Abstract
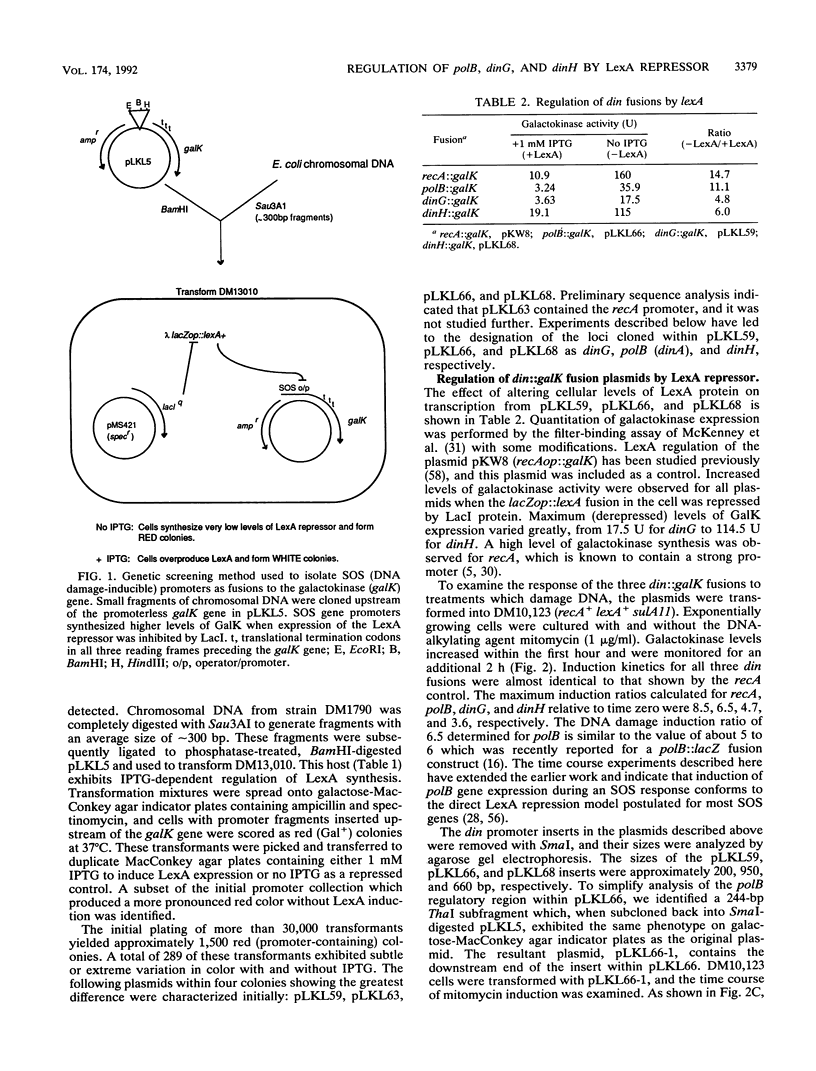
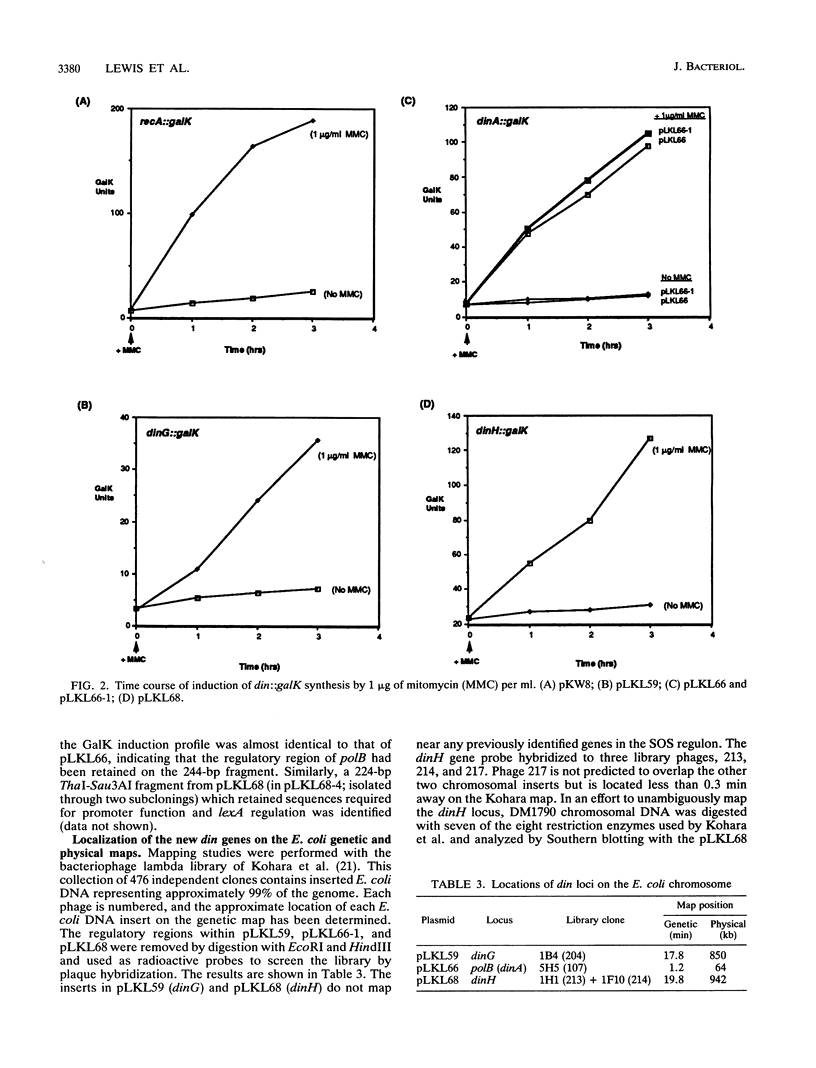
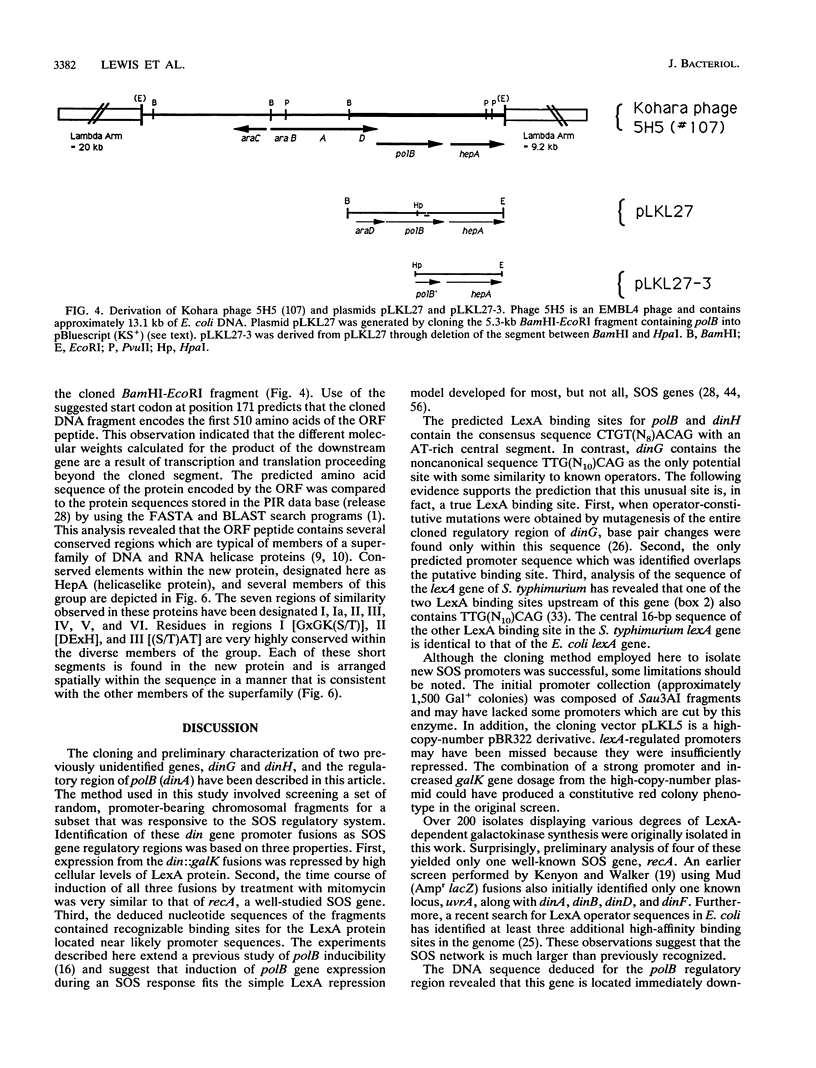
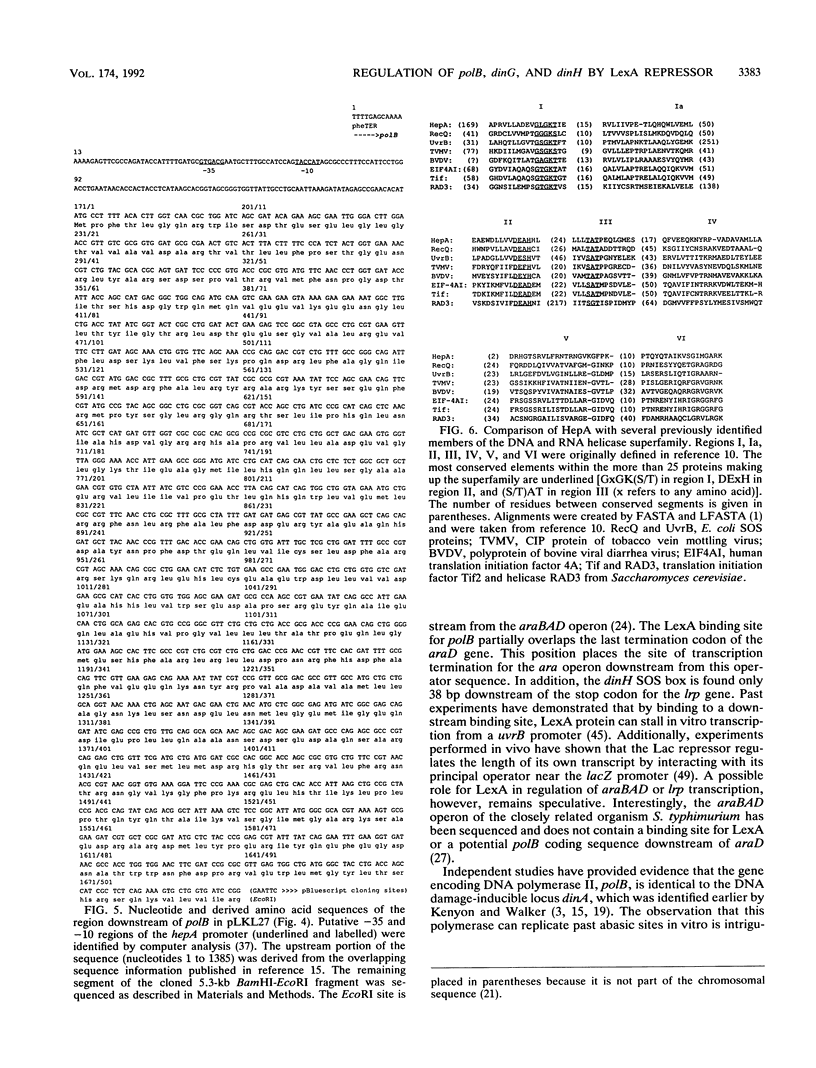
A new genetic screening method has been developed to isolate Escherichia coli promoters which are components of the SOS regulon. Plasmids containing the regulatory regions of polB (dinA) and two new loci, dinG and dinH, were characterized. Galactokinase gene fusion experiments indicated that transcription of these genes is inducible by treatment with mitomycin and conforms to a classical model of SOS regulation involving simple LexA repression. Mapping studies using the E. coli DNA library of Kohara et al. (Y. Kohara, K. Akiyama, and K. Isono, Cell 50:495-508, 1987) revealed that dinG and dinH are located at 17.8 and 19.8 min on the chromosome, respectively. The nucleotide sequence of the dinH regulatory region contains a segment which is very similar to previously characterized binding sites for LexA protein. An asymmetric, noncanonical 20-bp LexA operator in the cloned dinG promoter region was identified. Additional experiments have revealed that the nucleotide sequence of the gene immediately downstream of the DNA damage-inducible polB locus encodes a polypeptide which has extensive sequence homology to several known and putative DNA and RNA helicase proteins. This gene, which is not regulated by the LexA repressor, has been designated hepA. The predicted amino acid sequence of the product of hepA contains several highly conserved sequence motifs that are also found in enzymes such as the RecQ and UvrB proteins of E. coli and the Rad3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins: the LexA protein and the arginine repressor use different strategies for functional specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5089–5105. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner C. A., Hays S., McEntee K., Goodman M. F. DNA polymerase II is encoded by the DNA damage-inducible dinA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7663–7667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner C. A., Randall S. K., Rayssiguier C., Radman M., Eritja R., Kaplan B. E., McEntee K., Goodman M. F. Purification and characterization of an inducible Escherichia coli DNA polymerase capable of insertion and bypass at abasic lesions in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18946–18952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaregola S., D'Ari R., Huisman O. Quantitative evaluation of recA gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):430–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00334135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Belin D., Nagamine Y. A pSC101-derived plasmid which shows no sequence homology to other commonly used cloning vectors. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Chambers P., Emmerson P. T. Identification of the Escherichia coli recN gene product as a major SOS protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):653–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.653-658.