Abstract
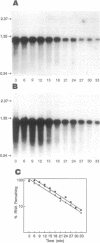
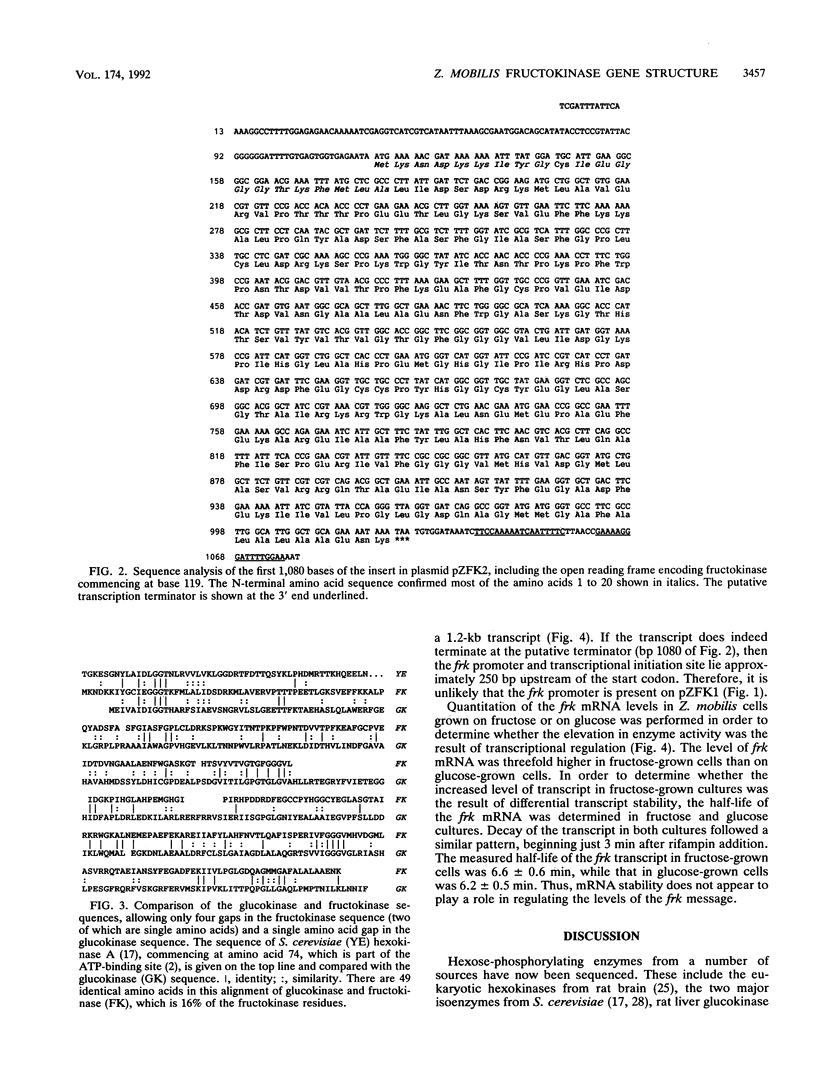
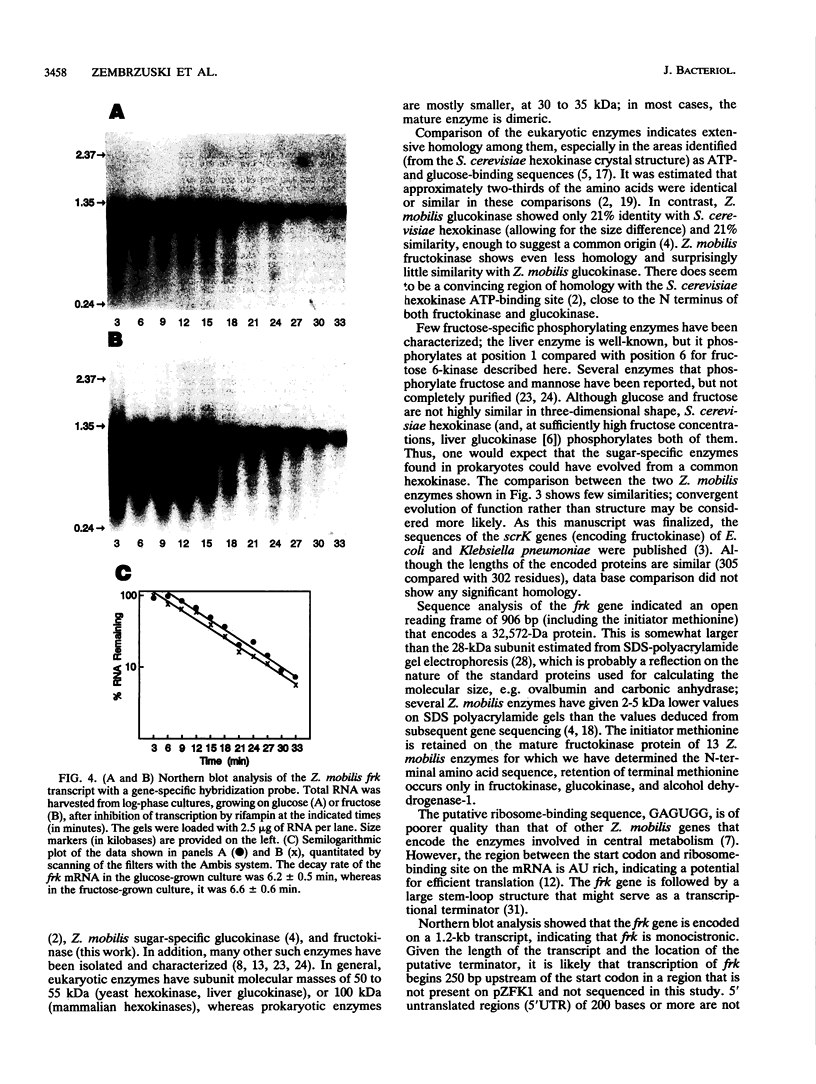
The frk gene encoding the enzyme fructokinase (fructose 6-phosphotransferase [EC 2.7.1.4]) from Zymomonas mobilis has been isolated on a partial TaqI digest fragment of the genome and sequenced. An open reading frame of 906 bp corresponding to 302 amino acids was identified on a 3-kbp TaqI fragment. The deduced amino acid sequence corresponds to the first 20 amino acids (including an N-terminal methionine) determined by amino acid sequencing of the purified protein. The 118 bp preceding the methionine codon on this fragment does not appear to contain a promoter sequence. There was weak expression of the active enzyme in the recombinant Escherichia coli clone under control of the lac promoter on the pUC plasmid. Comparison of the amino acid sequence with that of the glucokinase enzyme (EC 2.7.1.2) from Z. mobilis reveals relatively little homology, despite the fact that fructokinase also binds glucose and has kinetic and structural properties similar to those of glucokinase. Also, there is little homology with hexose kinases that have been sequenced from other organisms. Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that the frk transcript is 1.2 kb long. Fructokinase activity is elevated up to twofold when Z. mobilis was grown on fructose instead of glucose, and there was a parallel increase in frk mRNA levels. Differential mRNA stability was not a factor, since the half-lives of the frk transcript were 6.2 min for glucose-grown cells and 6.6 min for fructose-grown cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreone T. L., Printz R. L., Pilkis S. J., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. The amino acid sequence of rat liver glucokinase deduced from cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulkemeyer P., Ebner R., Heilenmann G., Jahreis K., Schmid K., Wrieden S., Lengeler J. W. Molecular analysis of two fructokinases involved in sucrose metabolism of enteric bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2913–2922. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnell W. O., Yi K. C., Conway T. Sequence and genetic organization of a Zymomonas mobilis gene cluster that encodes several enzymes of glucose metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7227–7240. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7227-7240.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. S., Jr, Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex between yeast hexokinase A and glucose. II. Detailed comparisons of conformation and active site configuration with the native hexokinase B monomer and dimer. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 25;140(2):211–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas M. L., Rabajille E., Niemeyer H. Fructose is a good substrate for rat liver 'glucokinase' (hexokinase D). Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2220363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvalle J. A., Asensio C. Distribution of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-dependent hexose kinases in microorganisms. Biosystems. 1978 Aug;10(3):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarco A. A., Romano A. H. d-Glucose Transport System of Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.151-157.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goward C. R., Hartwell R., Atkinson T., Scawen M. D. The purification and characterization of glucokinase from the thermophile Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):415–420. doi: 10.1042/bj2370415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran P., Karunakaran T., Cami B., Mukundan A. G., Preziosi L., Baratti J. Cloning and sequencing of the sacA gene: characterization of a sucrase from Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6727–6735. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6727-6735.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesman T. L., Barnell W. O., Conway T. Cloning, characterization, and nucleotide sequence analysis of a Zymomonas mobilis phosphoglucose isomerase gene that is subject to carbon source-dependent regulation. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3215–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3215-3223.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopetzki E., Entian K. D., Mecke D. Complete nucleotide sequence of the hexokinase PI gene (HXK1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;39(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie K. F., Conway T., Aldrich H. C., Ingram L. O. Expression of Zymomonas mobilis adhB (encoding alcohol dehydrogenase II) and adhB-lacZ operon fusions in recombinant Z. mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4577–4582. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4577-4582.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F., Ureta T. Amino acid sequence homology between yeast hexokinases and rat hexokinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):714–719. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale A. D., Scopes R. K., Wettenhall R. E., Hoogenraad N. J. Pyruvate decarboxylase of Zymomonas mobilis: isolation, properties, and genetic expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1024–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1024-1028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter E. V., Chassy B. M., Holmlund C. E. Partial purification and properties of a mannofructokinase from Streptococcus mutans SL-1. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.43-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico V., Anderson R. L. An adenosine 5'-triphosphate:hexose 6-phosphotransferase specific for D-mannose and D-fructose from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Purification, properties, and evidence for a single enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5086–5092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab D. A., Wilson J. E. Complete amino acid sequence of rat brain hexokinase, deduced from the cloned cDNA, and proposed structure of a mammalian hexokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2563–2567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. Purification of glycolytic enzymes by using affinity-elution chromatography. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):253–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1610253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K., Testolin V., Stoter A., Griffiths-Smith K., Algar E. M. Simultaneous purification and characterization of glucokinase, fructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):627–634. doi: 10.1042/bj2280627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachelek C., Stachelek J., Swan J., Botstein D., Konigsberg W. Identification, cloning and sequence determination of the genes specifying hexokinase A and B from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):945–963. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swings J., De Ley J. The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):1–46. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.1-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase H., Fukushi H., Ueda N., Maeda Y., Toyoda A., Tonomura K. Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the intracellular invertase gene from Zymomonas mobilis. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 May;55(5):1383–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachariou M., Scopes R. K. Glucose-fructose oxidoreductase, a new enzyme isolated from Zymomonas mobilis that is responsible for sorbitol production. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.863-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]