Abstract
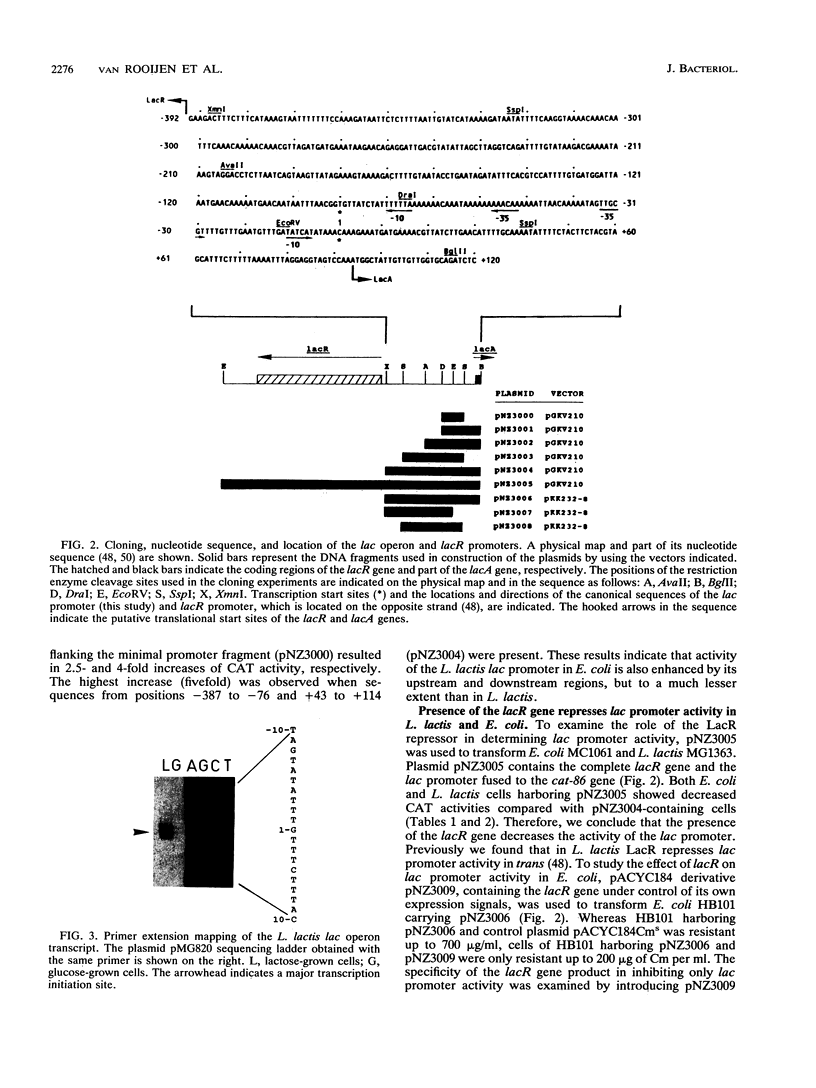
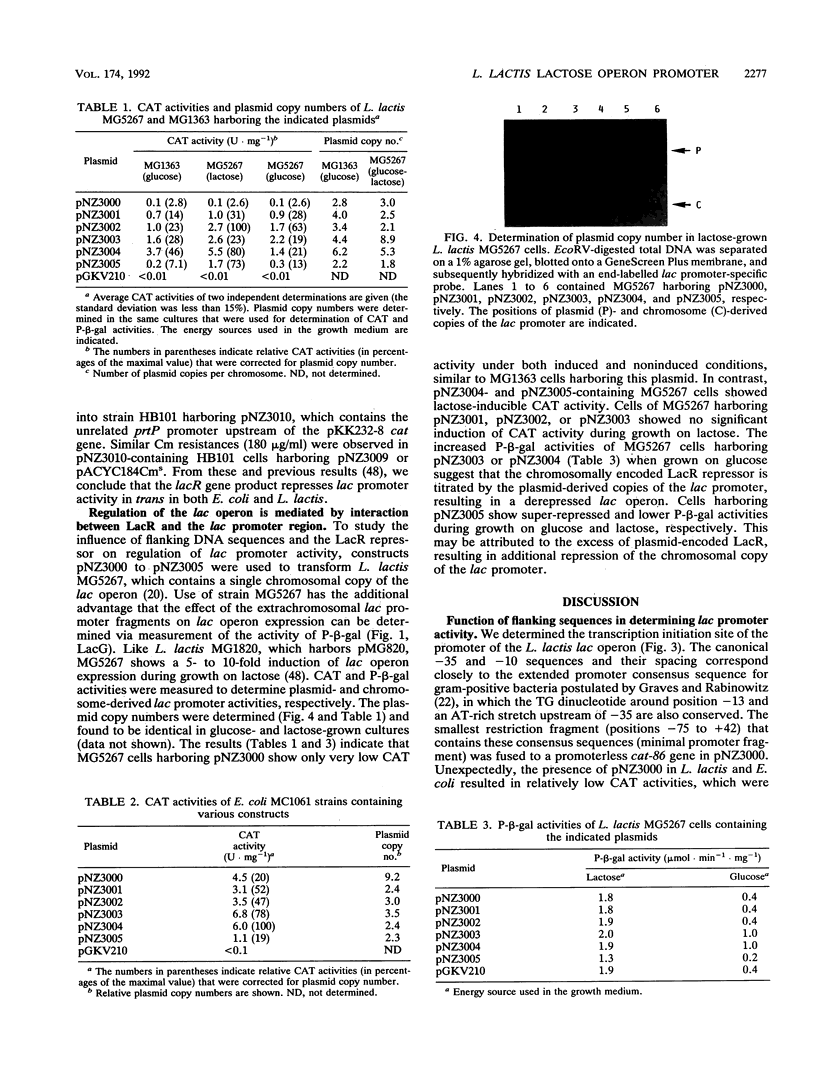
We determined the location, activity, and regulation of the promoter of the Lactococcus lactis 8-kb lactose operon (lacABCDFEGX), which encodes the enzymes of the lactose phosphotransferase system and the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway. The lac promoter sequence corresponds closely to the consensus promoter described for gram-positive bacteria and is located in a back-to-back configuration with the promoter of the divergently transcribed lacR gene, which encodes the LacR repressor. The transcription start sites used under induced (lactose) and noninduced (glucose) conditions were determined. The minimal promoter region that could be isolated on a single restriction fragment included sequences ranging from -75 to +42. The effect of the presence of flanking sequences and the lacR gene on promoter activity and regulation was studied in Escherichia coli and L. lactis strains by using transcriptional fusions with promoterless chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter genes. The results showed that transcriptional regulation of the lac operon is mediated by the interaction between the LacR repressor, the lac promoter, and sequences in the noncoding region between the lacR and lacA genes. Sequences flanking the minimal promoter region appeared to enhance lac promoter activity much more in L. lactis (5- to 38-fold) than in E. coli (1.3- to 5-fold).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck C. F., Warren R. A. Divergent promoters, a common form of gene organization. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):318–326. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.318-326.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Nilsson G., von Gabain A., Cohen S. N. The stability of E. coli gene transcripts is dependent on determinants localized to specific mRNA segments. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90741-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D0galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus: pathway of D-galactose 6-phosphate degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90761-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Plasmid vectors for the selection of promoters. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi H. C., Hsieh J. C., Hui C. F., Tam M. F. Modified method for double stranded DNA sequencing and synthetic oligonucleotide purification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10382–10382. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandanell G., Hammer K. Two operator sites separated by 599 base pairs are required for deoR repression of the deo operon of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3333–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David S., van der Rest M. E., Driessen A. J., Simons G., de Vos W. M. Nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the Lactococcus lactis citrate permease gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5789-5794.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos W. M., Gasson M. J. Structure and expression of the Lactococcus lactis gene for phospho-beta-galactosidase (lacG) in Escherichia coli and L. lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):1833–1846. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-1833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Jin S. F., Raffel G., Sonenshein A. L. Multiple regulatory sites in the Bacillus subtilis citB promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5408–5415. