Abstract
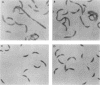
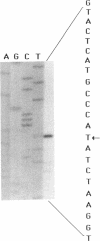
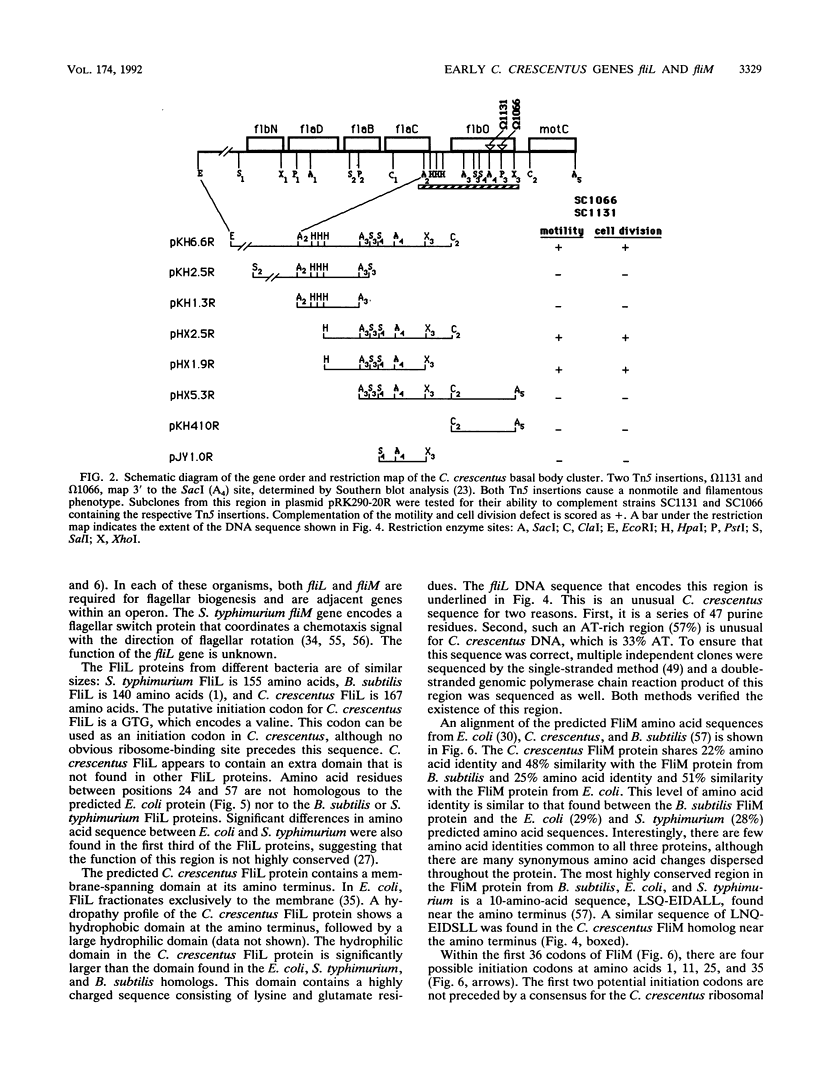
The biogenesis of the Caulobacter crescentus polar flagellum requires the expression of more than 48 genes, which are organized in a regulatory hierarchy. The flbO locus is near the top of the hierarchy, and consequently strains with mutations in this locus are nonmotile and lack the flagellar basal body complex. In addition to the motility phenotype, mutations in this locus also cause abnormal cell division. Complementing clones restore both motility and normal cell division. Sequence analysis of a complementing subclone revealed that this locus encodes at least two proteins that are homologs of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli flagellar proteins FliL and FliM. FliM is thought to be a switch protein and to interface with the flagellum motor. The C. crescentus fliL and fliM genes form an operon that is expressed early in the cell cycle. Tn5 insertions in the fliM gene prevent the transcription of class II and class III flagellar genes, which are lower in the regulatory hierarchy. The start site of the fliLM operon lies 166 bp from the divergently transcribed flaCBD operon that encodes several basal body genes. Sequence comparison of the fliL transcription start site with those of other class I genes, flaS and flaO, revealed a highly conserved 29-bp sequence in a potential promoter region that differs from sigma 70, sigma 54, sigma 32, and sigma 28 promoter sequences, suggesting that at least three class I genes share a unique 5' regulatory region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Caramori T., Crabb W. D., Scoffone F., Galizzi A. The flaA locus of Bacillus subtilis is part of a large operon coding for flagellar structures, motility functions, and an ATPase-like polypeptide. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3573–3579. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3573-3579.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley M. R., Gomes S. L., Alexander W., Shapiro L. Genetic analysis of a temporally transcribed chemotaxis gene cluster in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):333–341. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champer R., Bryan R., Gomes S. L., Purucker M., Shapiro L. Temporal and spatial control of flagellar and chemotaxis gene expression during Caulobacter cell differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:831–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champer R., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Cascade regulation of Caulobacter flagellar and chemotaxis genes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90716-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall A., Gober J. W., Shapiro L. Identification of a Caulobacter basal body structural gene and a cis-acting site required for activation of transcription. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6066–6076. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6066-6076.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall A., Zhuang W. Y., Quon K., Shapiro L. Expression of an early gene in the flagellar regulatory hierarchy is sensitive to an interruption in DNA replication. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1760–1768. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1760-1768.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederikse P. H., Shapiro L. An Escherichia coli chemoreceptor gene is temporally controlled in Caulobacter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen K. L., Hughes K. T. Molecular characterization of flgM, a gene encoding a negative regulator of flagellin synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6453–6459. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6453-6459.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen K. L., Hughes K. T. Negative regulatory loci coupling flagellin synthesis to flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2301–2310. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2301-2310.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Alley M. R., Shapiro L. Positional information during Caulobacter cell differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):324–329. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Champer R., Reuter S., Shapiro L. Expression of positional information during cell differentiation of Caulobacter. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90646-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Shapiro L. Integration host factor is required for the activation of developmentally regulated genes in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1494–1504. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes S. L., Gober J. W., Shapiro L. Expression of the Caulobacter heat shock gene dnaK is developmentally controlled during growth at normal temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3051–3059. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3051-3059.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Shapiro L. Identification of a gene cluster involved in flagellar basal body biogenesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90718-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ely B. Isolation of spontaneously derived mutants of Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1977 May;86(1):25–32. