Abstract
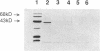
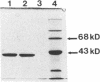
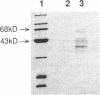
Rhizobium meliloti, a symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing soil bacterium with complex flagella, as well as other members of the family Rhizobiaceae, rapidly lost motility when suspended in buffers lacking divalent cations but retained good motility in buffers containing calcium, magnesium, barium, or strontium. Loss of motility was associated with loss of flagella from the cells. Analysis of flagella by sedimentation, gel electrophoresis, and electron microscopy revealed that removal of divalent cations from the complex flagella of R. meliloti resulted in extensive dissociation of the flagellar filaments into low-molecular-weight subunits. Accordingly, divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium that are normally present at high concentrations in the soil solution may be crucial to the assembly and rigidity of complex flagella.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman K., Nulty E., Su L. H. Mutations in the two flagellin genes of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3716–3723. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3716-3723.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Crist-Estes D. K., Bauer W. D. Chemotaxis of Rhizobium meliloti to the plant flavone luteolin requires functional nodulation genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3164–3169. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3164-3169.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangola P., Rosen B. P. Maintenance of intracellular calcium in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12570–12574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Koshland D. E., Jr Response to a metal ion-citrate complex in bacterial sensing. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.798-804.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kape R., Parniske M., Werner D. Chemotaxis and nod Gene Activity of Bradyrhizobium japonicum in Response to Hydroxycinnamic Acids and Isoflavonoids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):316–319. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.316-319.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupski G., Götz R., Ober K., Pleier E., Schmitt R. Structure of complex flagellar filaments in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.361-366.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Lodderstaedt G., Schmitt R. Purification and biochemical properties of complex flagella isolated from Rhizobium lupini H13-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 21;535(1):110–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield C. I., Inniss W. E. A rapid, simple method for staining bacterial flagella. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1311–1313. doi: 10.1139/m77-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J. Chamber for bacterial chemotaxis experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):729–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.729-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleier E., Schmitt R. Expression of two Rhizobium meliloti flagellin genes and their contribution to the complex filament structure. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2077–2085. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2077-2085.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleier E., Schmitt R. Identification and sequence analysis of two related flagellin genes in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1467–1475. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1467-1475.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher M., Watterson D. M. Analysis of differences between coomassie blue stain and silver stain procedures in polyacrylamide gels: conditions for the detection of calmodulin and troponin C. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Kijne J. W., Lugtenberg B. J. Involvement of both cellulose fibrils and a Ca2+-dependent adhesin in the attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4294–4301. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4294-4301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Kijne J. W., Lugtenberg B. J. Roles of flagella, lipopolysaccharide, and a Ca2+-dependent cell surface protein in attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):569–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.569-572.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Logman T. J., Boerrigter M. E., Kijne J. W., Lugtenberg B. J. Purification and partial characterization of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae Ca2+-dependent adhesin, which mediates the first step in attachment of cells of the family Rhizobiaceae to plant root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4054–4062. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4054-4062.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg S., DeRosier D. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Pairwise perturbation of flagellin subunits. The structural basis for the differences between plain and complex bacterial flagellar filaments. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Chan Y. K., Wheatcroft R., Yang A. F., Han S. H. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for C4-dicarboxylate transport and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are located on a megaplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):927–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.927-934.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Mg2+, Ca2+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase as receptor for divalent cations in bacterial sensing. Science. 1976 Jul 30;193(4251):405–408. doi: 10.1126/science.132702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]