Abstract
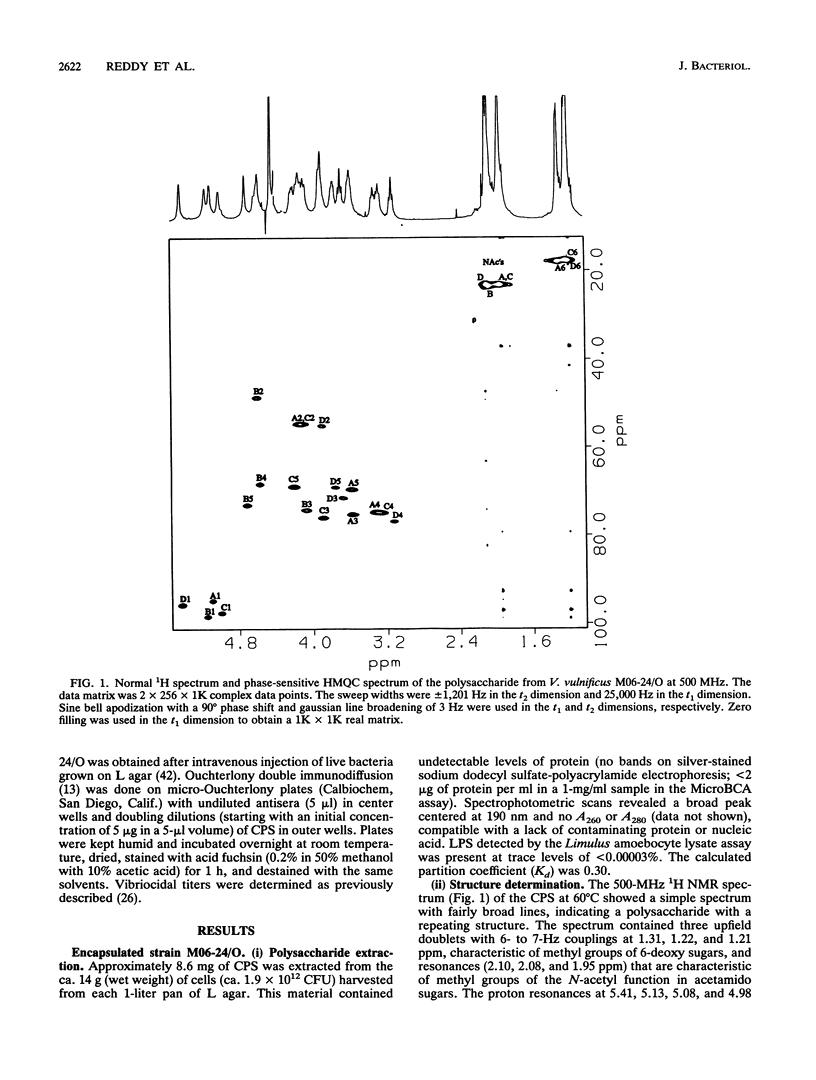
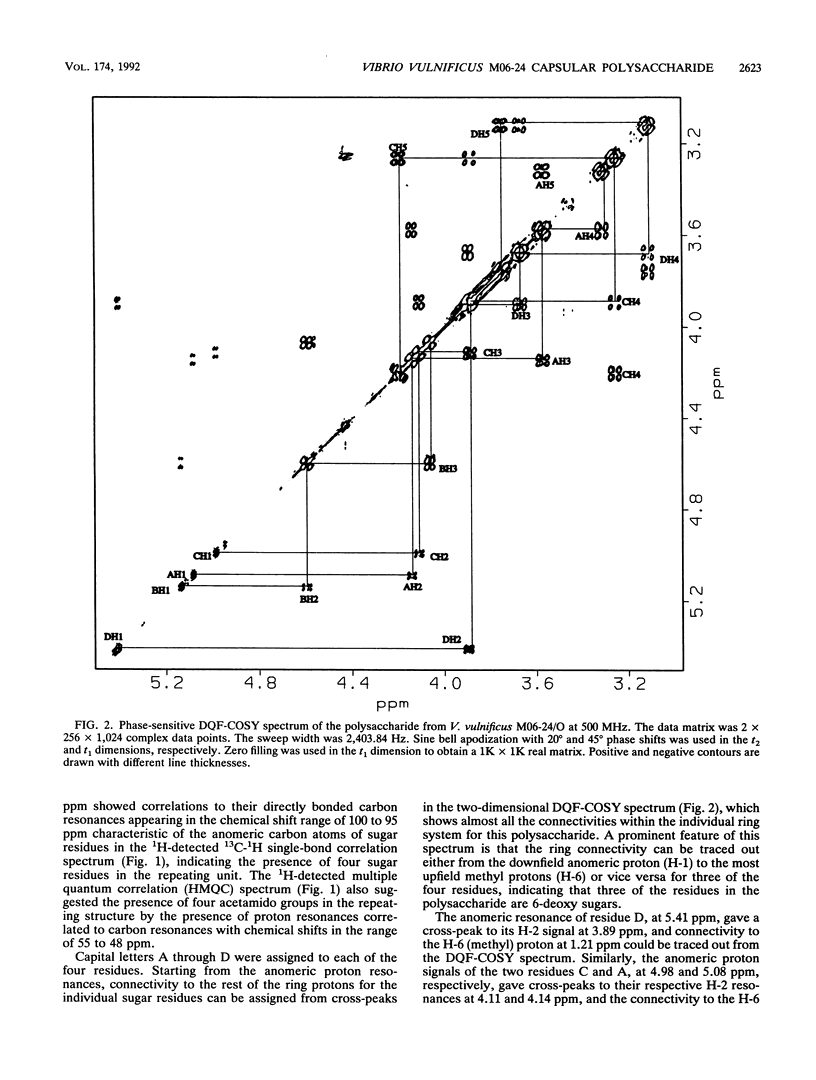
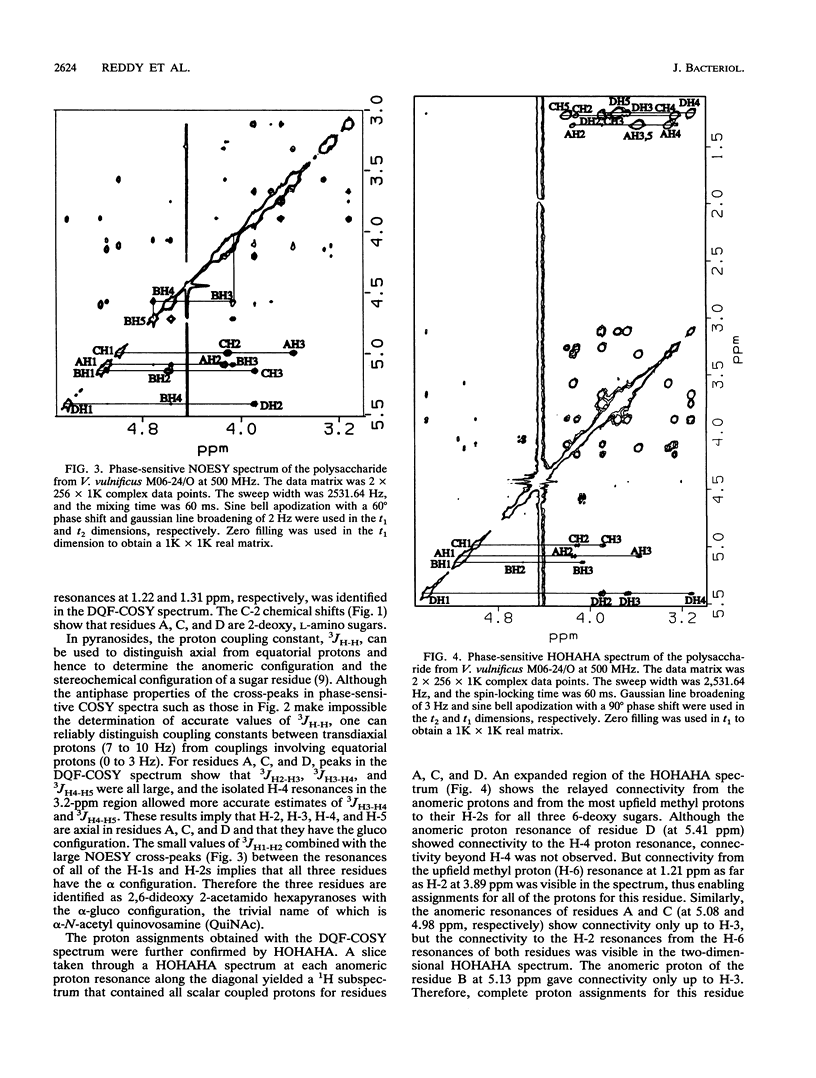
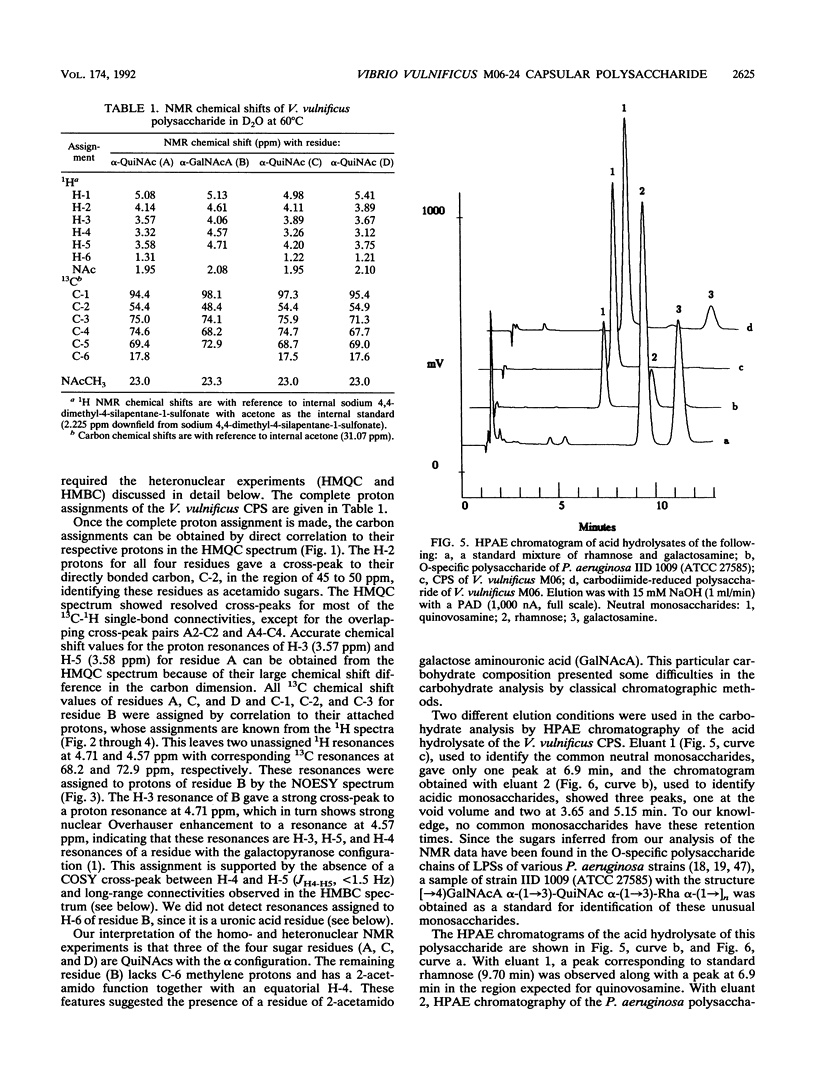
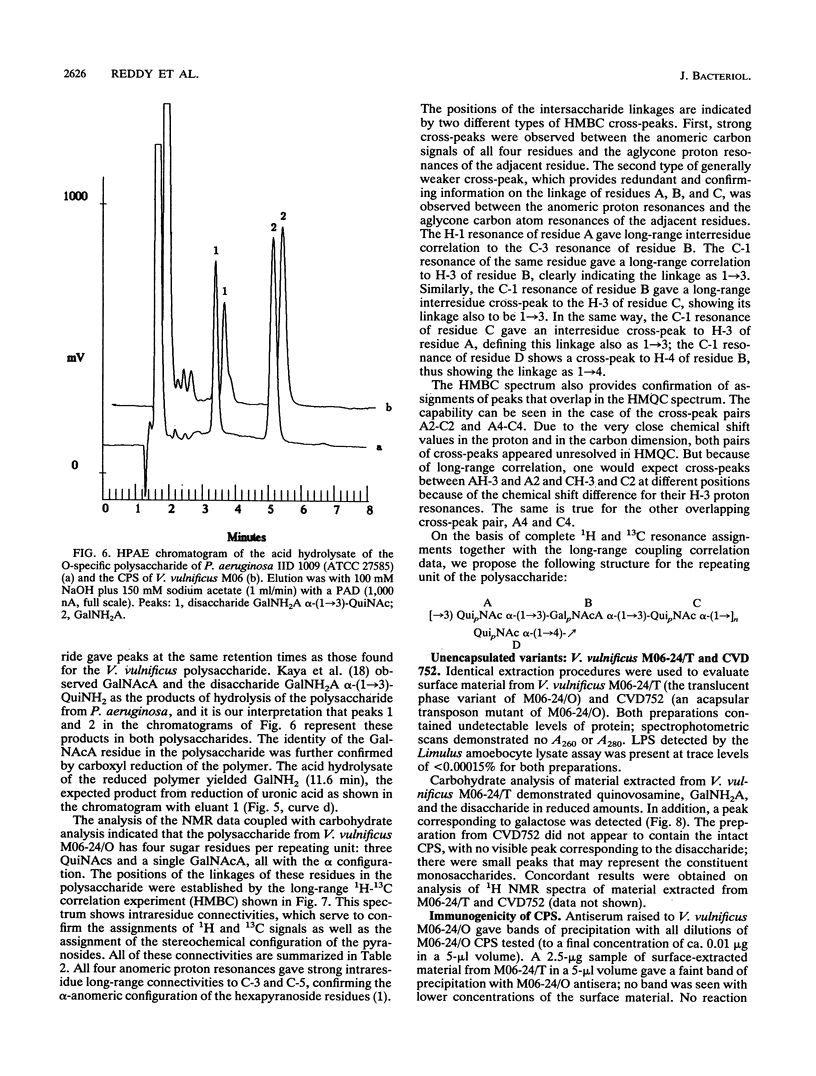
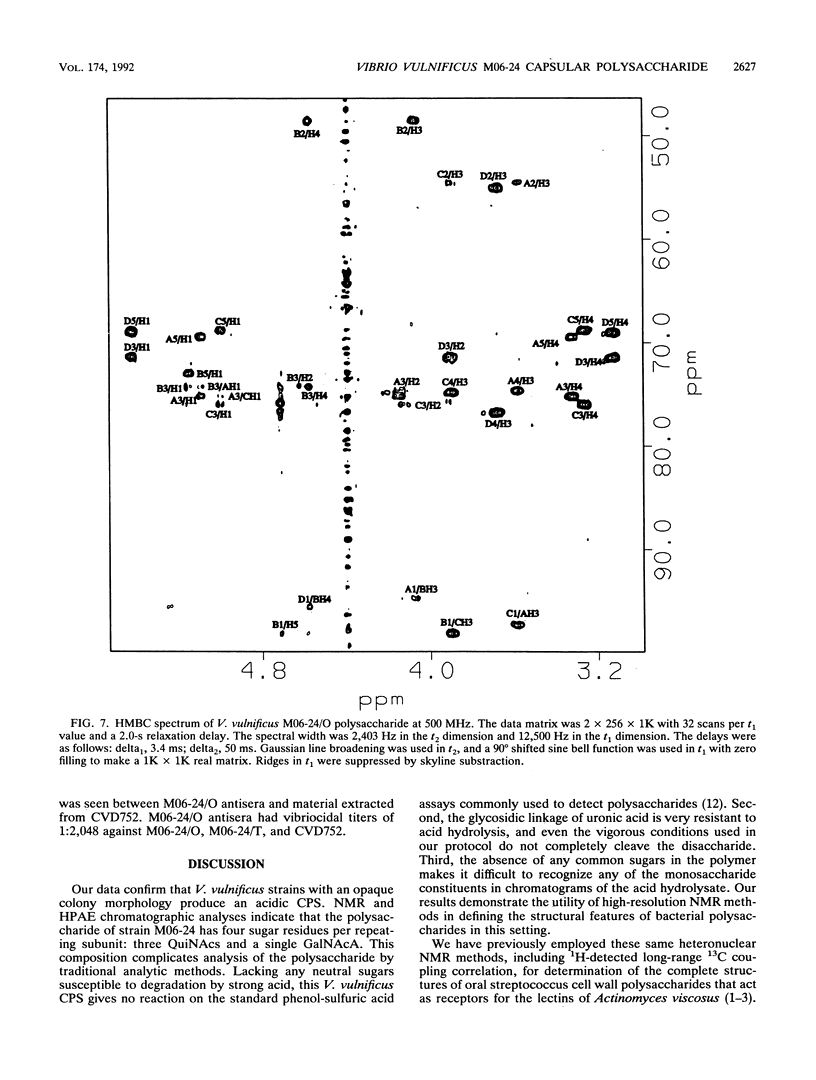
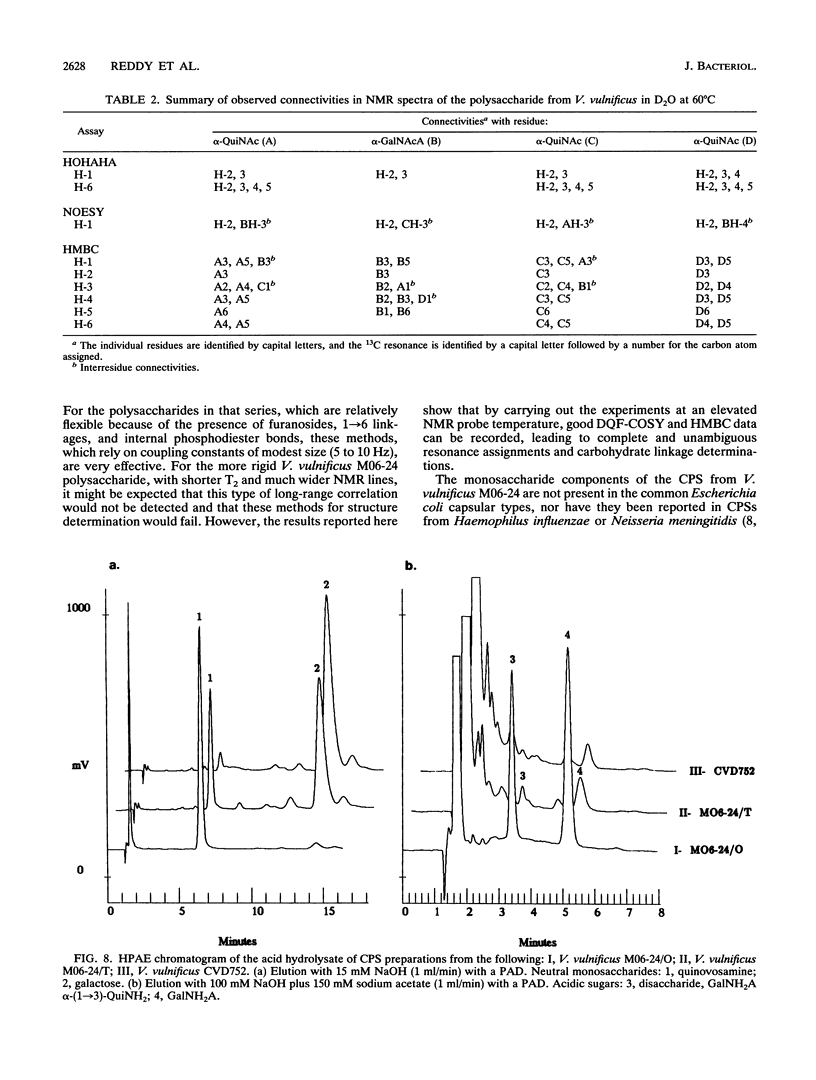
Virulence of Vibrio vulnificus has been strongly associated with encapsulation and an opaque colony morphology. Capsular polysaccharide was purified from a whole-cell, phosphate-buffered saline-extracted preparation of the opaque, virulent phase of V. vulnificus M06-24 (M06-24/O) by dialysis, centrifugation, enzymatic digestion, and phenol-chloroform extraction. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis of the purified polysaccharide showed that the polymer was composed of a repeating structure with four sugar residues per repeating subunit: three residues of 2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxyhexopyranose in the alpha-gluco configuration (QuiNAc) and an additional residue of 2-acetamido hexouronate in the alpha-galactopyranose configuration (GalNAcA). The complete carbohydrate structure of the polysaccharide was determined by heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. The 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra were completely assigned, and vicinal coupling relationships were used to establish the stereochemistry of each sugar residue, its anomeric configuration, and the positions of the glycosidic linkages. The complete structure is: [----3) QuipNAc alpha-(1----3)-GalpNAcA