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium: analysis with temperature-sensitive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1327–1339. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1327-1339.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. B., Dingwall A., Bryan R., Champer R., Shapiro L. Temporal regulation and overlap organization of two Caulobacter flagellar genes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90365-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Homma M., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M. Flagellar switch of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3247–3257. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3247-3257.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Fusions of flagellar operons to lactose genes on a mu lac bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):16–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.16-26.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Suzuki H., Ishidsu J. I., Iino T. The role of cAMP in flagellation of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 31;142(4):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00271253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Sequence of the flaA (cheC) locus of Escherichia coli and discovery of a new gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1007–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1007-1012.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Ohya Y., Iino T. Transcriptional analysis of the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.741-747.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy B., Marczynski G. T., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Regulatory interactions between phospholipid synthesis and DNA replication in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5523–5530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5523-5530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy Z. G., Bryan R. A., Reuter S. H., Shapiro L. Control of synthesis and positioning of a Caulobacter crescentus flagellar protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):626–635. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magariyama Y., Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S. Genetic and behavioral analysis of flagellar switch mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4359–4369. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4359-4369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakooti J., Komeda Y., Matsumura P. DNA sequence analysis, gene product identification, and localization of flagellar motor components of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2728–2734. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2728-2734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D. A., Newton A. Ntr-like promoters and upstream regulatory sequence ftr are required for transcription of a developmentally regulated Caulobacter crescentus flagellar gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3218–3227. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3218-3227.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D., Minnich S., Chen L. S., Newton A. A set of positively regulated flagellar gene promoters in Caulobacter crescentus with sequence homology to the nif gene promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):939–943. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N., Ramakrishnan G., Mullin D., Raymond G. Genetic switching in the flagellar gene hierarchy of Caulobacter requires negative as well as positive regulation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6651–6655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N. Regulation of the cell division cycle and differentiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:689–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Kutsukake K., Suzuki H., Iino T. Gene fliA encodes an alternative sigma factor specific for flagellar operons in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00261713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter S. H., Shapiro L. Asymmetric segregation of heat-shock proteins upon cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenlein P. V., Gallman L. S., Winkler M. E., Ely B. Nucleotide sequence of the Caulobacter crescentus flaF and flbT genes and an analysis of codon usage in organisms with G + C-rich genomes. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90130-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Gober J. W. Positioning of gene products during Caulobacter cell differentiation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:85–97. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Characterization of Escherichia coli flagellar mutants that are insensitive to catabolite repression. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1196–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1196-1203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbiah S., Harrison S. C. A method for multiple sequence alignment with gaps. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90592-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuberi A. R., Bischoff D. S., Ordal G. W. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis gene encoding a flagellar switch protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):710–719. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.710-719.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]