Abstract
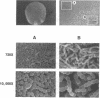
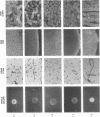
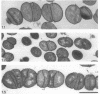
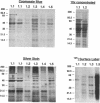
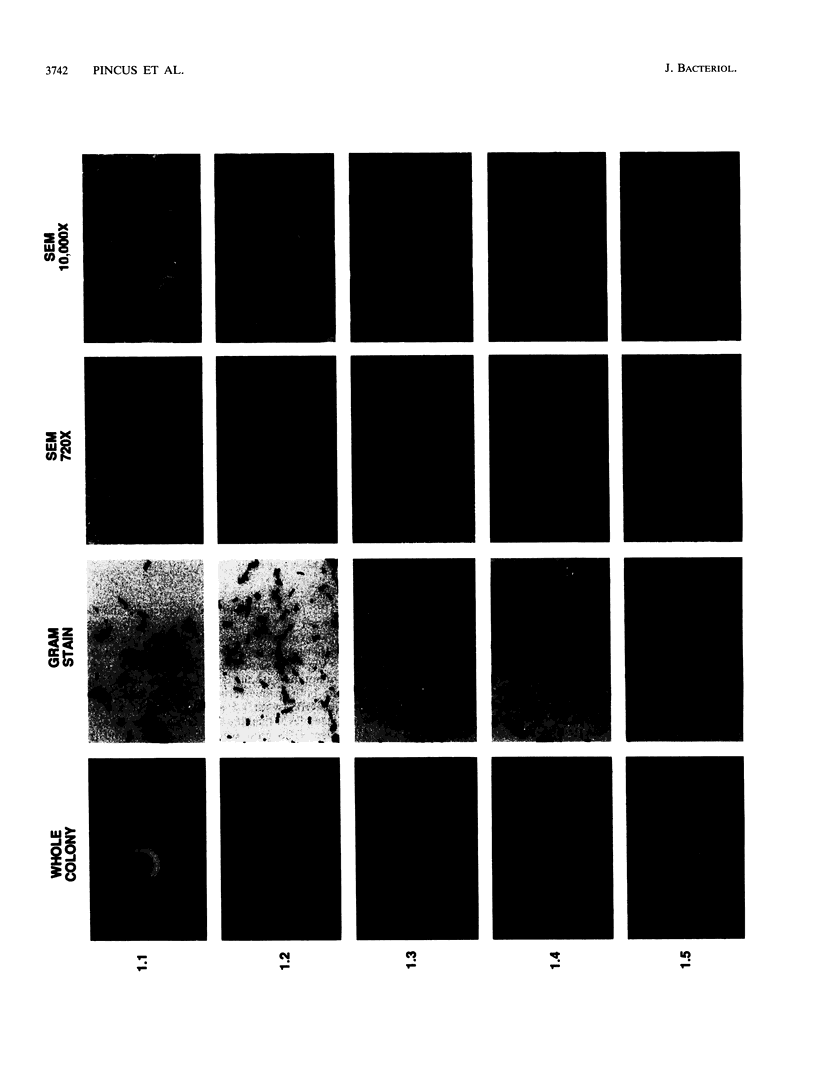
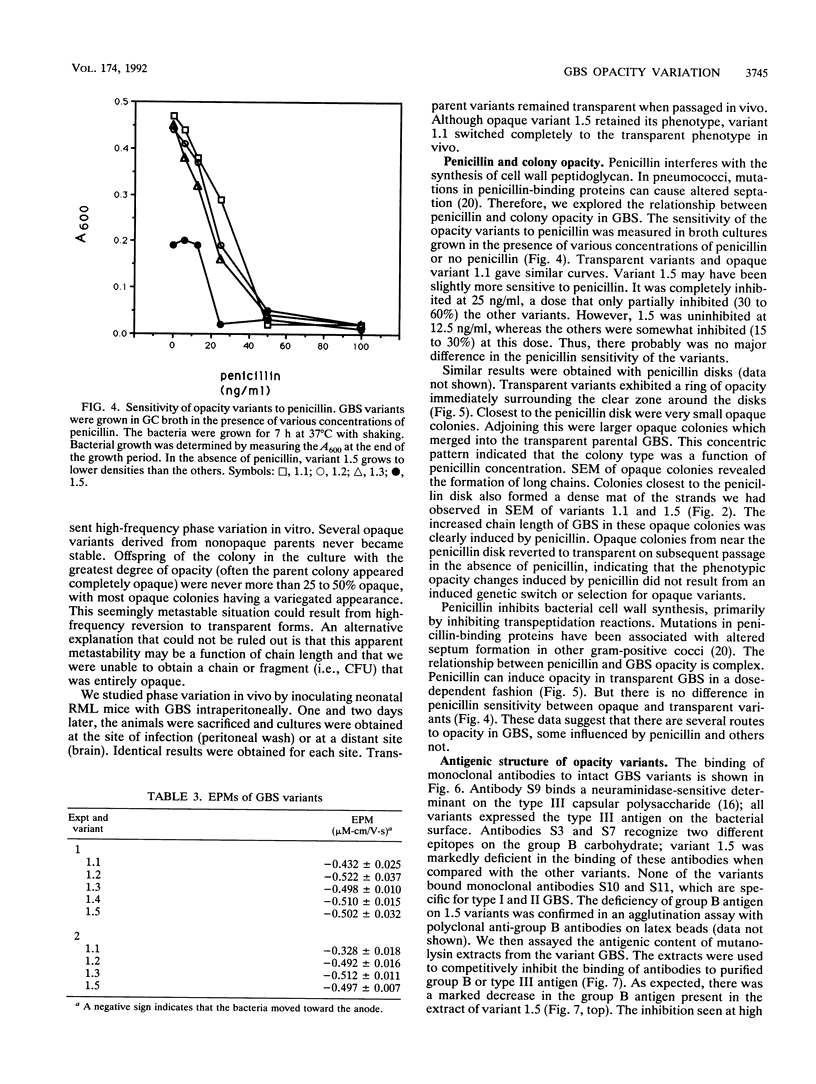
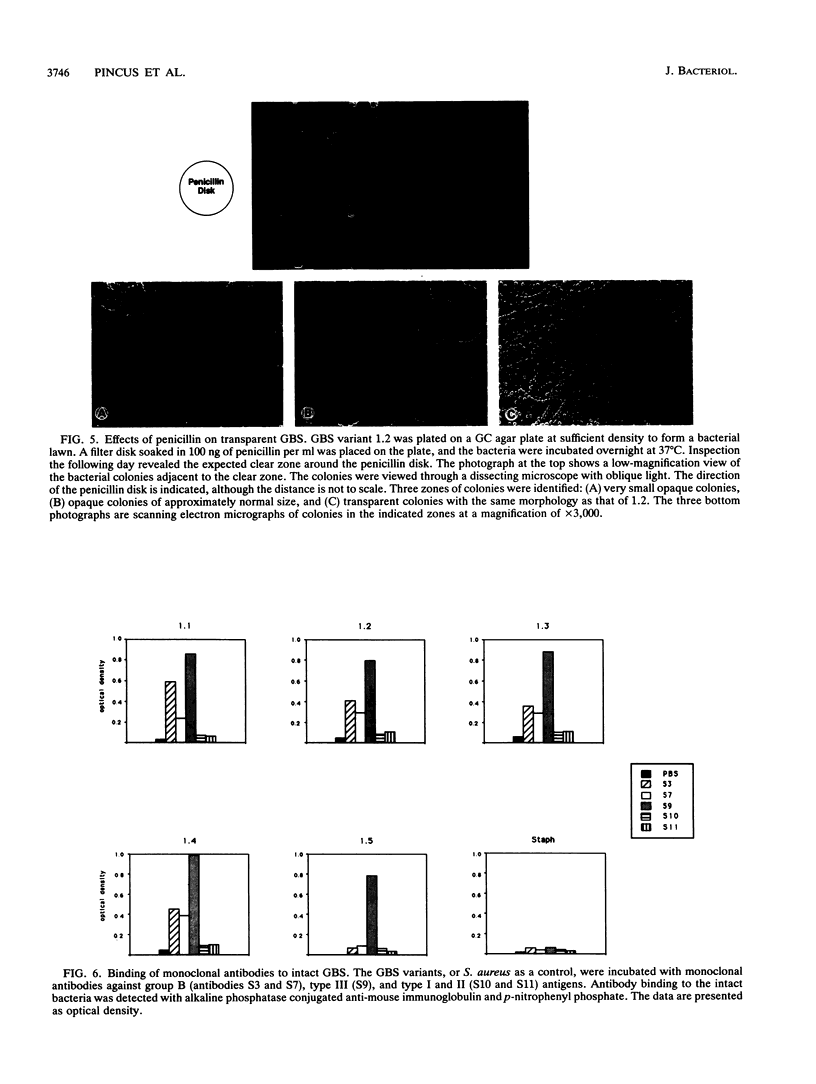
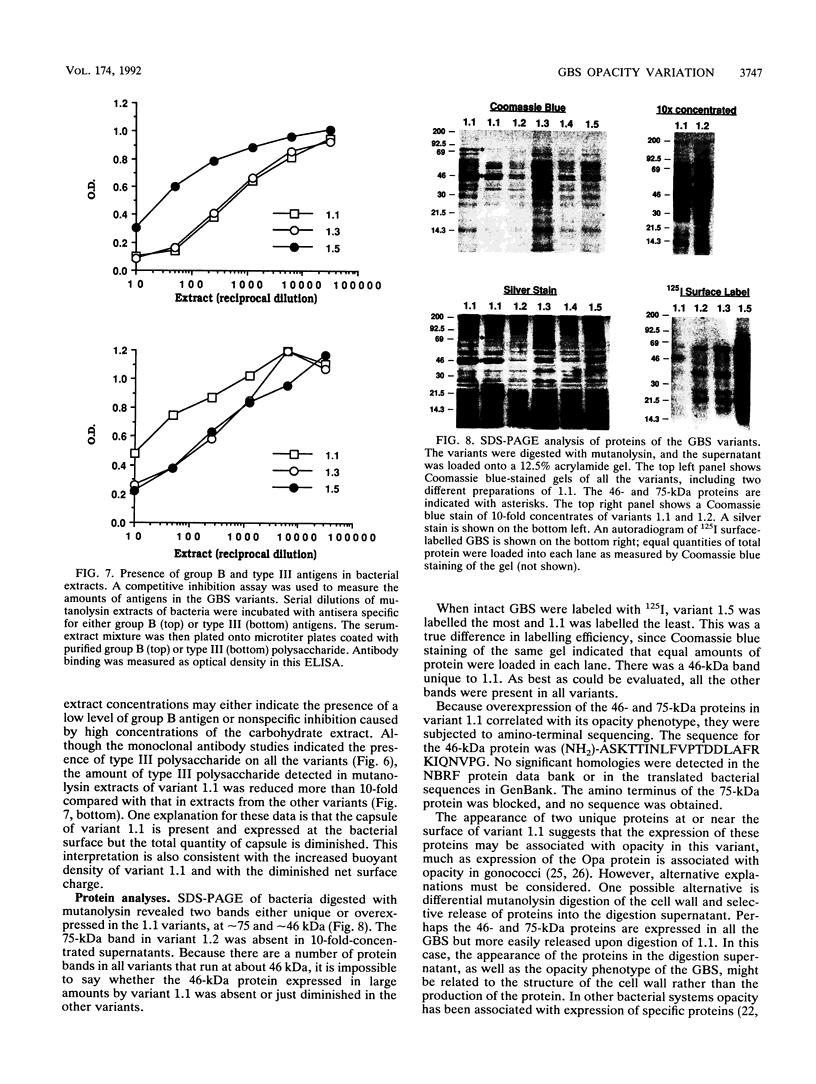
Colony opacity variants were detected for type III group B streptococci (GBS). Transparent colonies predominate in the parent GBS, with occasional colonies having opaque portions. Two stable opaque variants (1.1 and 1.5) were compared with three transparent clones (1.2, 1.3, and 1.4). All grew well on blood agar and on GC medium, but variant 1.1 failed to grow on Todd-Hewitt medium. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy demonstrated that colony opacity correlated with bacterial aggregation status, with opaque variants forming longer and more organized chains. Opaque-transparent switches were observed in both directions for most variants, with transparent to opaque noted most frequently, but 1.5 did not switch at all. Switching of the opacity phenotype was observed both in vitro and in neonatal mice. Relationships between colony opacity and several cell surface phenomena were explored. (i) Opaque variant 1.1 had two surface proteins (46 and 75 kDa) that were either unique or greatly overexpressed. (ii) Variant 1.1 was deficient in type III polysaccharide, while 1.5 lacked group B antigen. Diminished capsular polysaccharide of variant 1.1 was reflected in reduced negative electrophoretic mobility and in increased buoyant density. (iii) Transparent variant colonies growing closest to a penicillin disk were opaque, but colonial variants did not differ in their sensitivity to penicillin. These data indicate that GBS can exist in both opaque and transparent forms, with opaque appearance occurring by multiple routes. Opaque variants grow poorly on Todd-Hewitt medium generally used for isolation of GBS, so any possible relationships between opacity variation and pathogenesis of GBS infection are unknown.