Abstract
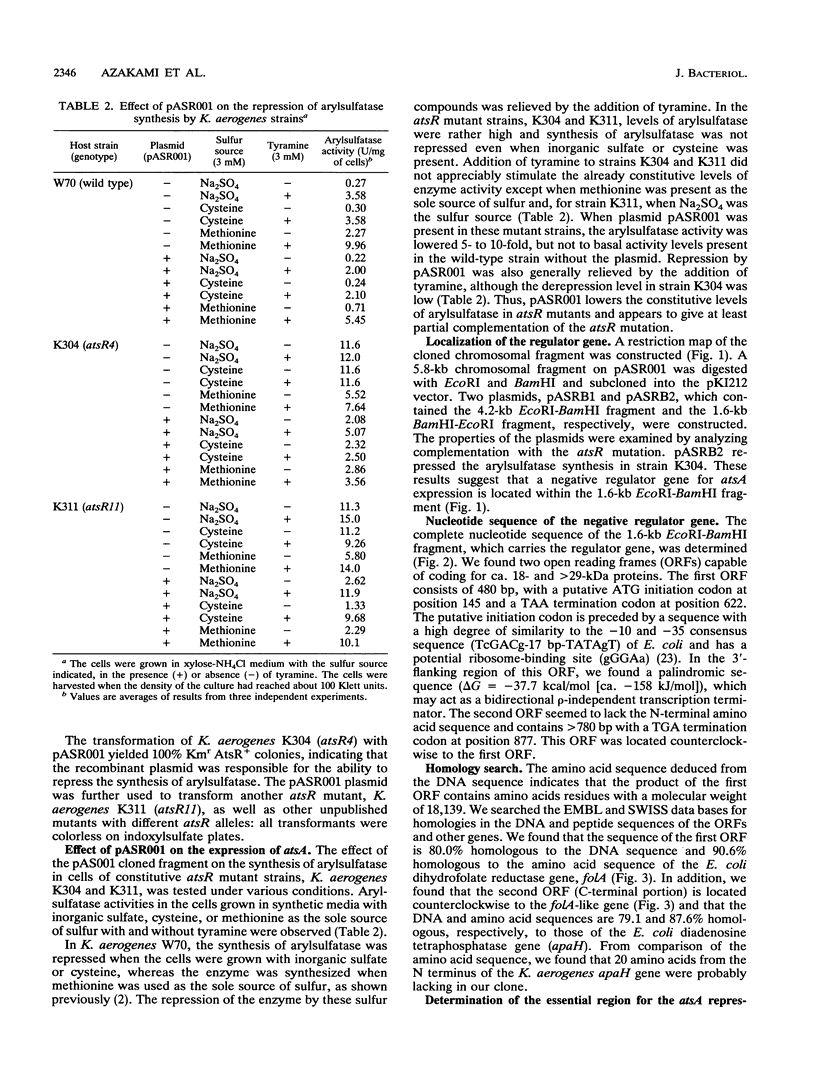
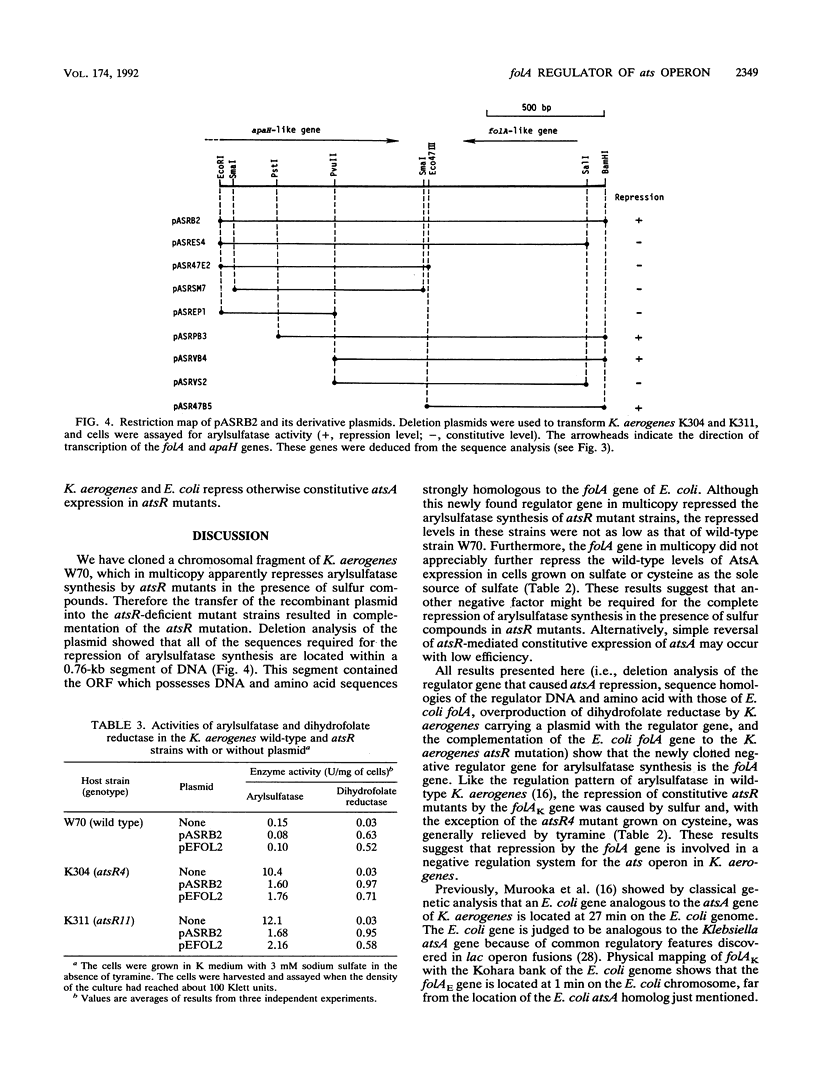
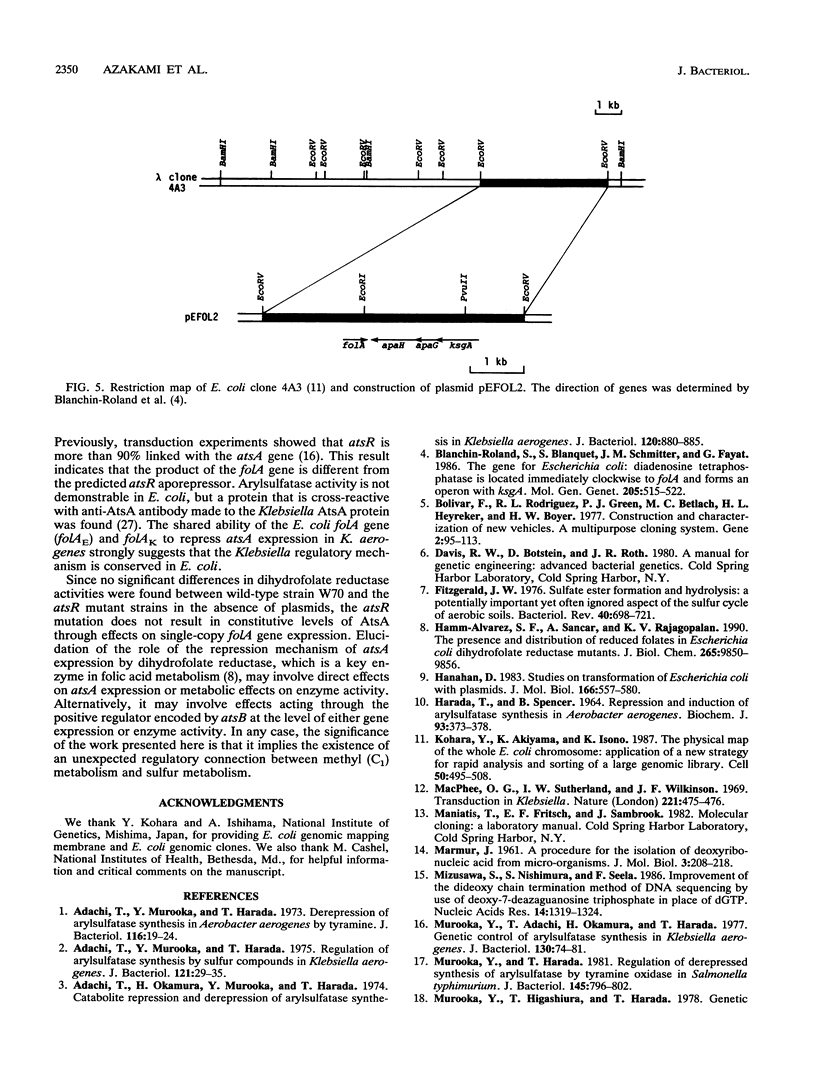
A negative regulator gene for synthesis of arylsulfatase in Klebsiella aerogenes was cloned. Deletion analysis showed that the regulator gene was located within a 1.6-kb cloned segment. Transfer of the plasmid, which contains the cloned fragment, into constitutive atsR mutant strains of K. aerogenes resulted in complementation of atsR; the synthesis of arylsulfatase was repressed in the presence of inorganic sulfate or cysteine, and this repression was relieved, in each case, by the addition of tyramine. The nucleotide sequence of the 1.6-kb fragment was determined. From the amino acid sequence deduced from the DNA sequence, we found two open reading frames. One of them lacked the N-terminal region but was highly homologous to the gene which codes for diadenosine tetraphosphatase (apaH) in Escherichia coli. The other open reading frame was located counterclockwise to the apaH-like gene. This gene was highly homologous to the gene which codes for dihydrofolate reductase (folA) in E. coli. We detected 30 times more activity of dihydrofolate reductase in the K. aerogenes strains carrying the plasmid, which contains the arylsulfatase regulator gene, than in the strains without plasmid. Further deletion analysis showed that the K. aerogenes folA gene is consistent with the essential region required for the repression of arylsulfatase synthesis. Transfer of a plasmid containing the E. coli folA gene into atsR mutant cells of K. aerogenes resulted in repression of the arylsulfatase synthesis. Thus, we conclude that the folA gene codes a negative regulator for the ats operon.