Abstract
We describe the cloning, sequencing, regulation, and mutational analysis of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum fixK-like gene whose product belongs to the family of Fnr-Crp-related regulatory proteins. The predicted 237-amino-acid FixK protein was found to share between 28 and 38% sequence identity with the Escherichia coli Fnr protein, other bacterial Fnr-like proteins (FnrN, Anr, and HlyX), and two rhizobial FixK proteins. The B. japonicum fixK-like gene, when expressed from a lac promoter, could functionally complement an fnr mutant strain of E. coli and activate transcription from an fnr-dependent promoter in the E. coli background; this activation was sixfold higher in anaerobic cultures than in aerobically grown cells, a finding that suggested oxygen sensitivity of the FixK protein and was consistent with the presence of a cysteine-rich, putatively oxygen-responsive domain at its N-terminal end. Similar to the situation in Rhizobium meliloti, expression of the fixK gene in B. japonicum was shown to be induced at low O2 tension and this induction was dependent on the two-component regulatory system FixLJ. Despite this dependency, however, a B. japonicum fixK mutant did not have the phenotypic characteristics of B. japonicum fixL and fixJ mutants: the fixK mutant was neither Fix- in symbiosis with soybean plants nor defective in anaerobic respiration with nitrate as the terminal electron acceptor. Also, the fixK mutant was unaffected in the expression of one of the two B. japonicum sigma 54 genes, rpoN1, which was previously shown to be controlled by the fixLJ genes. When fixK was introduced into the B. japonicum fixJ mutant and expressed therein from a constitutive promoter (i.e., uncoupling it from regulation by FixJ), the FixK protein thus synthesized fully restored anaerobic nitrate respiration in that strain. We interpret this to mean that the B. japonicum wild type has two homologs of fixLJ-regulated fixK genes which can functionally substitute for each other.
Full text
PDF


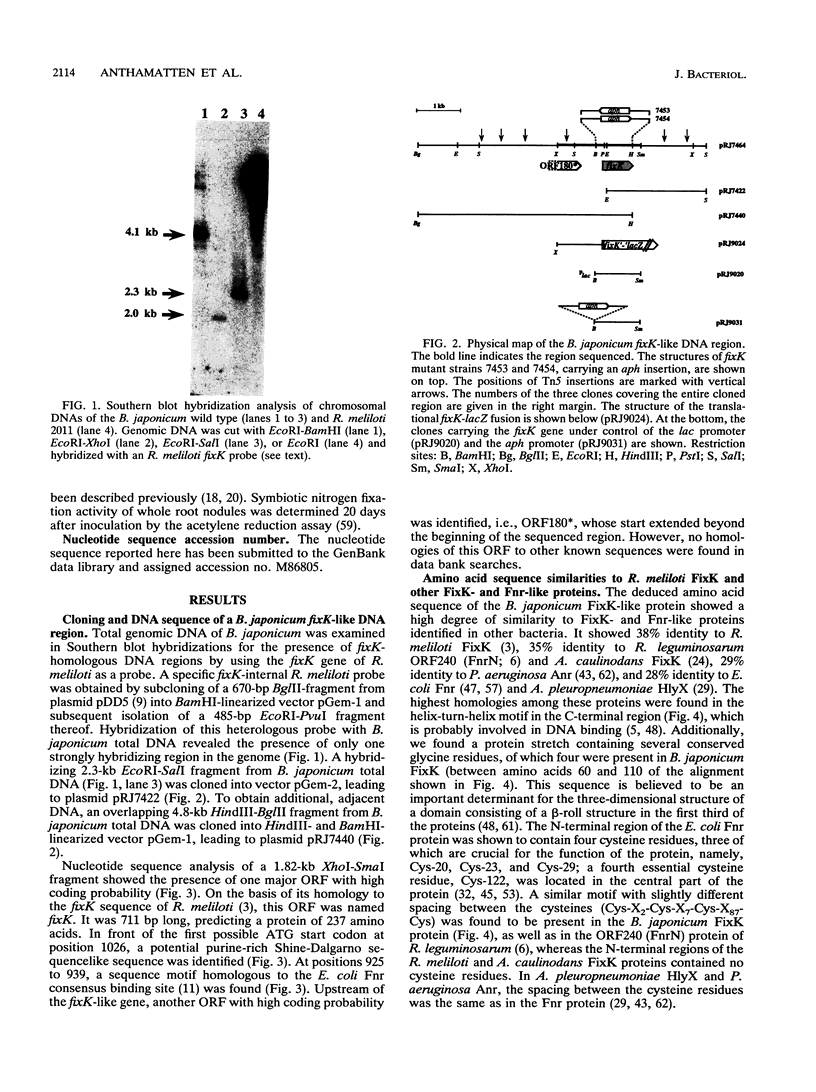


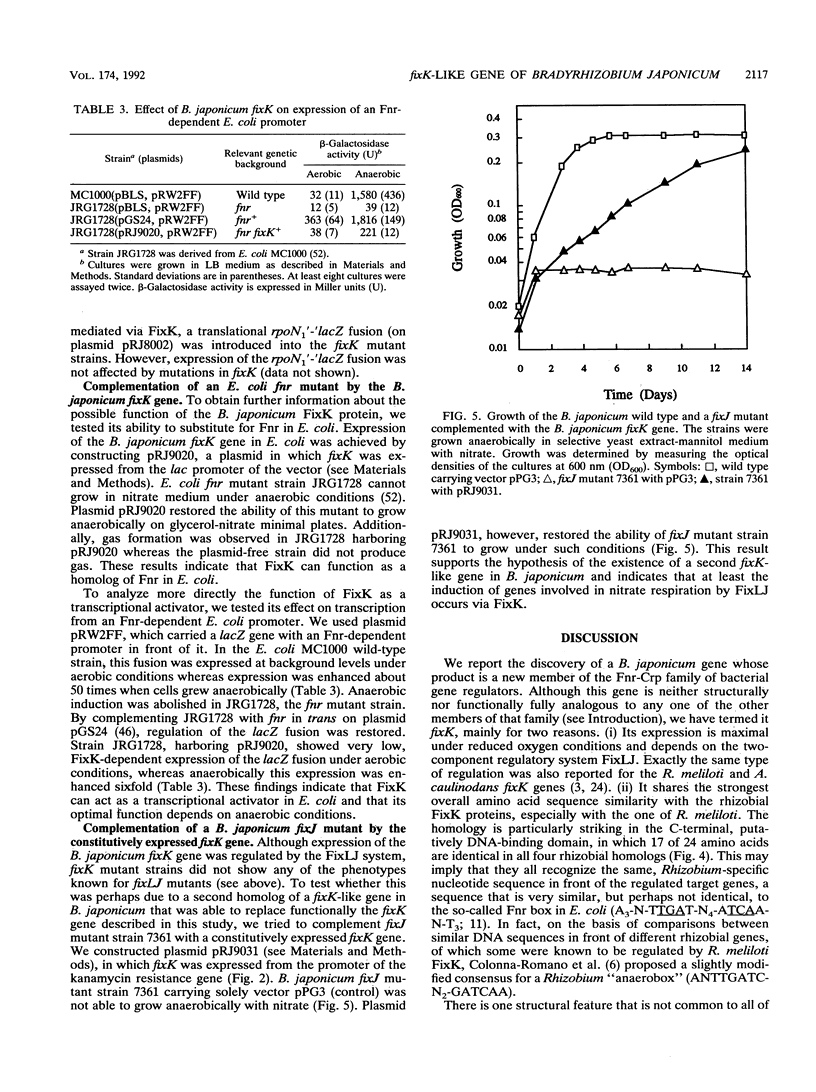



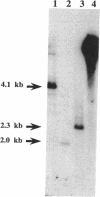
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. The regulatory status of the fixL- and fixJ-like genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum may be different from that in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):38–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00282640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Daveran-Mingot M. L., David M., Jacobs J., Garnerone A. M., Kahn D. fixK, a gene homologous with fnr and crp from Escherichia coli, regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively in Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Santero E., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein FIXJ from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5914–5917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5914-5917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherfils J., Gibrat J. F., Levin J., Batut J., Kahn D. Model-building of Fnr and FixK DNA-binding domains suggests a basis for specific DNA recognition. J Mol Recognit. 1989 Nov;2(3):114–121. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna-Romano S., Arnold W., Schlüter A., Boistard P., Pühler A., Priefer U. B. An Fnr-like protein encoded in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae shows structural and functional homology to Rhizobium meliloti FixK. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):138–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00315806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel R. M., Appleby C. A. Anaerobic-nitrate, symbiotic and aerobic growth of Rhizobium japonicum: effects on cytochrome P 450 , other haemoproteins, nitrate and nitrite reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Domergue O., Pognonec P., Kahn D. Transcription patterns of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic plasmid pSym: identification of nifA-independent fix genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2239–2244. