Abstract
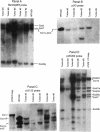
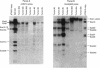
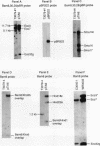
During crown gall tumorigenesis, part of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid, the T-DNA, integrates into plant DNA. Direct repeats define the left and right ends of the T-DNA, but tumorigenesis requires only the right-hand repeat. Virulence (vir) genes act in trans to mobilize the T-DNA into plant cells. Transfer of T-DNA begins when the VirD endonuclease cleaves within the right-hand border repeat. Although the T-DNA right-border repeat promotes T-DNA transmission best in its normal orientation, an inverted right border exhibits reduced but significant activity. Two models may account for this diminished tumorigenesis. The right border may function bidirectionally, with strong activity only in its wild-type orientation, or it may promote T-DNA transfer in a unidirectional manner such that, with an inverted right border, transfer proceeds around the entire Ti plasmid before reaching the T-DNA. To determine whether a substantial portion of the Ti plasmid is transferred to plant cells, as predicted by the unidirectional-transfer hypothesis, we examined T-DNAs in tumors induced by strains containing a Ti plasmid with a right border inverted with respect to the T-DNA oncogenes. These tumors contained extremely long T-DNAs corresponding to most or all of the Ti plasmid. To test whether the right border can function bidirectionally, we inserted T-DNAs with either a properly oriented or an inverted right border into a specific site in the A. tumefaciens chromosome. A border situated to transfer the oncogenes first directed T-DNA transfer even from the bacterial chromosome, whereas a border in the opposite (inverted) orientation did not transfer the oncogenes to plant cells. Our results indicate that the right-border repeat functions in a unidirectional manner.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi D. E., Klee H., Amasino R. M., Nester E. W., Gordon M. P. T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5994–5998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Yanofsky M. F., Leroux B., Ma D. Q., Nester E. W. Processing of the T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens generates border nicks and linear, single-stranded T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1046-1055.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry G. F., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T., Brand L. Identification of a cloned cytokinin biosynthetic gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. Nuclear dna amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 27;274(933):227–274. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. B., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Genetic analysis of integration mediated by single T-DNA borders. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.655-664.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Currier T. C., Farrand S. K., Bendich A. J., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA and PS8 bacteriophage DNA not detected in crown gall tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3672–3676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Drummond M. H., Merio D. J., Sciaky D., Montoya A. L., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Stable incorporation of plasmid DNA into higher plant cells: the molecular basis of crown gall tumorigenesis. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Saiki R. K., Yadav N., Gordon M. P., Quetier F. T-DNA from Agrobacterium Ti plasmid is in the nuclear DNA fraction of crown gall tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Ward J. E., Winans S. C., Nester E. W. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virE2 gene product is a single-stranded-DNA-binding protein that associates with T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2659–2667. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2659-2667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citovsky V., DE Vos G., Zambryski P. Single-Stranded DNA Binding Protein Encoded by the virE Locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):501–504. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4851.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Evidence for diverse types of large plasmids in tumor-inducing strains of Agrobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.157-165.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Agrobacterium tumefaciens virE operon encodes a single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrand S. K., O'Morchoe S. P., McCutchan J. Construction of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 recA mutant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5314–5321. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5314-5321.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Simpson R. B., Ream L. W., White F. F., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of crown gall: fine structure map of the T-DNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghai J., Das A. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid encodes a DNA-relaxing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3109–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietl C., Koukolíková-Nicola Z., Hohn B. Mobilization of T-DNA from Agrobacterium to plant cells involves a protein that binds single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella A., Chen Z. M., Van Montagu M., Wang K. VirD proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens are required for the formation of a covalent DNA--protein complex at the 5' terminus of T-strand molecules. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4055–4062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Roelvink P. W., Hooykaas P. J., Schilperoort R. A. Delivery of T-DNA from the Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosome into plant cells. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2485–2490. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsters M., de Waele D., Depicker A., Messens E., van Montagu M., Schell J. Transfection and transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 11;163(2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00267408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Winsor B. A., De Vos G., Zambryski P. Activation of the T-DNA transfer process in Agrobacterium results in the generation of a T-strand-protein complex: Tight association of VirD2 with the 5' ends of T-strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswal R. K., Veluthambi K., Gelvin S. B., Slightom J. L. Double-stranded cleavage of T-DNA and generation of single-stranded T-DNA molecules in Escherichia coli by a virD-encoded border-specific endonuclease from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5035–5045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5035-5045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos H., Inzé D., Caplan A., Sormann M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Genetic analysis of T-DNA transcripts in nopaline crown galls. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1057–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos H., Timmerman B., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Genetic analysis of transfer and stabilization of Agrobacterium DNA in plant cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2151–2160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leemans J., Deblaere R., Willmitzer L., De Greve H., Hernalsteens J. P., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Genetic Identification of functions of TL-DNA transcripts in octopine crown galls. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):147–152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Hellmiss R., Ream W. Overdrive, a T-DNA transmission enhancer on the A. tumefaciens tumour-inducing plasmid. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1137–1142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ream L. W. T-DNA border sequences required for crown gall tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5112–5116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ream L. W., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Multiple mutations in the T region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1660–1664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong L. J., Karcher S. J., Gelvin S. B. Genetic and molecular analyses of picA, a plant-inducible locus on the Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5110–5120. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5110-5120.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Weiler E. W., Schröder J. The T-region of Ti plasmids codes for an enzyme synthesizing indole-3-acetic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. H., Watson M. D., Carter G. H., Shaw C. H. The right hand copy of the nopaline Ti-plasmid 25 bp repeat is required for tumour formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6031–6041. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. B., O'Hara P. J., Kwok W., Montoya A. L., Lichtenstein C., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. DNA from the A6S/2 crown gall tumor contains scrambled Ti-plasmid sequences near its junctions with plant DNA. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1005–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., Zambryski P. Activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression generates multiple single-stranded T-strand molecules from the pTiA6 T-region: requirement for 5' virD gene products. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):857–863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the susceptible plant cell: a novel adaptation of extracellular recognition and DNA conjugation. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. Bacteria-yeast conjugation. Generic trans-kingdom sex? Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):190–191. doi: 10.1038/340190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Reeves S., Thomashow M. F. Crown gall oncogenesis: evidence that a T-DNA gene from the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid pTiA6 encodes an enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of indoleacetic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Larebeke N., Engler G., Holsters M., Van den Elsacker S., Zaenen I., Schilperoort R. A., Schell J. Large plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens essential for crown gall-inducing ability. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):169–170. doi: 10.1038/252169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veluthambi K., Ream W., Gelvin S. B. Virulence genes, borders, and overdrive generate single-stranded T-DNA molecules from the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1523–1532. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1523-1532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Herrera-Estrella L., Van Montagu M., Zambryski P. Right 25 bp terminus sequence of the nopaline T-DNA is essential for and determines direction of DNA transfer from agrobacterium to the plant genome. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., VAN Montagu M., Zambryski P. C. Site-Specific Nick in the T-DNA Border Sequence as a Result of Agrobacterium vir Gene Expression. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):587–591. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4788.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B., Currier T. C., Gordon M. P., Chilton M. D., Nester E. W. Plasmid required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):255–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.255-264.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav N. S., Vanderleyden J., Bennett D. R., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Short direct repeats flank the T-DNA on a nopaline Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Porter S. G., Young C., Albright L. M., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a site-specific endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90604-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Nester E. W. Association of the virD2 protein with the 5' end of T strands in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3367–3374. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3367-3374.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P. Basic processes underlying Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer to plant cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P., Depicker A., Kruger K., Goodman H. M. Tumor induction by Agrobacterium tumefaciens: analysis of the boundaries of T-DNA. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):361–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]