alpha-(1----3)-QuipNAc alpha-(1----]n QuipNAc alpha-(1----4)-increases The polysaccharide was produced by a translucent phase variant of M06-24 (M06-24/T) but not by a translucent, acapsular transposon mutant (CVD752). Antibodies to the polysaccharide were demonstrable in serum from rabbits inoculated with M06-24/O.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeygunawardana C., Bush C. A., Cisar J. O. Complete structure of the cell surface polysaccharide of Streptococcus oralis ATCC 10557: a receptor for lectin-mediated interbacterial adherence. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6528–6540. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeygunawardana C., Bush C. A., Cisar J. O. Complete structure of the cell surface polysaccharide of Streptococcus oralis C104: a 600-MHz NMR study. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8568–8577. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeygunawardana C., Bush C. A., Cisar J. O. Complete structure of the polysaccharide from Streptococcus sanguis J22. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):234–248. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels E. M., Schneerson R., Egan W. M., Szu S. C., Robbins J. B. Characterization of the Salmonella paratyphi C Vi polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3159–3164. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3159-3164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi S. J., Schneerson R., Egan W., Vann W. F., Robbins J. B., Shiloach J. Identity between polysaccharide antigens of Moraxella nonliquefaciens, group B Neisseria meningitidis, and Escherichia coli K1 (non-O acetylated). Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):732–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.732-736.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godchaux W., 3rd, Gorski L., Leadbetter E. R. Outer membrane polysaccharide deficiency in two nongliding mutants of Cytophaga johnsonae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1250–1255. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1250-1255.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. D., Kreger A. S. Purification and characterization of an extracellular cytolysin produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.62-72.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K. Structure and biosynthesis of the capsular antigens of Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:19–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya S., Araki Y., Ito E. The structure of the O-polysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IID 1009 (ATCC 27585). J Biochem. 1989 Jan;105(1):35–38. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaya S., Araki Y., Ito E. The structure of the O-specific chain of lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IID 1012 (ATCC 27588). J Biochem. 1989 Jan;105(1):29–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysner C. A., Abeyta C., Jr, Wekell M. M., DePaola A., Jr, Stott R. F., Leitch J. M. Virulent strains of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from estuaries of the United States West Coast. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1349–1351. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1349-1351.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klontz K. C., Lieb S., Schreiber M., Janowski H. T., Baldy L. M., Gunn R. A. Syndromes of Vibrio vulnificus infections. Clinical and epidemiologic features in Florida cases, 1981-1987. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Aug 15;109(4):318–323. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-4-318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Kreger A. S. Purification and characterization of an elastolytic protease of Vibrio vulnificus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1783–1791. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Gray L. D., Testa J. Protection of mice against Vibrio vulnificus disease by vaccination with surface antigen preparations and anti-surface antigen antisera. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.537-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Siebeling R. J. Identification of Vibrio vulnificus O serovars with antilipopolysaccharide monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1684–1688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1684-1688.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Black R. E. Cholera and other vibrioses in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):343–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Kroll J. S. The role of bacterial polysaccharide