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2239-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H M, Hennecke H. Direct response of Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA-mediated nif gene regulation to cellular oxygen status. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):621–626. doi: 10.1007/BF00331174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galimand M., Gamper M., Zimmermann A., Haas D. Positive FNR-like control of anaerobic arginine degradation and nitrate respiration in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1598–1606. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1598-1606.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Trageser M., Six S., Unden G., Guest J. R. Characterization of the FNR protein of Escherichia coli, an iron-binding transcriptional regulator. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 May 22;244(1310):137–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Hitz S., Hennecke H. Identification of nodS and nodU, two inducible genes inserted between the Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodYABC and nodIJ genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):308–316. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H., Günther I., Binder F. A novel cloning vector for the direct selection of recombinant DNA in E. coli. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by metal-protein complexes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1621–1628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Adaptation of Escherichia coli to respiratory conditions: regulation of gene expression. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Mandon K., Arigoni F., Desnoues N., Elmerich C. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azorhizobium caulinodans: identification of a fixK-like gene, a positive regulator of nifA. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1983–1991. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Yu C., Maier R. J. Common cis-acting region responsible for transcriptional regulation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum hydrogenase by nickel, oxygen, and hydrogen. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):3993–3999. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.3993-3999.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Fritsche S., Knobel H., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H., Fischer H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has two differentially regulated, functional homologs of the sigma 54 gene (rpoN). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1125–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1125-1138.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J., Williams R., Bell A., Chan B., Busby S. Comparison of promoter activities in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of a new broad-host-range promoter-probe plasmid. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 15;55(1-2):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90199-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes J. I., Kim J. E., Lian C. J., Soltes G. A. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hlyX gene homology with the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4587–4592. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4587-4592.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung C. R., Somerville J. E., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Structure of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene hemA encoding 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase. Gene. 1987;54(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melville S. B., Gunsalus R. P. Mutations in fnr that alter anaerobic regulation of electron transport-associated genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18733–18736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P. Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecher A., Zinoni F., Jatisatienr C., Wirth R., Hennecke H., Böck A. On the redox control of synthesis of anaerobically induced enzymes in enterobacteriaceae. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Nov;136(2):131–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00404787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., De La Vega H., Flores M., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A., Pardo M. A., Azpiroz R., De Lourdes Girard M., Calva E., Palacios R. Nitrogenase reductase: A functional multigene family in Rhizobium phaseoli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1170–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renalier M. H., Batut J., Ghai J., Terzaghi B., Gherardi M., David M., Garnerone A. M., Vasse J., Truchet G., Huguet T. A new symbiotic cluster on the pSym megaplasmid of Rhizobium meliloti 2011 carries a functional fix gene repeat and a nod locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2231–2238. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2231-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G. Identification and molecular characterization of a transcriptional regulator from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 exhibiting structural and functional similarity to the FNR protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1469–1481. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Fong Y. C., Iyer V. N. A portable DNA sequence carrying the cohesive site (cos) of bacteriophage lambda and the mob (mobilization) region of the broad-host-range plasmid RK2: a module for the construction of new cosmids. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrocks A. D., Green J., Guest J. R. In vivo and in vitro mutants of FNR the anaerobic transcriptional regulator of E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81248-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Guest J. R. Amplification and product identification of the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Oct;128(10):2221–2228. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-10-2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the fnr gene and primary structure of the Enr protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6119–6130. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Rice D. W., Guest J. R. Homology between CAP and Fnr, a regulator of anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. E., Guest J. R. Isolation and properties of fumarate reductase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.563-570.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Activation of the lac operon of Escherichia coli by a mutant FNR protein. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):53–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Inactivation of the FNR protein of Escherichia coli by targeted mutagenesis in the N-terminal region. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):701–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trageser M., Spiro S., Duchêne A., Kojro E., Fahrenholz F., Guest J. R., Unden G. Isolation of intact FNR protein (Mr 30,000) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trageser M., Unden G. Role of cysteine residues and of metal ions in the regulatory functioning of FNR, the transcriptional regulator of anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Trageser M. Oxygen regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli: control of anaerobic respiration by the FNR protein. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 Feb;59(2):65–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00445650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Reimmann C., Galimand M., Haas D. Anaerobic growth and cyanide synthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depend on anr, a regulatory gene homologous with fnr of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]