Abstract
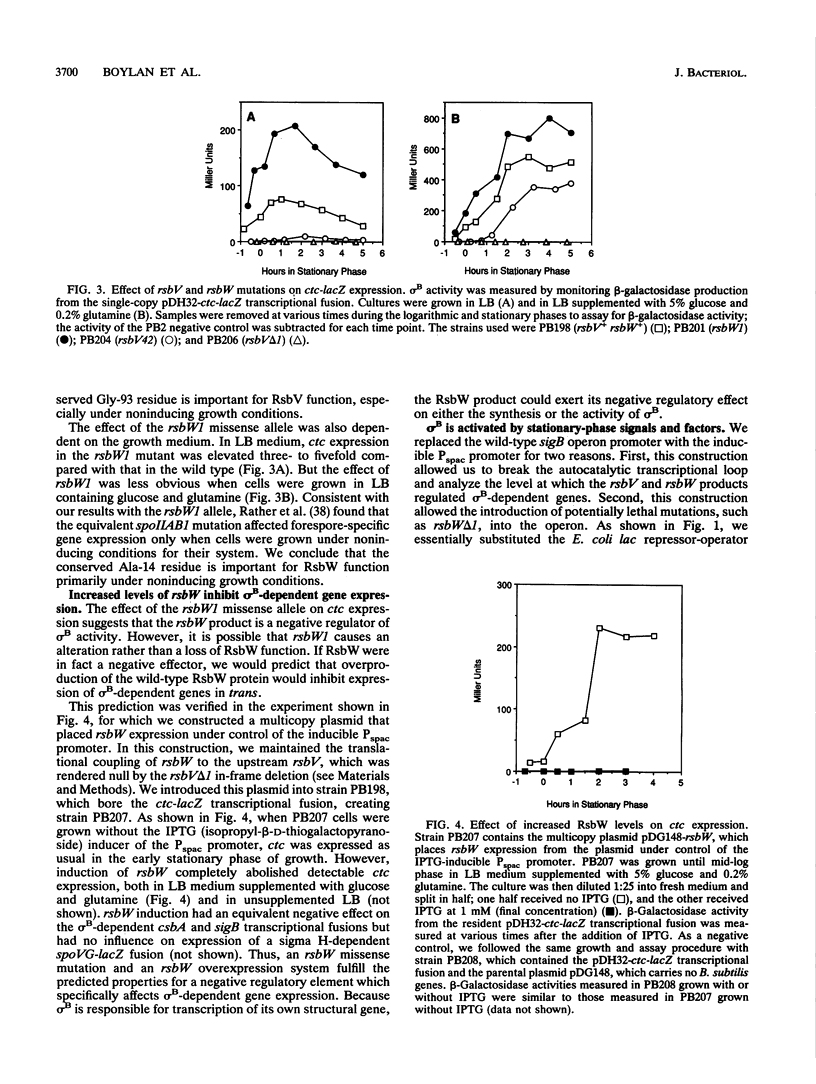
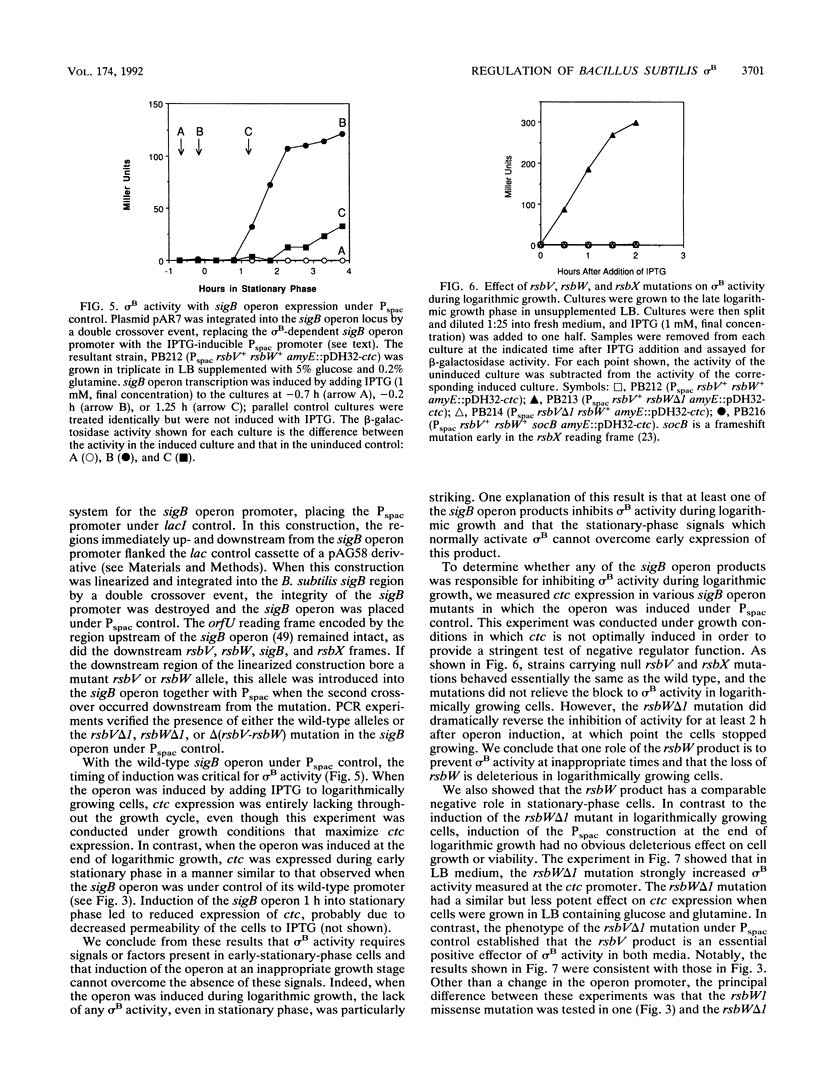
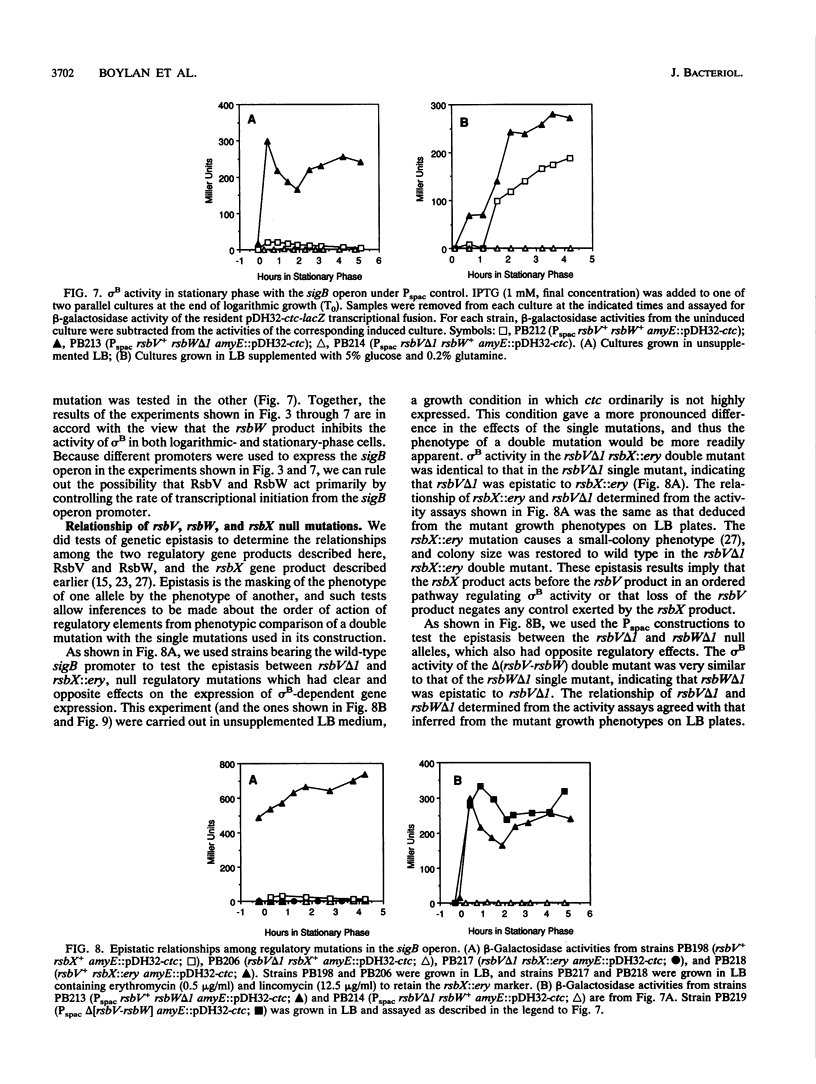
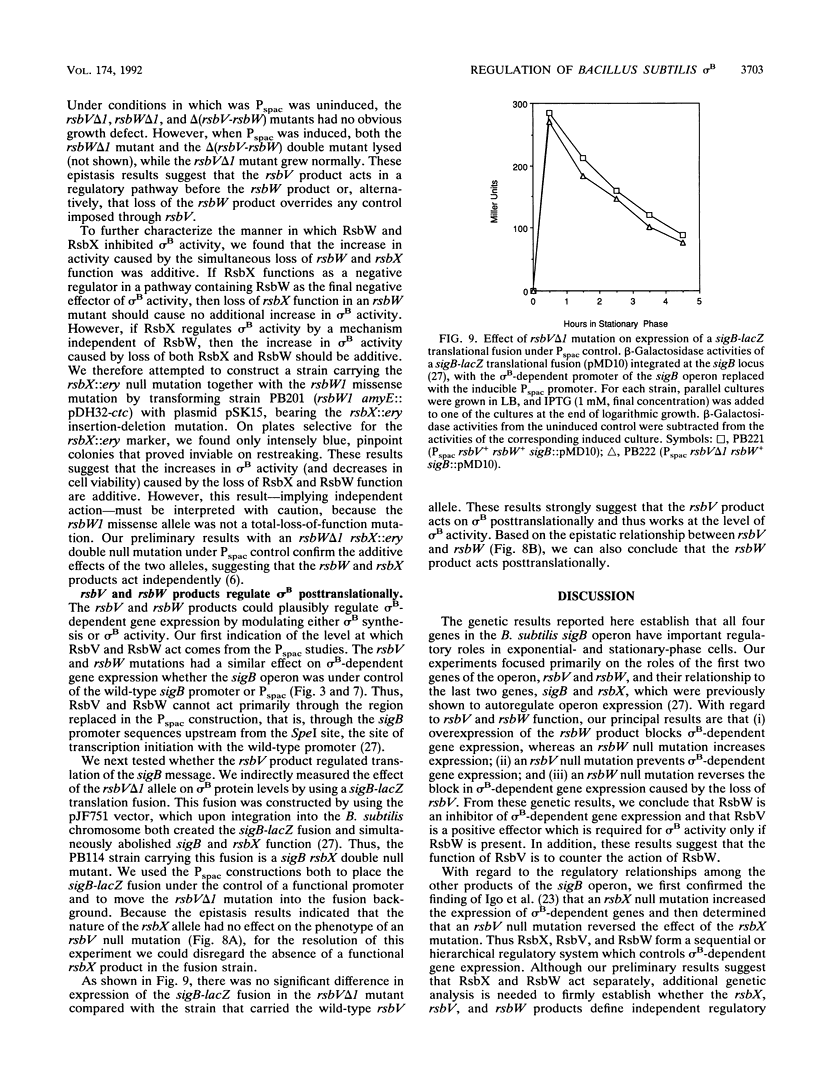
Alternative transcription factor sigma B of Bacillus subtilis controls a stationary-phase regulon induced under growth conditions that do not favor sporulation. Little is known about the metabolic signals and protein factors regulating the activity of sigma B. The operon containing the sigma B structural gene has the gene order orfV-orfW-sigB-rsbX, and operon expression is autoregulated positively by sigma B and negatively by the rsbX product (rsbX = regulator of sigma B). To establish the roles of the orfV and orfW products, orfV and orfW null and missense mutations were constructed and tested for their effects on expression of the sigma B-dependent genes ctc and csbA. These mutations were tested in two contexts: in the first, the sigB operon was under control of its wild-type, sigma B-dependent promoter, and in the second, the sigB operon promoter was replaced by the inducible Pspac promoter. The principal findings are that (i) the orfV (now called rsbV) product is a positive regulator of sigma B-dependent gene expression; (ii) the orfW (now called rsbW) product is a negative regultor of such expression; (iii) sigma B is inactive during logarithmic growth unless the rsbW product is absent; (iv) the rsbX, rsbV, and rsbW products have a hierarchical order of action; and (v) both the rsbV and rsbW products appear to regulate sigma B activity posttranslationally. There are likely to be at least two routes by which information can enter the system to regulate sigma B: via the rsbX product, and via the rsbV and rsbW products.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band L., Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis trpE and trpD genes. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. Characterization of a regulatory network that controls sigma B expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):749–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.749-757.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnie C., Lampe M., Losick R. Gene encoding the sigma 37 species of RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Chun K. T., Edson B. A., Price C. W. Early-blocked sporulation mutations alter expression of enzymes under carbon control in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00334696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Suh J. W., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Gene encoding the alpha core subunit of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase is cotranscribed with the genes for initiation factor 1 and ribosomal proteins B, S13, S11, and L17. