Abstract
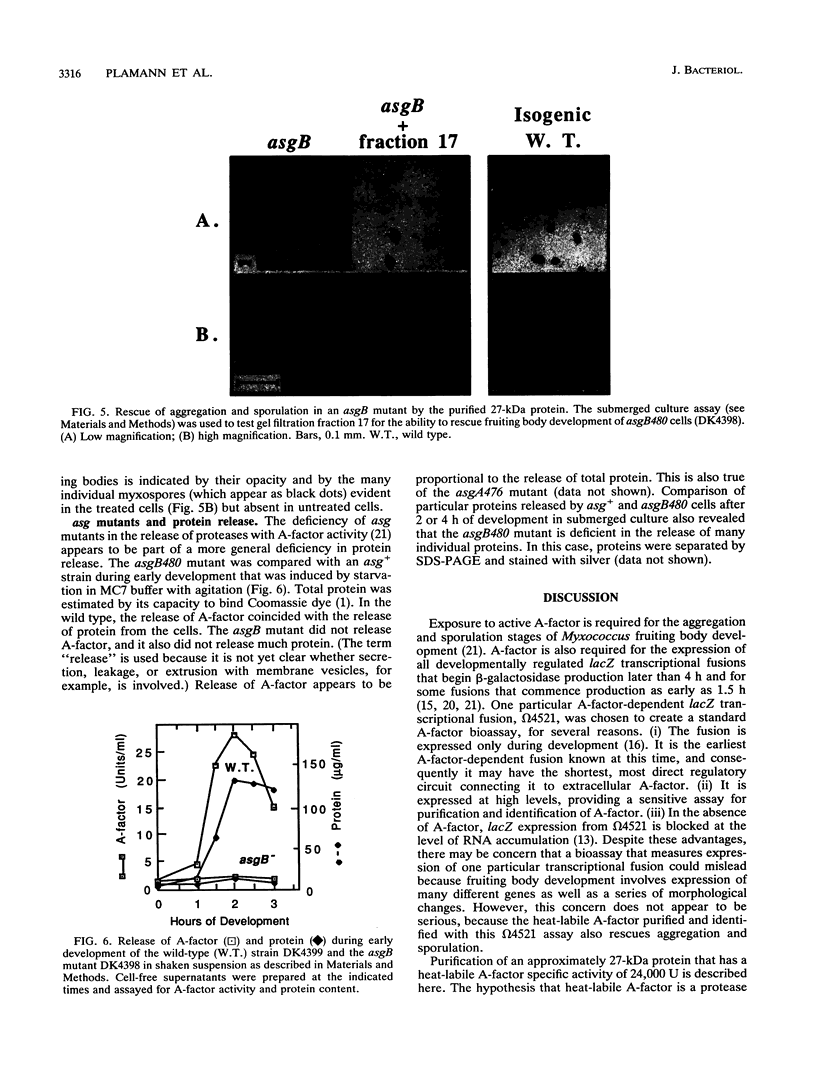
The asg mutants of Myxococcus xanthus are defective in the production of an extracellular substance, called A-factor, that is required for expression of a set of fruiting body-specific genes. A-factor is released by wild-type cells (asg+) after 1 to 2 h of development. When A-factor is added to asg mutant cells, it restores expression of their A-factor-dependent genes. Rescue of beta-galactosidase production in an asg mutant carrying the A-factor-dependent lacZ transcriptional fusion (omega 4521) was used to assay A-factor activity. According to this assay, two types of substances with A-factor activity are present in conditioned medium. One type is heat stable and of low molecular weight; the other is heat labile and of high molecular weight. An approximately 27-kDa protein with heat-labile A-factor activity was purified from conditioned medium. The purified protein has proteolytic activity as well as A-factor activity. The substrate specificity of the 27-kDa protease resembles that of trypsin. A smaller protein with both heat-labile A-factor activity and proteolytic activity was identified. Its substrate specificity differs from that of the 27-kDa protein. In addition, trypsin and other proteases were found to have heat-labile A-factor activity. Trypsin inhibitory protein from soybeans neutralizes the A-factor activity of trypsin in parallel with its neutralization of protease activity, showing that the proteolytic activity of trypsin is necessary for its A-factor activity. The 27-kDa protein rescues the aggregation and sporulation defects of an asgB mutant in submerged culture as well as its ability to express beta-galactosidase from an asg-dependent lac fusion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filloux A., Bally M., Ball G., Akrim M., Tommassen J., Lazdunski A. Protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria: transport across the outer membrane involves common mechanisms in different bacteria. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4323–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., Dworkin M. Cell surface antigens during submerged development of Myxococcus xanthus examined with monoclonal antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.505-511.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., Dworkin M. Isolation of additional monoclonal antibodies directed against cell surface antigens of Myxococcus xanthus cells undergoing submerged development. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5953–5955. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5953-5955.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnosspelius G. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease from Myxococcus virescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.17-25.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus: pattern of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Kroos L., Kuspa A. Cell interactions govern the temporal pattern of Myxococcus development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:823–830. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Suppressors that permit A-signal-independent developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1460–1470. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1460-1470.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Genes required for developmental signalling in Myxococcus xanthus: three asg loci. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2762-2772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Plamann L., Kaiser D. Identification of heat-stable A-factor from Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3319–3326. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3319-3326.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R., Kuner J., Hagen D., Manoil C., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions of Myxococcus xanthus: analysis of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1394–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1394-1404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeba P. Y. Iodination of Myxococcus xanthus during development. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1033-1041.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeba P. Y. Isolation of a surface glycoprotein from Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):644–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.644-650.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]