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5408-5415.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Roch J. M., Prentki P., Krisch H. M. The stability of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 mRNA: a 5' leader sequence that can stabilize mRNA transcripts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii T., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Organization of the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):313–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. M., Giannini J. K., Leung T. W., Crosthwaite J. C. Upstream sequence activation of Escherichia coli argT promoter in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):813–822. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., Leenhouts K. J., Haandrikman A. J., Ledeboer A. M., Venema G. Nucleotide sequence of the cell wall proteinase gene of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.231-238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Campbell-like integration of heterologous plasmid DNA into the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.394-400.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Sartorius J., Niemöller M., Genenger G., v Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. The interaction of the recognition helix of lac repressor with lac operator. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3145–3153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Translational attenuation as the regulator of inducible cat genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.1-6.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Gasson M. J. Cloning, expression and location of the Streptococcus lactis gene for phospho-beta-D-galactosidase. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):331–340. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Effect of polyadenine-containing curved DNA on promoter utilization in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11743–11749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Rotational orientation of upstream curved DNA affects promoter function in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10451–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin L., Fridén H., Dehlin E., Rutberg L., von Gabain A. The importance of the 5'-region in regulating the stability of sdh mRNA in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1881–1889. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachaliel N., Melnick J., Gafny R., Glaser G. Ribosome associated protein(s) specifically bind(s) to the upstream activator sequence of the E. coli rrnA P1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9811–9822. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler S., Eismann E. R., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. The three operators of the lac operon cooperate in repression. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):973–979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskouian B., Stewart G. C. Cloning and characterization of the repressor gene of the Staphylococcus aureus lactose operon. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5459–5465. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5459-5465.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskouian B., Stewart G. C. Repression and catabolite repression of the lactose operon of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3804–3812. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3804-3812.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Royer T. J., Mainzer S. E., Schmidt B. F. Lactose transport system of Streptococcus thermophilus: a hybrid protein with homology to the melibiose carrier and enzyme III of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase systems. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.244-253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault P., Gaillardin C., Heslot H. Product of the Lactococcus lactis gene required for malolactic fermentation is homologous to a family of positive regulators. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3108–3114. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3108-3114.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. L., Polzin K. M., McKay L. L. Characterization of the genetic element coding for lactose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis KP3. Plasmid. 1989 Jul;22(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Simons G., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M. Primary structure and organization of the gene for a procaryotic, cell envelope-located serine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13579–13585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickert M. J., Chambliss G. H. Genetic analysis of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3656–3666. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3656-3666.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos W. M., Boerrigter I., van Rooyen R. J., Reiche B., Hengstenberg W. Characterization of the lactose-specific enzymes of the phosphotransferase system in Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22554–22560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos W. M., de Vries S. C., Venema G. Cloning and expression of the Escherichia coli recA gene in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asseldonk M., Rutten G., Oteman M., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Simons G. Cloning of usp45, a gene encoding a secreted protein from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MG1363. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90428-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., de Vos W. M. Molecular cloning, transcriptional analysis, and nucleotide sequence of lacR, a gene encoding the repressor of the lactose phosphotransferase system of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18499–18503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rooijen R. J., van Schalkwijk S., de Vos W. M. Molecular cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway gene cluster of the lactose operon of Lactococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7176–7181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Lelie D., Chavarri F., Venema G., Gasson M. J. Identification of a new genetic determinant for cell aggregation associated with lactose plasmid transfer in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):201–206. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.201-206.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Construction of cloning, promoter-screening, and terminator-screening shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):540–542. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.540-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




