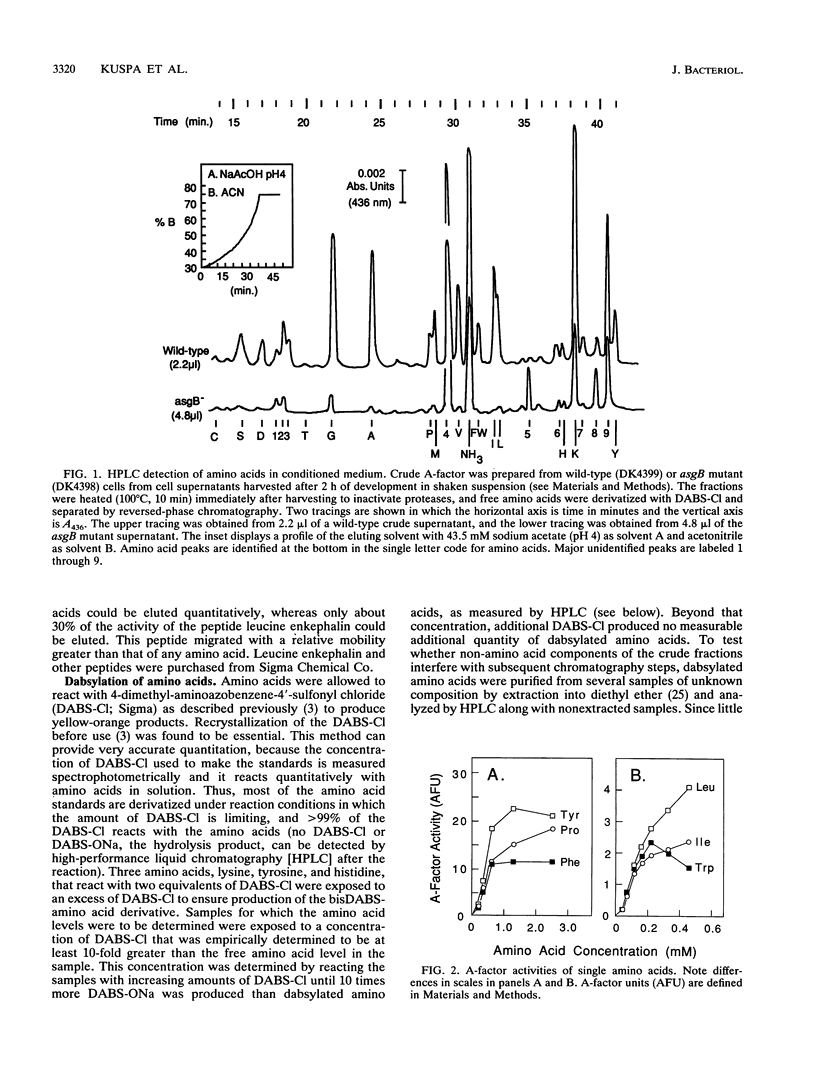
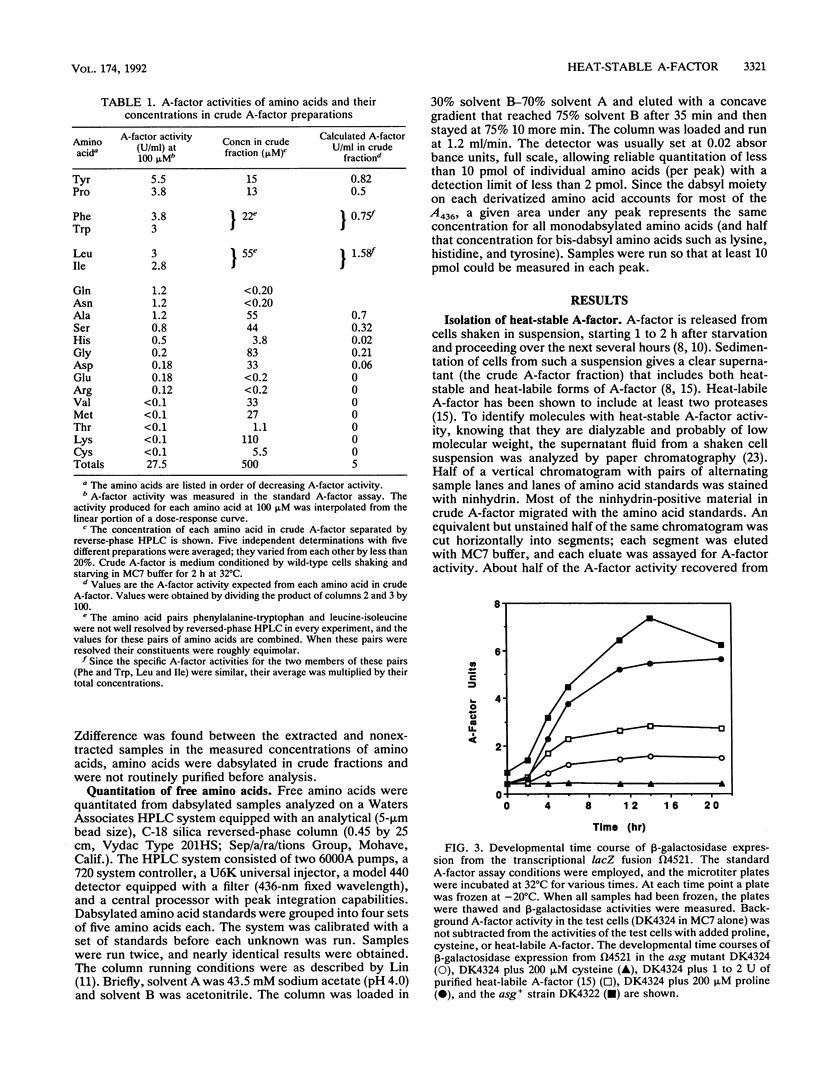
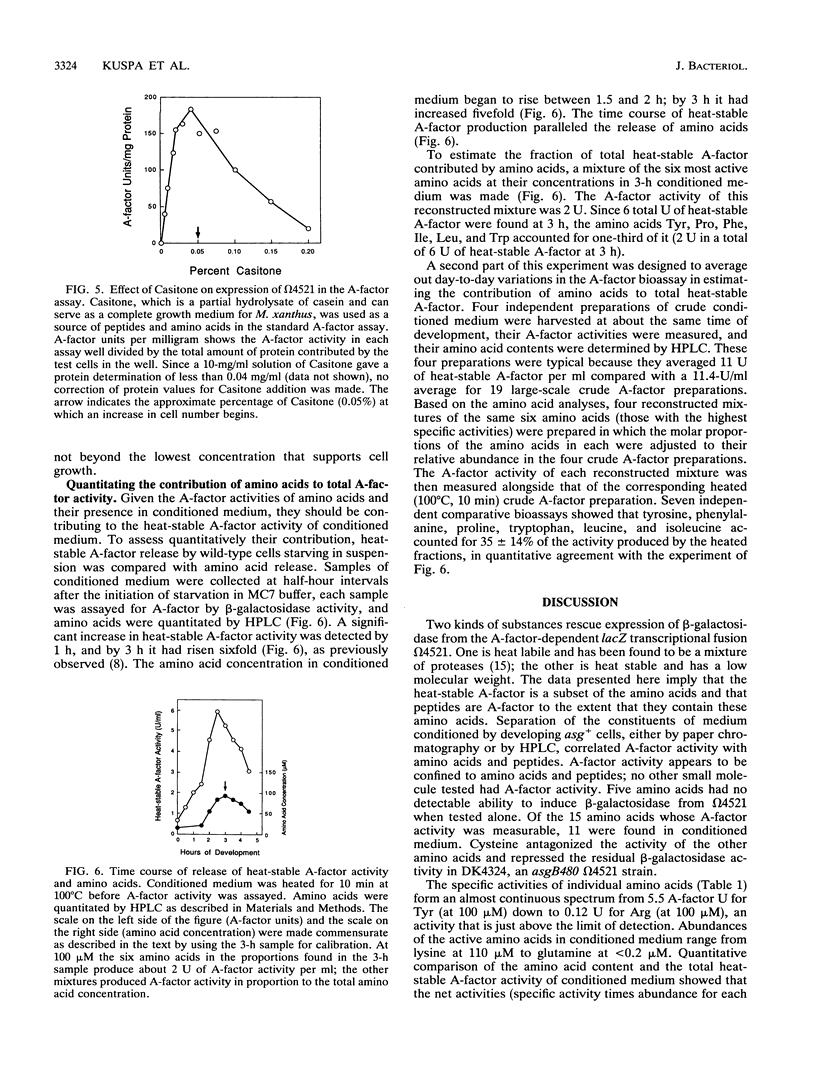
Abstract
The asg mutants of Myxococcus xanthus fail to produce a set of related substances called A-factor. A-factor is released into the medium and is required early in fruiting body development. Lacking A-factor, the asg mutants are defective in aggregation, sporulation, and expression of most genes whose products appear later than 1 h after development is induced by starvation. Previous work has shown that these defects are reversed when A-factor, released by developing wild-type cells, is added to asg mutant cells. Part of the material in conditioned medium with A-factor activity is heat stable and dialyzable. This low-molecular-weight A-factor consists of a mixture of amino acids and peptides. Fifteen single amino acids have A-factor activity, and 11 of these are found in conditioned medium. Mixtures of amino acids have a total activity approximately equal to the sum of the activities of their constituents. Conditioned medium also contains peptides with A-factor activity. Pure peptides have A-factor activity, and their specific activities are equal to or less than the sum of the activities of their constituent amino acids. There is no evidence for a specialized A-factor peptide in conditioned medium, one with a specific activity greater than the sum of its constituent amino acids. About half of the heat-stable A-factor activity in conditioned medium can be accounted for by free amino acids, and the remaining half can be accounted for by peptides. It is argued that heat-stable A-factor induces A-dependent gene expression not by the nutritional action of amino acids but through a chemosensory circuit.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y., Knecht R., Braun D. G. Amino acid analysis in the picomole range by precolumn derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:41–48. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Suppressors that permit A-signal-independent developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1460–1470. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1460-1470.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. A global analysis of developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):252–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Genes required for developmental signalling in Myxococcus xanthus: three asg loci. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2762-2772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Blank V., Brade G., Higgins C. F. Peptide chemotaxis in E. coli involves the Tap signal transducer and the dipeptide permease. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):253–256. doi: 10.1038/321253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Higgins C. F., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Hoch J. A. The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Proteins that rescue A-signal-defective mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3311–3318. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3311-3318.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Keller K. H., Dworkin M. Cell density-dependent growth of Myxococcus xanthus on casein. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):770–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.770-777.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfelder G., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Composition of lipopolysaccharides from Myxococcus fulvus and other fruiting and non-fruiting myxobacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Dworkin M. Excreted adenosine is a cell density signal for the initiation of fruiting body formation in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Murein components rescue developmental sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):462–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.462-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W., Thomson S. Comparison of polysaccharides produced by Myxococcus strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):124–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


