Abstract
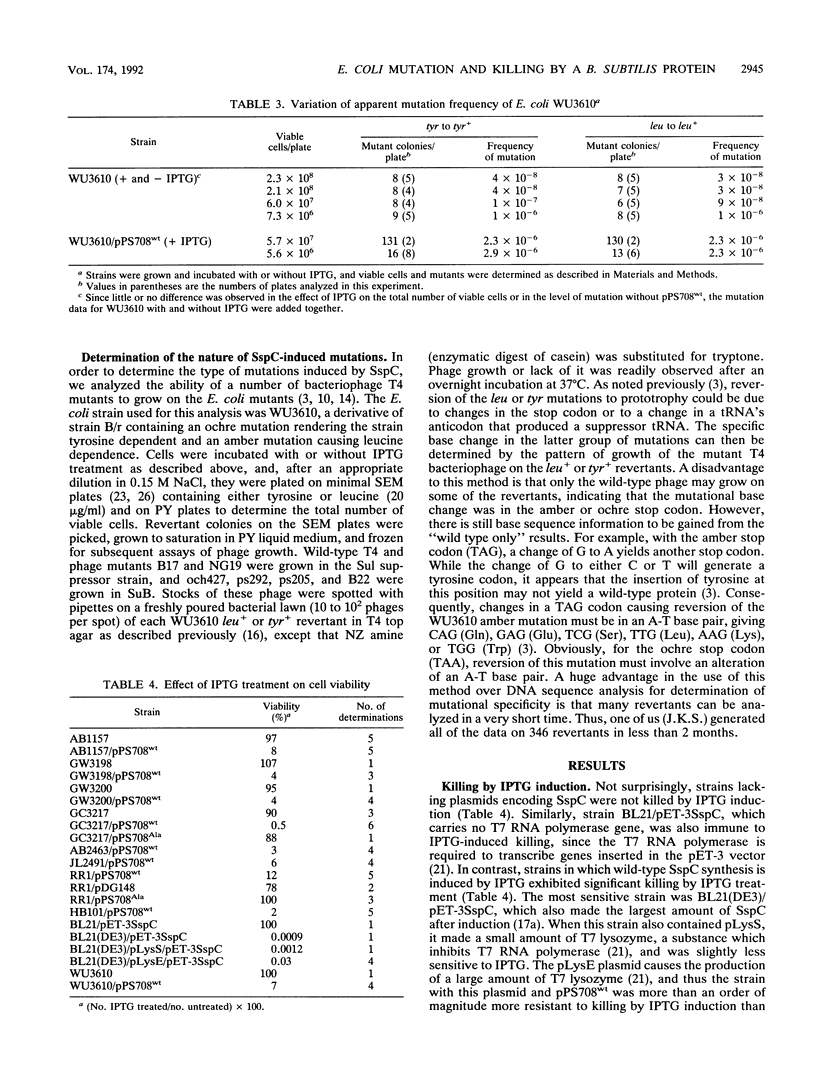
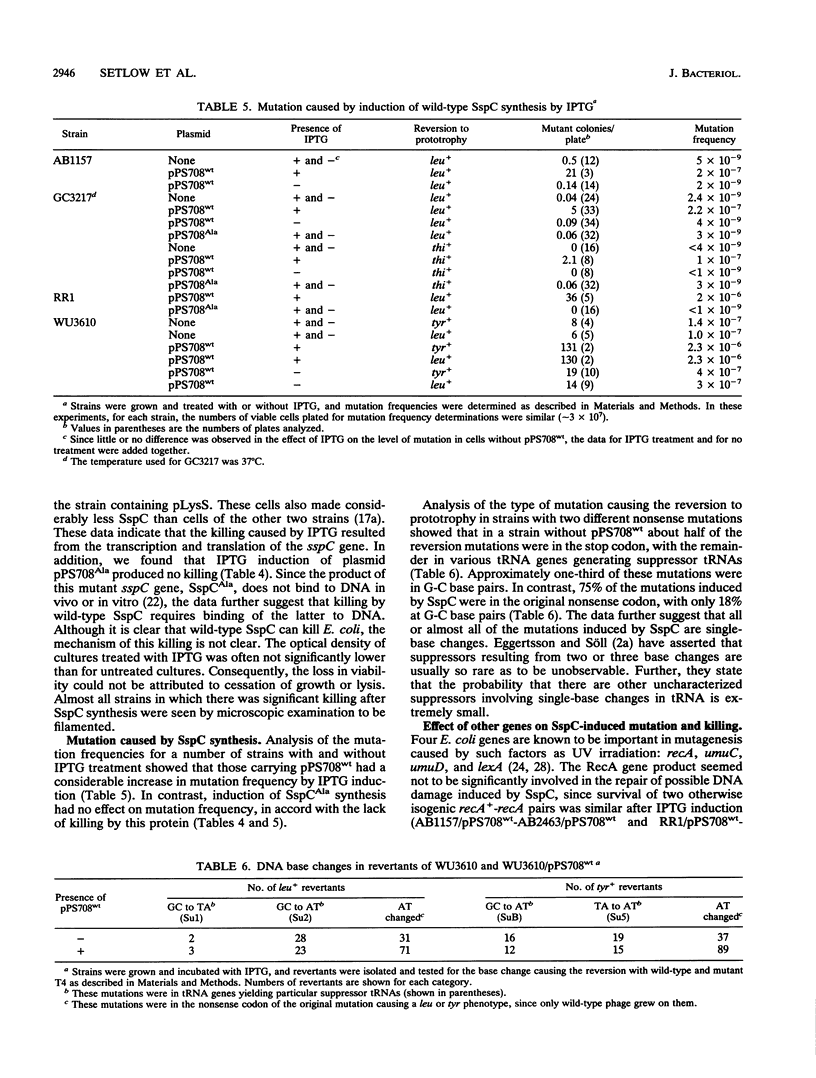
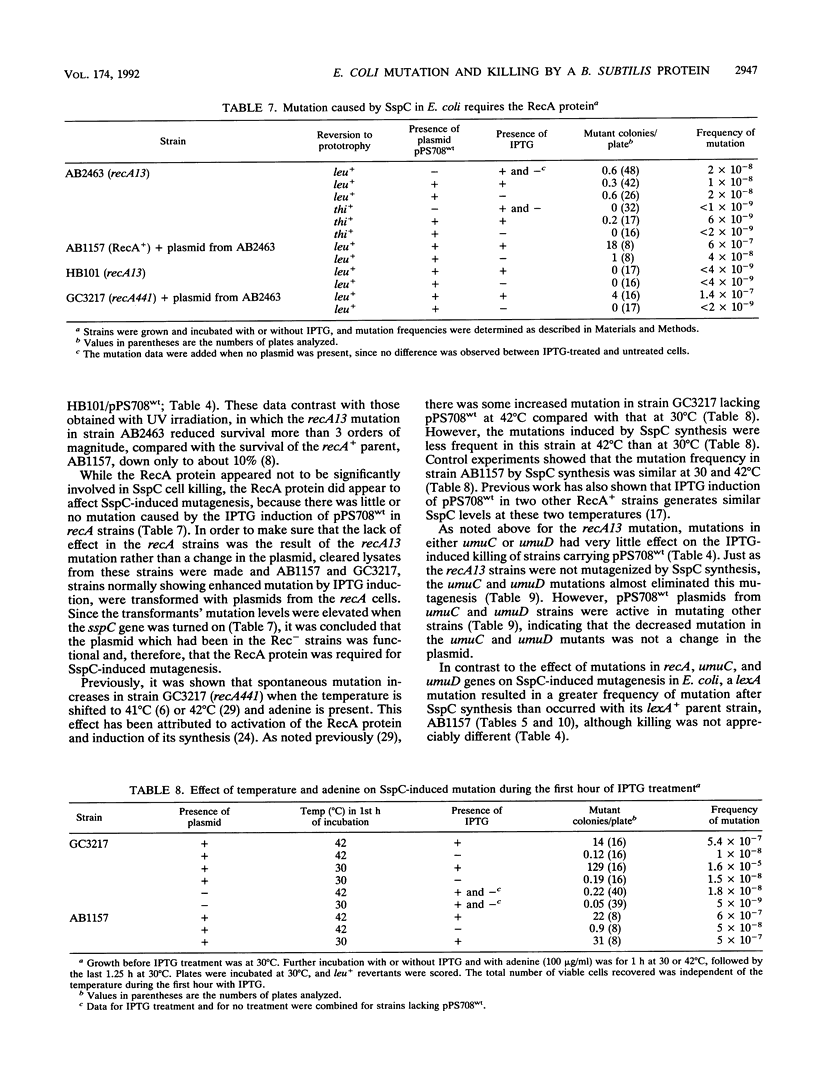
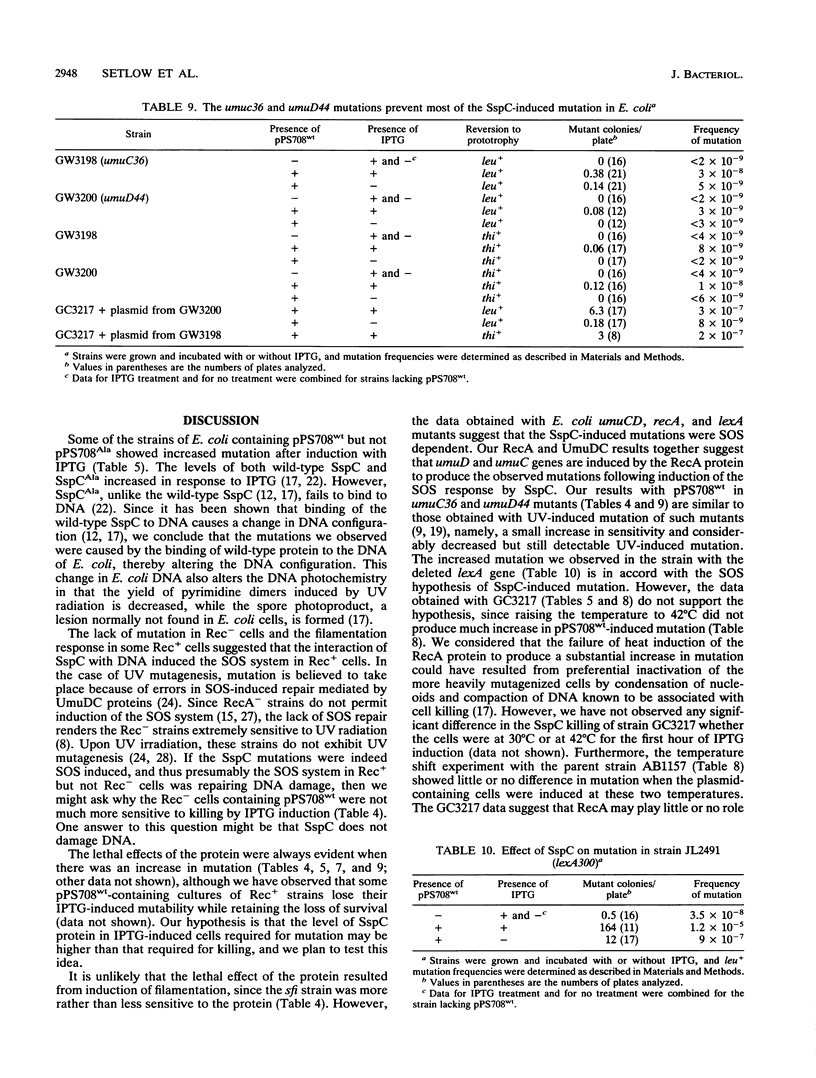
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis gene coding for SspC, a small, acid-soluble protein, caused both killing and mutation in a number of Escherichia coli B and K-12 strains. SspC was previously shown to bind E. coli DNA in vivo, and in vitro this protein binds DNA and converts it into an A-like conformation. Analysis of revertants of nonsense mutations showed that SspC caused single-base changes, and a greater proportion of these were at A-T base pairs. Mutation in the recA gene abolished the induction of mutations upon synthesis of SspC, but the killing was only slightly greater than in RecA+ cells. Mutations in the umuC and umuD genes eliminated most of the mutagenic effect of SspC but not the killing, while the lexA mutation increased mutagenesis but did not appreciably affect the killing. Since there was neither killing nor mutation of E. coli after synthesis of a mutant SspC which does not bind DNA, it appears likely that the binding of wild-type SspC to DNA, with the attendant conformational change, was responsible for the killing and mutation. A strain containing the B. subtilis gene that is constitutive for the RecA protein at 42 degrees C showed a lower frequency of mutation when that temperature was used to induce the RecA protein than when the temperature was 30 degrees C, where the RecA level is low, suggesting that at the elevated temperature the high RecA level could be