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes by tyramine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.19-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Regulation of arylsulfatase synthesis by sulfur compounds in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.29-35.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi T., Okamura H., Murooka Y., Harada T. Catabolite repression and derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):880–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.880-885.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchin-Roland S., Blanquet S., Schmitter J. M., Fayat G. The gene for Escherichia coli diadenosine tetraphosphatase is located immediately clockwise to folA and forms an operon with ksgA. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):515–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00338091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W. Sulfate ester formation and hydrolysis: a potentially important yet often ignored aspect of the sulfur cycle of aerobic soils. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):698–721. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.698-721.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm-Alvarez S. F., Sancar A., Rajagopalan K. V. The presence and distribution of reduced folates in Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase mutants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9850–9856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Spencer B. Repression and induction of arylsulphatase synthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):373–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0930373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee D. G., Sutherland I. W., Wilkinson J. F. Transduction in Klebsiella. Nature. 1969 Feb 1;221(5179):475–476. doi: 10.1038/221475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Adachi T., Okamura H., Harada T. Genetic control of arylsulfatase synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.74-81.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Harada T. Regulation of derepressed synthesis of arylsulfatase by tyramine oxidase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):796–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.796-802.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Ishibashi K., Yasumoto M., Sasaki M., Sugino H., Azakami H., Yamashita M. A sulfur- and tyramine-regulated Klebsiella aerogenes operon containing the arylsulfatase (atsA) gene and the atsB gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2131–2140. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2131-2140.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Morrison J. F. Catalytic mechanism of the dihydrofolate reductase reaction as determined by pH studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2753–2758. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Morrison J. F. Kinetic mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by dihydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3757–3765. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino H., Ishibashi K., Sakaue M., Yamashita M., Murooka Y. Gene cloning of the maoA gene and overproduction of a soluble monoamine oxidase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991 Aug;35(5):606–610. doi: 10.1007/BF00169624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Comparative immunological studies on arylsulfatase in bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae: occurrence of latent arylsulfatase protein regulated by sulfur compounds and tyramine. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):536–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.536-541.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