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2553–2562. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2553-2562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Thomas M. D., Price C. W. Genetic method to identify regulons controlled by nonessential elements: isolation of a gene dependent on alternate transcription factor sigma B of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7856–7866. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7856-7866.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. L., 3rd, Moran C. P., Jr New RNA polymerase sigma factor under spo0 control in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9438–9442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. P., Prior S. E., Barstow D. A., Minton N. P. The pMTL nic- cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Oke V., Driks A., Losick R., Lu S., Kroos L. A forespore checkpoint for mother cell gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90362-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. L., Kalman S. S., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Gene encoding the 37,000-dalton minor sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase: isolation, nucleotide sequence, chromosomal locus, and cryptic function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.771-778.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Variety of sporulation phenotypes resulting from mutations in a single regulatory locus, spoIIA, in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2091–2101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J. Inducible expression of regulatory genes in Bacillus subtilis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:223–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85022-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pE194, a plasmid that specifies inducible resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin type B antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):804–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.804-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Losick R. Regulation of a promoter that is utilized by minor forms of RNA polymerase holoenzyme in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M., Lampe M., Ray C., Schafer W., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Genetic studies of a secondary RNA polymerase sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3464–3469. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3464-3469.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaacks K. J., Healy J., Losick R., Grossman A. D. Identification and characterization of genes controlled by the sporulation-regulatory gene spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4121–4129. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4121-4129.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman S., Duncan M. L., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Similar organization of the sigB and spoIIA operons encoding alternate sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5575–5585. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5575-5585.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kunkel B., Losick R. Switch protein alters specificity of RNA polymerase containing a compartment-specific sigma factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):526–529. doi: 10.1126/science.2492118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Establishment of cell type by compartmentalized activation of a transcription factor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1948031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattheakis L., Vu L., Sor F., Nomura M. Retroregulation of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins L14 and L24 by feedback repressor S8 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):448–452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Johnson W. C., Losick R. Close contacts between sigma 37-RNA polymerase and a Bacillus subtilis chromosomal promoter. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):709–713. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90399-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Losick R. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus subtilis promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase containing sigma 37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5979–5990. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Márquez L. M., Helmann J. D., Ferrari E., Parker H. M., Ordal G. W., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of sigma D-dependent functions in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3435-3443.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. W., Doi R. H. Genetic mapping of rpoD implicates the major sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase in sporulation initiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(1):88–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00397991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Coppolecchia R., DeGrazia H., Moran C. P., Jr Negative regulator of sigma G-controlled gene expression in stationary-phase Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):709–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.709-715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray C., Hay R. E., Carter H. L., Moran C. P., Jr Mutations that affect utilization of a promoter in stationary-phase Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):610–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.610-614.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Margolis P., Duncan L., Coppolecchia R., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Control of developmental transcription factor sigma F by sporulation regulatory proteins SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9221–9225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bonamy C., Karmazyn-Campelli C. Processing of a sporulation sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis: how morphological structure could control gene expression. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Kunkel B., Kroos L., Losick R. Chromosomal rearrangement generating a composite gene for a developmental transcription factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):507–512. doi: 10.1126/science.2536191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Losick R. Cascades of sigma factors revisited. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1801–1806. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Stragier P., Setlow P. Identification of a new sigma-factor involved in compartmentalized gene expression during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatti K. M., Moran C. P., Jr Promoter recognition by sigma-37 RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin M. D., Jarvis K. A., Raven S. E., Fort P. Effects of transition mutations in the regulatory locus spoIIA on the incidence of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):959–962. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spoO genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