inhibiting binding of the B. subtilis protein to DNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggertsson G., Söll D. Transfer ribonucleic acid-mediated suppression of termination codons in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):354–374. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.354-374.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elespuru R. K., Stupar L. L., Gordon J. A. Discrimination of mutagenic intermediates derived from alkylating agents by mutational patterns generated in Escherichia coli. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jul;12(7):1161–1167. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet light-induced responses of an mfd mutant of Escherichia coli B/r having a slow rate of dimer excision. Mutat Res. 1975 Jun;28(3):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P., SIMSON E., THERIOT L. A LOCUS THAT CONTROLS FILAMENT FORMATION AND SENSITIVITY TO RADIATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12. Genetics. 1964 Feb;49:237–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Shinoura Y. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Escherichia coli deficient in induction of mutations by ultraviolet light. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 14;156(2):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00283484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Shinoura Y., Templin A., Clark A. J. Analysis of ultraviolet light-induced suppressor mutations in the strain of Escherichia coli K-12 AB1157: an implication for molecular mechanisms of UV mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):283–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00425840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Low K. B. Specificity of mutagenesis resulting from the induction of the SOS system in the absence of mutagenic treatment. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr S. C., Sokolov N. V., He C. M., Setlow P. Binding of small acid-soluble spore proteins from Bacillus subtilis changes the conformation of DNA from B to A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow B., Setlow P. Binding of DNA in vitro by a small, acid-soluble spore protein from Bacillus subtilis and the effect of this binding on DNA topology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6900–6906. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6900-6906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Person S., Phillips S., Funk F. A determination of mutagen specificity in bacteria using nonsense mutants of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):437–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radman M. SOS repair hypothesis: phenomenology of an inducible DNA repair which is accompanied by mutagenesis. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5A:355–367. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2895-7_48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Paoletti C. Control of UV induction of recA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Hand A. R., Setlow P. Synthesis of a Bacillus subtilis small, acid-soluble spore protein in Escherichia coli causes cell DNA to assume some characteristics of spore DNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1642–1653. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1642-1653.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus species: structure, synthesis, genetics, function, and degradation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:319–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinborn G. Uvm mutants of Escherichia coli K12 deficient in UV mutagenesis. I. Isolation of uvm mutants and their phenotypical characterization in DNA repair and mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Sep 20;165(1):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00270380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Rojo F., Setlow P. Effects of mutant small, acid-soluble spore proteins from Bacillus subtilis on DNA in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4827–4835. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4827-4835.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M., Kogoma T. Involvement of the activated form of RecA protein in SOS mutagenesis and stable DNA replication in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7539–7543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Radiation-induced mutations and their repair. Science. 1966 Jun 3;152(3727):1345–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3727.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet-induced mutation and DNA repair. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:487–514. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


