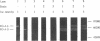Abstract
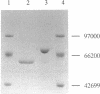
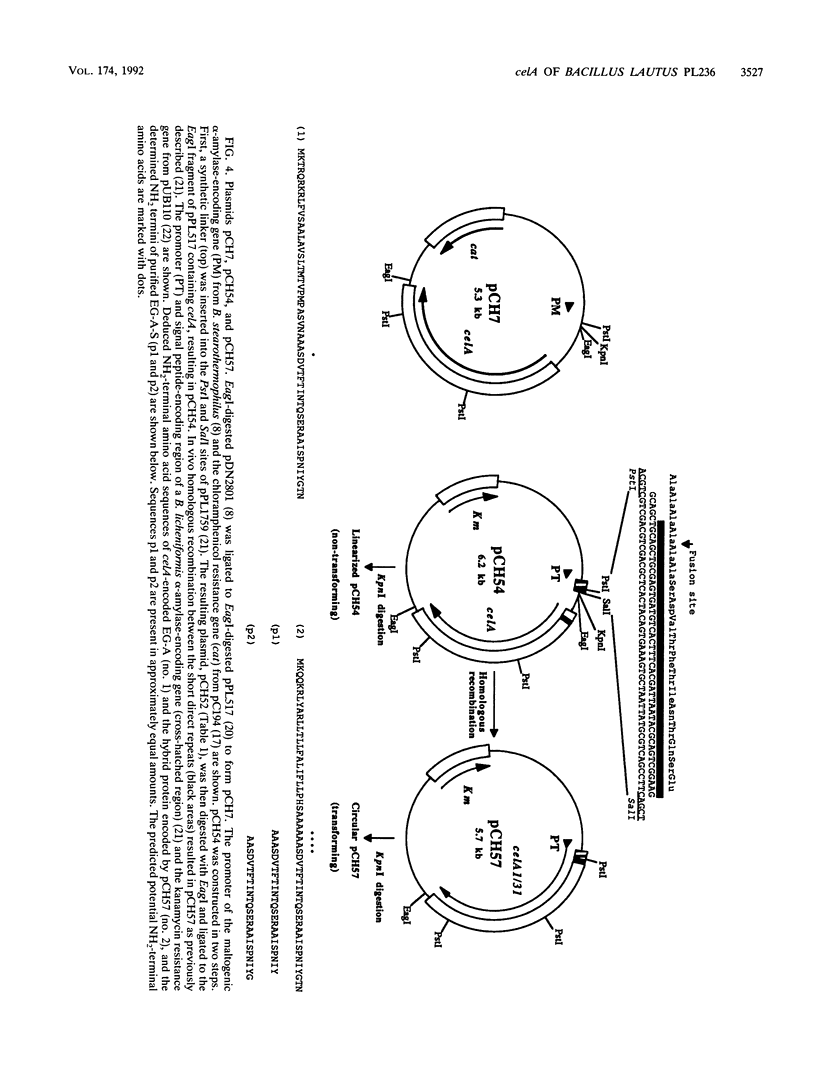
celA from the cellulolytic bacterium Bacillus lautus PL236 encodes EG-A, an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase. An open reading frame of 2,100 bp preceded by a ribosome-binding site encodes a protein with a molecular mass of 76,863 Da with a typical signal sequence. The NH2-terminal active domain of EG-A is not homologous to any reported cellulase or xylanase and may represent a new family of such enzymes. A 150-amino-acid COOH-terminal peptide is homologous to noncatalytic domains in several other cellulases (A. Meinke, N.R. Gilkes, D.G. Kilburn, R.C. Miller, Jr., and R.A.J. Warren, J. Bacteriol. 173:7126-7135, 1991). Upstream of celA, a partial open reading frame encodes a 145-amino-acid peptide which also belongs to the family mentioned. Zymogram analysis of extracts from Escherichia coli and supernatants of Bacillus subtilis and B. megaterium, including protease-deficient mutants thereof, which express celA, revealed two active proteins, EG-A-L and EG-A-S, with Mrs of 74,000 and 57,000, respectively. The proportion of EG-A-L to EG-A-S depends on the extracellular proteolytic activity of the host organism, indicating that EG-A-S arises from posttranslational proteolytic modification of EG-A-L. Since EG-A-S has an NH2 terminus corresponding to the predicted NH2-terminal sequence of EG-A, processing appears to take place between the catalytic and noncatalytic domains described. EG-A-L and EG-A-S were purified to homogeneity and shown to have almost identical characteristics with respect to activity against soluble substrates and pH and temperature dependency. EG-A-L binds strongly to cellulose, in contrast to EG-A-S, and has higher activity against insoluble substrates than the latter. We conclude that the COOH-terminal 17,000-Mr peptide of EG-A-L constitutes a cellulose-binding domain.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P., Cornet P., Aubert J. P. Sequence of a cellulase gene of the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):102–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.102-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. L., 3rd, Wang L. F., Doi R. H., Moran C. P., Jr rpoD operon promoter used by sigma H-RNA polymerase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1617–1621. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1617-1621.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diderichsen B., Wedsted U., Hedegaard L., Jensen B. R., Sjøholm C. Cloning of aldB, which encodes alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase, an exoenzyme from Bacillus brevis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4315–4321. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4315-4321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D. Replication and expression of plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1680–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaboriaud C., Bissery V., Benchetrit T., Mornon J. P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: an efficient new way to compare and analyse amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Henrissat B., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Domains in microbial beta-1, 4-glycanases: sequence conservation, function, and enzyme families. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):303–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.303-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Warren R. A., Miller R. C., Jr, Kilburn D. G. Precise excision of the cellulose binding domains from two Cellulomonas fimi cellulases by a homologous protease and the effect on catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10401–10407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wiggs J. L., Chamberlin M. J. Nucleotide sequences of two Bacillus subtilis promoters used by Bacillus subtilis sigma-28 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5991–6000. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B., Claeyssens M., Tomme P., Lemesle L., Mornon J. P. Cellulase families revealed by hydrophobic cluster analysis. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. T., White B. A. Molecular Cloning and Expression of Cellulase Genes from Ruminococcus albus 8 in Escherichia coli Bacteriophage lambda. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1752–1755. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1752-1755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauris S., Rücknagel K. P., Schwarz W. H., Kratzsch P., Bronnenmeier K., Staudenbauer W. L. Sequence analysis of the Clostridium stercorarium celZ gene encoding a thermoactive cellulase (Avicelase I): identification of catalytic and cellulose-binding domains. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(2):258–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00265062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen L., Hansen C. K., Poulsen G. B., Diderichsen B. In vivo genetic engineering: homologous recombination as a tool for plasmid construction. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90338-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Hansen C. K. Multiple endo-beta-1,4-glucanase-encoding genes from Bacillus lautus PL236 and characterization of the celB gene. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90135-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keggins K. M., Lovett P. S., Duvall E. J. Molecular cloning of genetically active fragments of Bacillus DNA in Bacillus subtilis and properties of the vector plasmid pUB110. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langsford M. L., Gilkes N. R., Singh B., Moser B., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A., Kilburn D. G. Glycosylation of bacterial cellulases prevents proteolytic cleavage between functional domains. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo A. C., MacKay R. M., Seligy V. L., Willick G. E. Bacillus subtilis beta-1,4-endoglucanase products from intact and truncated genes are secreted into the extracellular medium by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2287–2292. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2287-2292.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Lo A., Willick G., Zuker M., Baird S., Dove M., Moranelli F., Seligy V. Structure of a Bacillus subtilis endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9159–9170. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke A., Braun C., Gilkes N. R., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Unusual sequence organization in CenB, an inverting endoglucanase from Cellulomonas fimi. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.308-314.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke A., Gilkes N. R., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Multiple domains in endoglucanase B (CenB) from Cellulomonas fimi: functions and relatedness to domains in other polypeptides. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7126–7135. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7126-7135.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura A., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Nucleotide sequence of a cellulase gene of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 15;164(2):317–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro A., Chebrou M. C., Béguin P., Aubert J. P. Nucleotide sequence of the cellulase gene celF of Clostridium thermocellum. Res Microbiol. 1991 Nov-Dec;142(9):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owolabi J. B., Beguin P., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Warren R. A. Expression in Escherichia coli of the Cellulomonas fimi Structural Gene for Endoglucanase B. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):518–523. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.518-523.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva I., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Lehtovaara P., Sarvas M., Söderlund H., Takkinen K., Käriäinen L. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter and NH2-terminal signal peptide region of the alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Hay R. E., Ray G. L., Haldenwang W. G., Moran C. P., Jr Nucleotide sequences that define promoters that are used by Bacillus subtilis sigma-29 RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. M., Chambliss G. H. Endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene of Bacillus subtilis DLG. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2017–2025. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2017-2025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul D. J., Williams L. C., Love D. R., Chamley L. W., Bergquist P. L. Nucleotide sequence of a gene from Caldocellum saccharolyticum encoding for exocellulase and endocellulase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):439–439. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Ally A., Ally D., Pero J. Gene encoding a minor extracellular protease in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5557–5563. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5557-5563.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Rudolph C. F., Rufo G. A., Jr, Sullivan B. J., Theriault K. A., Ally D., Pero J. Gene encoding a novel extracellular metalloprotease in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1024–1029. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1024-1029.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloma A., Rufo G. A., Jr, Theriault K. A., Dwyer M., Wilson S. W., Pero J. Cloning and characterization of the gene for an additional extracellular serine protease of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6889–6895. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6889-6895.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Wood P. J. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.777-780.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Tersch M. A., Carlton B. C. Megacinogenic plasmids of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.872-877.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. C., Nathoo S., Pang A. S., Carne T., Wong S. L. Cloning, genetic organization, and characterization of a structural gene encoding bacillopeptidase F from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6845–6850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. Y., Ferrari E., Henner D. J. Cloning of the neutral protease gene of Bacillus subtilis and the use of the cloned gene to create an in vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.15-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]