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. Superfamily of UvrA-related NTP-binding proteins. Implications for rational classification of recombination/repair systems. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):583–591. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger-Schnarr M., Schnarr M., van Sluis C. A. In vitro study of the interaction of the LexA repressor and the UvrC protein with a uvrC regulatory region. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 17;198(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Yamamoto K., Ohnishi T. Induction of phr gene expression by irradiation of ultraviolet light in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):200–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00329860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino N., Nakayama K., Nakayama H. The recQ gene of Escherichia coli K12: primary structure and evidence for SOS regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):298–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00430442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H., Ishino Y., Toh H., Nakata A., Shinagawa H. Escherichia coli DNA polymerase II is homologous to alpha-like DNA polymerases. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):24–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00273583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H., Nakata A., Walker G. C., Shinagawa H. The Escherichia coli polB gene, which encodes DNA polymerase II, is regulated by the SOS system. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6268–6273. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6268-6273.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaasch M., Kaasch J., Quiñones A. Expression of the dnaN and dnaQ genes of Escherichia coli is inducible by mitomycin C. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00261175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Brent R., Ptashne M., Walker G. C. Regulation of damage-inducible genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. DNA-damaging agents stimulate gene expression at specific loci in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B., Little J. W. Dimerization of a specific DNA-binding protein on the DNA. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.1553548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamerichs R. M., Padilla A., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Ottleben G., Rüterjans H., Granger-Schnarr M., Oertel P., Schnarr M. The amino-terminal domain of LexA repressor is alpha-helical but differs from canonical helix-turn-helix proteins: a two-dimensional 1H NMR study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6863–6867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont I., Brumby A. M., Egan J. B. UV induction of coliphage 186: prophage induction as an SOS function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Gielow W., Martin R., Hamilton E., Fowler A. The organization of the araBAD operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Lei S. P., Studnicka G., Wilcox G. The araBAD operon of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. III. Nucleotide sequence of araD and its flanking regions, and primary structure of its product, L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase. Gene. 1985;34(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90303-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham B. E., Harper J. E., Mount D. W., Sancar G. B., Sancar A., Rupp W. D., Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. Analysis of mRNA synthesis following induction of the Escherichia coli SOS system. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Christman M. F., Jacobson F. S., Storz G., Ames B. N. Hydrogen peroxide-inducible proteins in Salmonella typhimurium overlap with heat shock and other stress proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8059–8063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers E. W., Mount D. W. Computer program for the IBM personal computer which searches for approximate matches to short oligonucleotide sequences in long target DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):501–508. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Consensus methods for finding and ranking DNA binding sites. Application to Escherichia coli promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Escherichia coli promoters. I. Consensus as it relates to spacing class, specificity, repeat substructure, and three-dimensional organization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5522–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Training back-propagation neural networks to define and detect DNA-binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):313–318. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. S., Sancar A. The LexA protein does not bind specifically to the two SOS box-like sequences immediately 5' to the phr gene. Mutat Res. 1989 Nov;218(3):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Ossanna N., Mount D. W. The Escherichia coli K-12 lexA2 gene encodes a hypocleavable repressor. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1975–1977. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1975-1977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. R., Ossanna N., Thliveris A. T., Ennis D. G., Mount D. W. Derepression of specific genes promotes DNA repair and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.1-4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Roger I., García-Sogo M., Navarro-Aviñ J. P., López-Acedo C., Macián F., Armengod M. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the dnaA-dnaN-recF operon of Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1991 Feb-Mar;73(2-3):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90220-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiñones A., Jüterbock W. R., Messer W. Expression of the dnaA gene of Escherichia coli is inducible by DNA damage. