Abstract
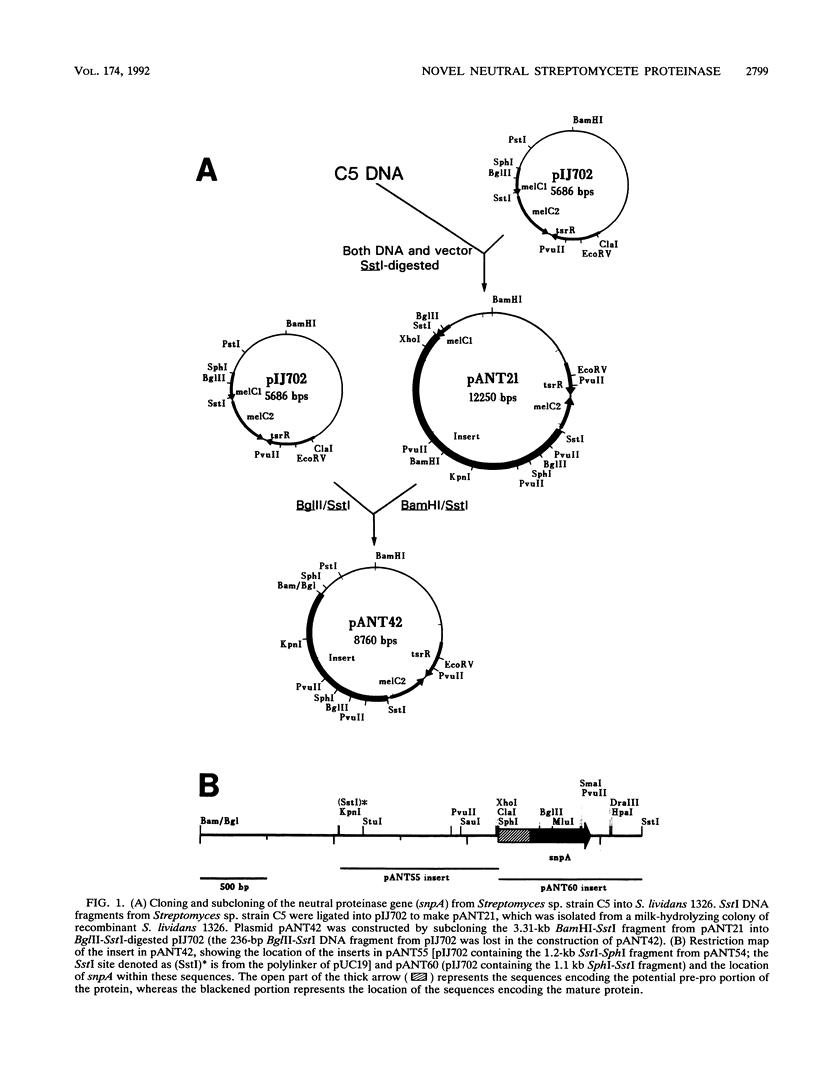
The gene encoding a novel milk protein-hydrolyzing proteinase was cloned on a 6.56-kb SstI fragment from Streptomyces sp. strain C5 genomic DNA into Streptomyces lividans 1326 by using the plasmid vector pIJ702. The gene encoding the small neutral proteinase (snpA) was located within a 2.6-kb BamHI-SstI restriction fragment that was partially sequenced. The molecular mass of the deduced amino acid sequence of the mature protein was determined to be 15,740, which corresponds very closely with the relative molecular mass of the purified protein (15,500) determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the purified neutral proteinase was determined, and the DNA encoding this sequence was found to be located within the sequenced DNA. The deduced amino acid sequence contains a conserved zinc binding site, although secondary ligand binding and active sites typical of thermolysinlike metalloproteinases are absent. The combination of its small size, deduced amino acid sequence, and substrate and inhibition profile indicate that snpA encodes a novel neutral proteinase.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aretz W., Koller K. P., Riess G. Proteolytic enzymes from recombinant Streptomyces lividans TK24. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernan V., Filpula D., Herber W., Bibb M., Katz E. The nucleotide sequence of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus and characterization of the gene product. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. The amino acid sequence of bovine carboxypeptidase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1389–1394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran S., Dhar S. C. Multiple proteases from Streptomyces moderatus. I. Isolation and purification of five extracellular proteases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Sep;257(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90582-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. C., Kuo T. C., Tsugita A., Lee Y. H. Extracellular metalloprotease gene of Streptomyces cacaoi: structure, nucleotide sequence and characterization of the cloned gene product. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90063-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekleva M. L., Titus J. A., Strohl W. R. Nutrient effects on anthracycline production by Streptomyces peucetius in a defined medium. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Mar;31(3):287–294. doi: 10.1139/m85-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DelMar E. G., Largman C., Brodrick J. W., Geokas M. C. A sensitive new substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):316–320. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proteases B and C are synthesized and secreted as zymogens without a signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9083–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z. X., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. Activity of a Streptomyces transcriptional terminator in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2665–2675. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duez C., Piron-Fraipont C., Joris B., Dusart J., Urdea M. S., Martial J. A., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Primary structure of the Streptomyces R61 extracellular DD-peptidase. 1. Cloning into Streptomyces lividans and nucleotide sequence of the gene. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J. A spectrophotometric assay for neutral protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Krygsman P., Liu C. J., Davey C. C., Malek L. T. Characterization and structure of genes for proteases A and B from Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3778–3784. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3778-3784.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Bouvier J., Bairoch A. A unique signature identifies a family of zinc-dependent metallopeptidases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Thompson C. J., Hopwood D. A. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2703–2714. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama T., Suda H., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Studies on inhibitory effect of phosphoramidon and its analogs on thermolysin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):727–731. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampel J. S., Strohl W. R. Transformation and transfection of anthracycline-producing streptomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):126–131. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.126-131.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Dosch D. C., Strohl W. R., Floss H. G. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the nosiheptide-resistance gene from Streptomyces actuosus. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90156-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichenstein H. S., Busse L. A., Smith G. A., Narhi L. O., McGinley M. O., Rohde M. F., Katzowitz J. L., Zukowski M. M. Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding extracellular metalloprotease from Streptomyces lividans. Gene. 1992 Feb 1;111(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90613-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Silver staining methods for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:230–239. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. M., Spilburg C. A. Purification of human collagenases with a hydroxamic acid affinity column. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5189–5195. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama K., Yoshimura K., Marumoto R., Kikuchi M., Lee I. S., Hase T., Matsubara H. Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5843–5855. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. J. Cysteine proteinases of cellular slime moulds. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Apr;13(2):288–290. doi: 10.1042/bst0130288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata S., Taguchi S., Kumagai I., Miura K. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of gene encoding Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor (SSI). J Biochem. 1989 Mar;105(3):367–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido D., Jiménez A. Optimization of gene expression in Streptomyces lividans by a transcription terminator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4227–4240. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. A., Kuhstoss S., Solenberg P., Schaus N. A., Rao R. N. A new shuttle cosmid vector, pKC505, for streptomycetes: its use in the cloning of three different spiramycin-resistance genes from a Streptomyces ambofaciens library. Gene. 1987;61(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. V., Elmore D. T. Kinetics and mechanism of catalysis by proteolytic enzymes. A comparison of the kinetics of hydrolysis of synthetic substrates by bovine alpha- and beta-trypsin. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):545–554. doi: 10.1042/bj1410545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufo G. A., Jr, Sullivan B. J., Sloma A., Pero J. Isolation and characterization of a novel extracellular metalloprotease from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1019–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1019-1023.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Rudolph C. F., Rufo G. A., Jr, Sullivan B. J., Theriault K. A., Ally D., Pero J. Gene encoding a novel extracellular metalloprotease in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1024–1029. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1024-1029.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Murakami S., Tsuji R. F., Ishida Y., Murakami K., Masaki A., Kawabe H., Arimura H., Nakano E., Motai H. Cloning and expression in yeast of a cDNA clone encoding Aspergillus oryzae neutral protease II, a unique metalloprotease. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):97–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00282453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wart H. E., Steinbrink D. R. A continuous spectrophotometric assay for Clostridium histolyticum collagenase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):356–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D., Rhodes C., Banner C., Nagle J., Filpula D. Genes for alkaline protease and neutral protease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens contain a large open reading frame between the regions coding for signal sequence and mature protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.811-819.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WUENSCH E., HEIDRICH H. G. ZUR QUANTITATIVEN BESTIMMUNG DER KOLLAGENASE. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1963;333:149–151. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1963.333.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. Y., Ferrari E., Henner D. J. Cloning of the neutral protease gene of Bacillus subtilis and the use of the cloned gene to create an in vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.15-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]