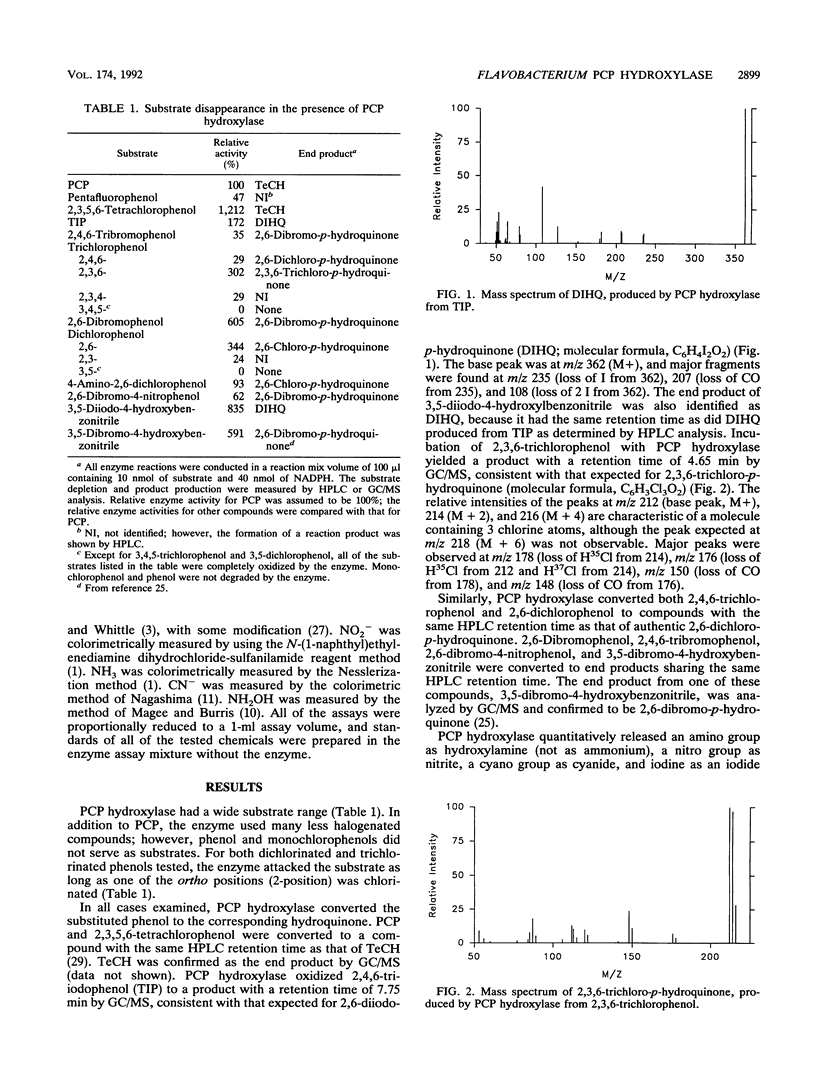
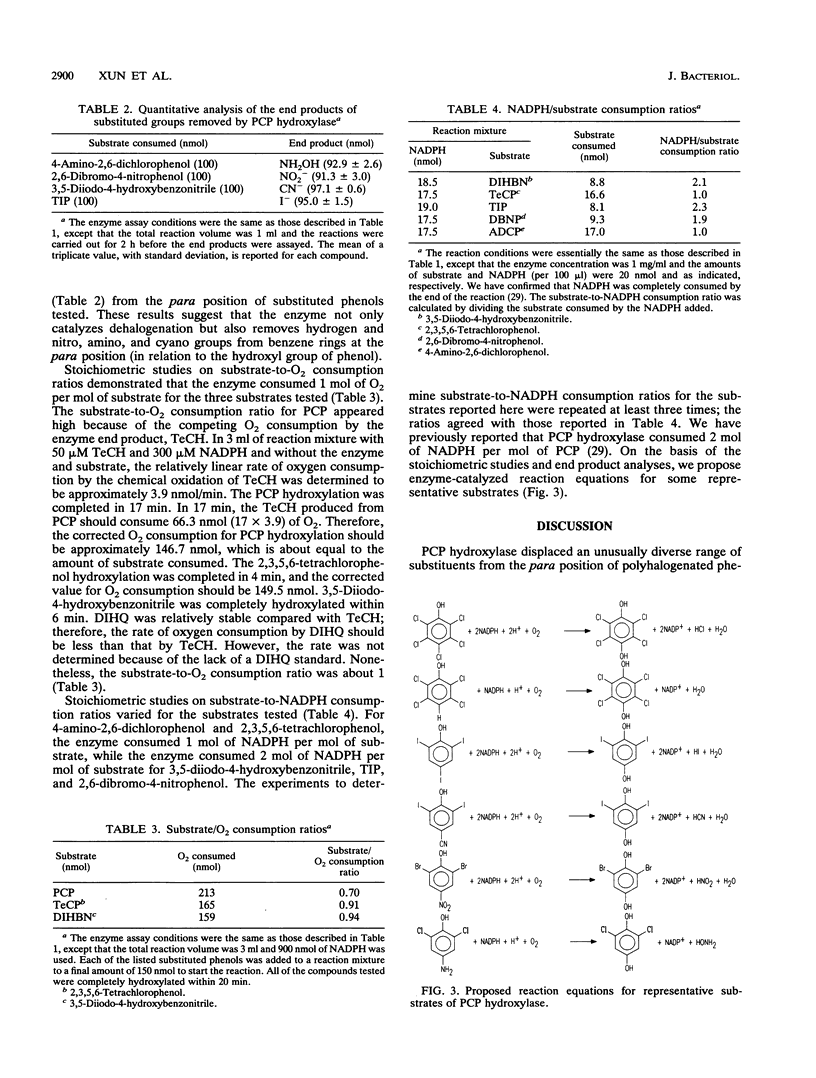
Abstract
An understanding of the enzymatic reactions catalyzing the degradation of substituted phenols, a major group of environmental pollutants, is required for the development of biological methods for the decontamination of halophenol-polluted sites. We found that a flavomonooxygenase, pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, isolated from a Flavobacterium sp., catalyzed a primary attack on a broad range of substituted phenols, hydroxylating the para position and removing halogen, nitro, amino, and cyano groups to produce halide, nitrite, hydroxylamine, and cyanide, respectively. Elimination of 1 mol of a halogen, nitro, or cyano group required 2 mol of NADPH, while only 1 mol of NADPH was required to remove 1 mol of an amino group or hydrogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. E. Toward a science of metabolic engineering. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1668–1675. doi: 10.1126/science.2047876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Chapalamadugu S. Biodegradation of halogenated organic compounds. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):59–79. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.59-79.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisalba O. Chemical wastes and their biodegradation--an overview. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1247–1257. doi: 10.1007/BF01990362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Entsch B., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Chapman P. J. Fluoride elimination from substrates in hydroxylation reactions catalyzed by p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4189–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Timmis K. N. Experimental evolution of catabolic pathways of bacteria. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Aug;4(8):228–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Wasserfallen A., Rose K., Timmis K. N. Redesigning metabolic routes: manipulation of TOL plasmid pathway for catabolism of alkylbenzoates. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):593–596. doi: 10.1126/science.3468623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W. Construction of bacterial strains with novel degradative capabilities for chloroaromatics. J Basic Microbiol. 1986;26(9):551–567. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3620260911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Microbial degradation of haloaromatics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Cooper J. M. Method of determining oxygen concentrations in biological media, suitable for calibration of the oxygen electrode. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber D. L., Crawford R. L. Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1512-1518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siuda J. F., DeBernardis J. F. Naturally occurring halogenated organic compounds. Lloydia. 1973 Jun;36(2):107–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp E., Xun L. Y., Orser C. S. Biodegradation of the herbicide bromoxynil (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) by purified pentachlorophenol hydroxylase and whole cells of Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723 is accompanied by cyanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):502–506. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.502-506.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L. Y., Orser C. S. Purification of a Flavobacterium pentachlorophenol-induced periplasmic protein (PcpA) and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene (pcpA). J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2920–2926. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2920-2926.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Biodegradation of triiodophenol by cell-free extracts of a pentachlorophenol-degrading Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90482-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xun L., Orser C. S. Purification and properties of pentachlorophenol hydroxylase, a flavoprotein from Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4447–4453. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4447-4453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kocher H. P. Purification and characterization of a bacterial nitrophenol oxygenase which converts ortho-nitrophenol to catechol and nitrite. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1789–1794. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1789-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