capsules as virulence factors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:65–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Warner R. A., Cleland D. R. Distribution of Vibrio vulnificus and other lactose-fermenting vibrios in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.985-998.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Lin W., Egan W., Hoff G. E., Robbins J. B. Form variation in Escherichia coli K1: determined by O-acetylation of the capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):669–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M., Sørensen O. W., Bodenhausen G., Wagner G., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Sakazaki R. On the serology of Vibrio vulnificus. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1984 Oct-Dec;37(5-6):241–246. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.37.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. M., White V. K., Zane S. F., Oliver J. D. Correlation between virulence and colony morphology in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.269-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. C., Merkel J. R. Collagenolytic activity of Vibrio vulnificus: potential contribution to its invasiveness. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1155-1156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Conrad H. E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycuronans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide-activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1383–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa J., Daniel L. W., Kreger A. S. Extracellular phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.458-463.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Robins-Browne R., Lior H., Prado V., Kaper J. B., Nataro J. P., Maneval D., Elsayed A., Levine M. M. Characterization of enteroadherent-aggregative Escherichia coli, a putative agent of diarrheal disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):70–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Morris J. G., Jr The extracellular cytolysin of Vibrio vulnificus: inactivation and relationship to virulence in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):192–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.192-197.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D., Morris J. G., Jr Phenotypic evaluation of acapsular transposon mutants of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1769–1773. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1769-1773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Kaya S., Sawada S., Kawamura T., Araki Y., Ito E. Characterization of a polysaccharide component of lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IID 1008 (ATCC 27584) as D-rhamnan. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):203–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ogawa M., Mizuguchi Y. Relation of capsular materials and colony opacity to virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.446-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