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J. Group B streptococcal infection in newborns: prevention at last? N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 26;314(26):1702–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606263142609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Sloyer J. L., Jr The electrophoretic mobility of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria: an electrokinetic analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):867–874. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGELSBACH H. T., BRAUN W., HERRING R. D. Studies on the variation of Bacterium tularense. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.557-569.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J., Baker C. J., Nicholson-Weller A. Capsular sialic acid prevents activation of the alternative complement pathway by type III, group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1278–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser D., Haines M., Bylund J., Higgins M. Variation in buoyant density of whole cells and isolated cell walls of Streptococcus faecium (ATCC 9790). J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4992–4995. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4992-4995.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser D., Higgins M. Buoyant density, growth rate, and the cell cycle in Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):669–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.669-673.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Haines M., Whalen M., Glaser D., Bylund J. Relationship between changes in buoyant density and formation of new sites of cell wall growth in cultures of streptococci (Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790) undergoing a nutritional shift-up. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4415–4419. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4415-4419.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M., Corwin D., Hayes S. F., Olszewski A., Todd W. J. Morphology of three strains of contagious equine metritis organism. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):94–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.94-108.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Connelly C. J., Moxon E. R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.389-395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson S., Granlund-Edstedt M., Sellin M., Holm S. E. Demonstration and characterization of buoyant-density subpopulations of group B Streptococcus type III. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):741–746. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty M. The nature of the opaque colony variation in group A streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):185–190. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Shigeoka A. O., Moe A. A., Ewing L. P., Hill H. R. Protective efficacy of IgM monoclonal antibodies in experimental group B streptococcal infection is a function of antibody avidity. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2779–2785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Tschachler E., Hayes S. F., Buller R. S., Reitz M. Variants selected by treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells with an immunotoxin. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Löfgren S., Tärnvik A. A capsule-deficient mutant of Francisella tularensis LVS exhibits enhanced sensitivity to killing by serum but diminished sensitivity to killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster C., Dobrinski B., Hakenbeck R. Unusual septum formation in Streptococcus pneumoniae mutants with an alteration in the D,D-carboxypeptidase penicillin-binding protein 3. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6499–6505. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6499-6505.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B., Schuchat A., Oxtoby M. J., Cochi S. L., Hightower A., Broome C. V. Invasive group B streptococcal disease in adults. A population-based study in metropolitan Atlanta. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1112–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Expression of M type 12 protein by a group A streptococcus exhibits phaselike variation: evidence for coregulation of colony opacity determinants and M protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2448–2455. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2448-2455.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., McCarty M. Electron microscopic studies on opaque colony variants of group A streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.505-511.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T. The relative importance of the capsule and the M-antigen in determining colony form of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Paoletti L. C., Kasper D. L., DiFabio J. L., Michon F., Holme K., Jennings H. J. Immunogenicity in animals of a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine against type III group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1428–1433. doi: 10.1172/JCI114858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]