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;227(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00260699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Weisemann J. M., Weinstock G. M. Temporal control of colicin E1 induction. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5028–5034. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5028-5034.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Sancar A., Little J. W., Rupp W. D. The uvrB gene of Escherichia coli has both lexA-repressed and lexA-independent promoters. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Roberts J. W. Nature of the SOS-inducing signal in Escherichia coli. The involvement of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):79–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarr M., Oertel-Buchheit P., Kazmaier M., Granger-Schnarr M. DNA binding properties of the LexA repressor. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90109-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarr M., Pouyet J., Granger-Schnarr M., Daune M. Large-scale purification, oligomerization equilibria, and specific interaction of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2812–2818. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitti M. A., Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. lac repressor blocks in vivo transcription of lac control region DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Arany Z., Orrego C., Eisenstadt E. DNA damage-inducible loci in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3587–3590. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3587-3590.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark T., Moses R. E. Interaction of the LexA repressor and the uvrC regulatory region. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):39–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thliveris A. T., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Repression of the E coli recA gene requires at least two LexA protein monomers. Biochimie. 1991 Apr;73(4):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90112-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Kelley P. M., Neidhardt F. C. Differential induction of heat shock, SOS, and oxidation stress regulons and accumulation of nucleotides in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.26-32.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Rapid mutational analysis of regulatory loci in Escherichia coli K-12 using bacteriophage M13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3801–3805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertman K. F., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence binding specificity of the LexA repressor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.376-384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Weiss B. Two divergently transcribed genes, soxR and soxS, control a superoxide response regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2864–2871. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2864-2871.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



