carried on a mobile genetic element (DEH) located on the chromosome of strain PP3. DEH recombined with target plasmid DNAs at high frequencies (e.g. 3.8 x 10(-4) per RP4.5 plasmid transferred). The regulated expression of dehI was detected in P. putida, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli strains containing derivative plasmids of RP4.5 and pWW0 recombined with DEH. Movement of DEH from the unstable RP4 derivatives pNJ5000 and pMR5 resulted in the insertion of DEH into the chromosome of RecA+ strains of P. putida but not in RecA+ nor RecA- strains of E. coli. Rescue of DEH from the chromosome of P. putida KT2441 onto plasmid RP4 involved recombination at a frequency (2.7 x 10(-4) per RP4 plasmid transferred) comparable to that observed in strain PP3. The DEH element was not classified as a conventional transposon because it did not move as a discrete DNA fragment: dehI-containing inserts in plasmid DNA targets varied in size between 6 and 13 kb. In addition, DEH exhibited a marked preference for insertion into a specific site on the plasmid pWW0, but its transposition, independent of host recombinational systems, remains to be demonstrated. However, the transposonlike characteristics of DEH included the conservation of restriction endonuclease sites, high-frequency recombination with different target replicons (plasmid and chromosomal DNA), and promiscuous insertion into plasmid RP4-based replicons. Therefore, it is proposed that DEH is an unusual mobile genetic element.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley S. A., Duggleby C. J., Worsey M. J., Williams P. A., Hardy K. G., Broda P. Two modes of loss of the Tol function from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 20;154(2):203–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00330838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H. Translocation of a discrete piece of deoxyribonucleic acid carrying an amp gene between replicons in Eschericha coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.1-6.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Ghosal D., Saedler H. Tn951: a new transposon carrying a lactose operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 6;160(2):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00267484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., De Block M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Schell J. IS-like element IS8 in RP4 plasmid and its involvement in cointegration. Gene. 1980 Sep;10(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. M., Timmis K. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7458–7462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Früh R., Watson J. M., Haas D. Construction of recombination-deficient strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00334835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germida James J. Growth of Indigenous Rhizobium leguminosarum and Rhizobium meliloti in Soils Amended with Organic Nutrients. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):257–263. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.257-263.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Microbial degradation of halogenated compounds. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):135–142. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman P., Milne G. W., Keister D. B. Carbon-halogen bond cleavage. 3. Studies on bacterial halidohrolases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):428–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Bennett P. M., Higginson S., Richmond M. H. Regional preference of insertion of Tn501 and Tn802 into RP1 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):313–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00267624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinter N. J. A broad-host-range cloning vector transposable to various replicons. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann M., Garg G. K., Gunsalus I. C. Fertility factors in Pseudomonas putida: selection and properties of high-frequency transfer and chromosome donors. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):28–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.28-34.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Plasmids that mobilize bacterial chromosome. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Sato G., Sasakawa C., Danbara H., Yoshikawa M. Identification of citrate utilization transposon Tn3411 from a naturally occurring citrate utilization plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):961–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.961-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Rogers J. E., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Transposition of Pseudomonas toluene-degrading genes and expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):179–180. doi: 10.1038/274179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Jager D., Witholt B. Degradation of n-haloalkanes and alpha, omega-dihaloalkanes by wild-type and mutants of Acinetobacter sp. strain GJ70. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):561–566. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.561-566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Takao M., Koiso A., Tonomura K. Genetic Rearrangement of Plasmids: In Vivo Recombination between a Dehalogenation Plasmid and Multiple-Resistance Plasmid RP4 in Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1544–1546. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1544-1546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keuning S., Janssen D. B., Witholt B. Purification and characterization of hydrolytic haloalkane dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.635-639.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Brevet J., Cohen S. N. Involvement of multiple translocating DNA segments and recombinational hotspots in the structural evolution of bacterial plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):333–360. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanka E., Lurz R., Fürste J. P. Molecular cloning and mapping of SphI restriction fragments of plasmid RP4. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrbach P. R., Ward J., Meulien P., Broda P. Physical mapping of TOL plasmids pWWO and pND2 and various R plasmid-TOL derivatives from Pseudomonas spp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1280–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1280-1283.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Cornelis G. Detection and characterization of Tn2501, a transposon included within the lactose transposon Tn951. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):866–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.866-871.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefer U. B., Burkardt H. J., Klipp W., Pühler A. ISR1: an insertion element isolated from the soil bacterium Rhizobium lupini. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):87–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Bennett P. M., Falkow S., Dodd H. M. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive derivative of RP1. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior E., Bull A. T., Slater J. H. Enzyme evolution in a microbial community growing on the herbicide Dalapon. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):476–479. doi: 10.1038/263476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. H., Weightman A. J., Hall B. G. Dehalogenase genes of Pseudomonas putida PP3 on chromosomally located transposable elements. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):557–567. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. W., Topping A. W., Slater J. H., Weightman A. J. Localization and functional analysis of structural and regulatory dehalogenase genes carried on DEH from Pseudomonas putida PP3. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1941–1947. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1941-1947.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Iino T. Identification and characterization of Tn4653, a transposon covering the toluene transposon Tn4651 on TOL plasmid pWW0. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):72–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00333400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Minegishi K., Iino T. Toluene transposons Tn4651 and Tn4653 are class II transposons. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1386–1393. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1386-1393.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weightman A. J., Weightman A. L., Slater J. H. Stereospecificity of 2-monochloropropionate dehalogenation by the two dehalogenases of Pseudomonas putida PP3: evidence for two different dehalogenation mechanisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1755–1762. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weightman A. J., Weightman A. L., Slater J. H. Toxic effects of chlorinated and brominated alkanoic acids on Pseudomonas putida PP3: selection at high frequencies of mutations in genes encoding dehalogenases. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1494–1501. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1494-1501.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Williams P. A. Rapid methods for the study of both stable and unstable plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):433–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]