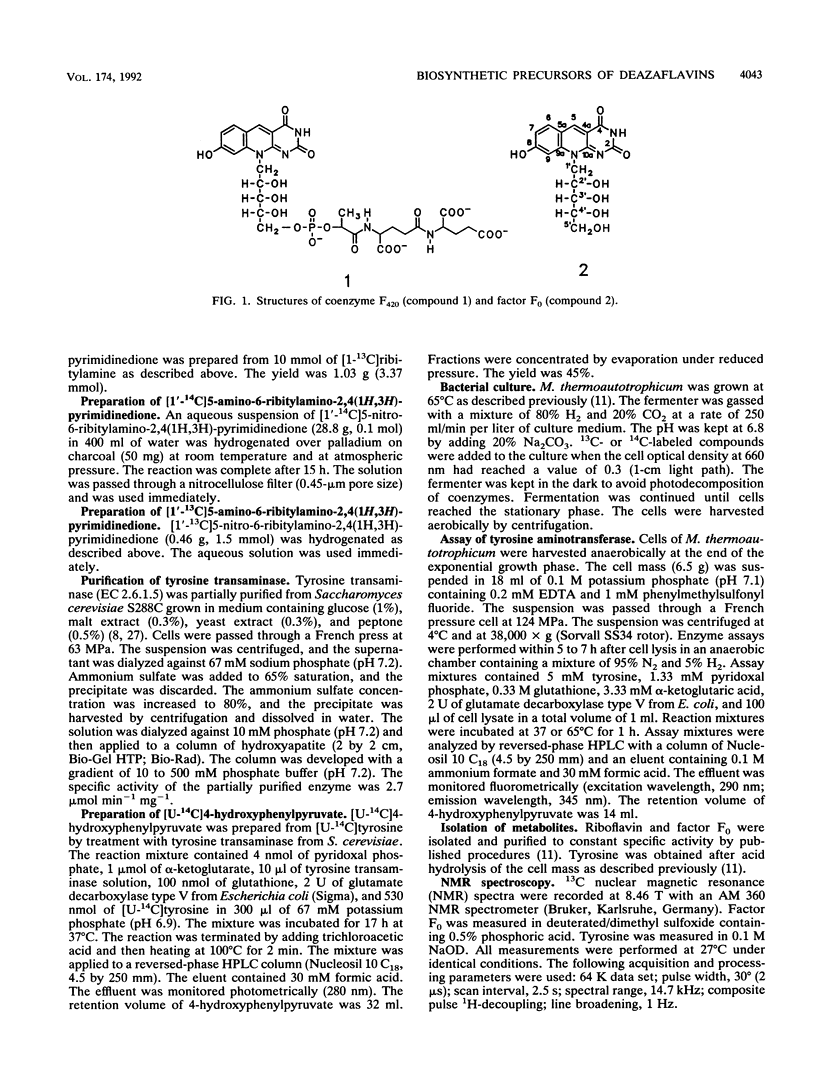
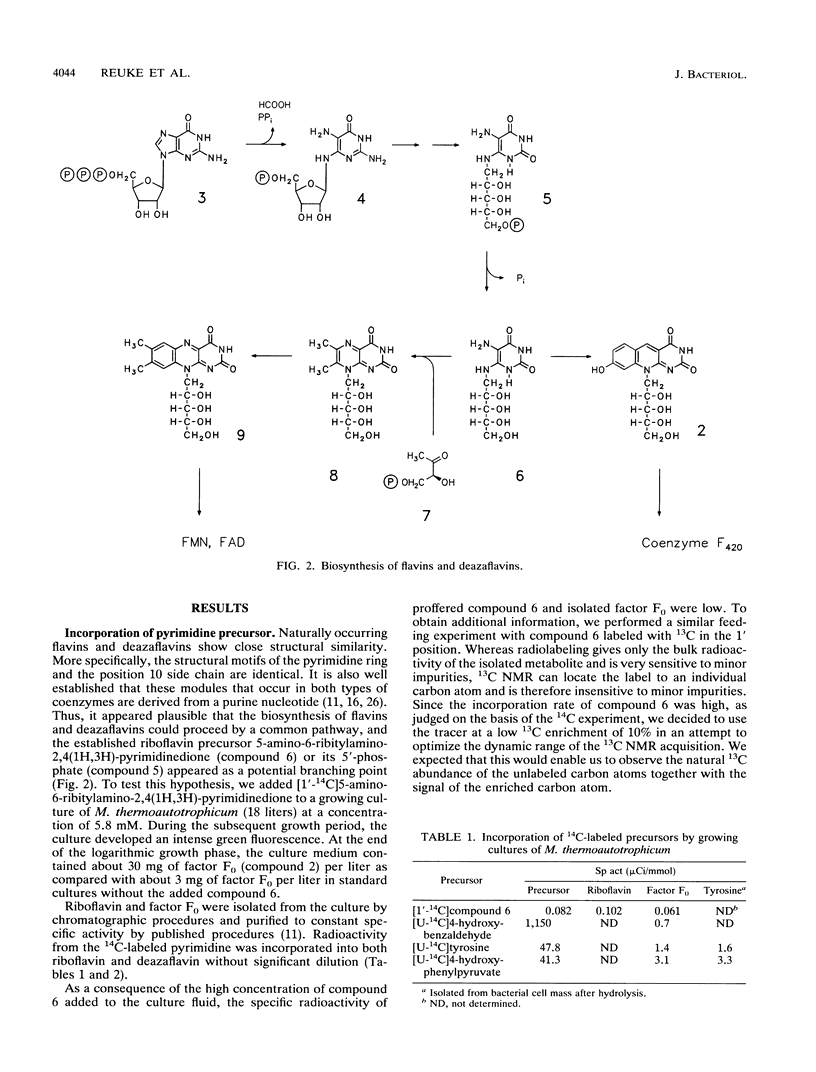
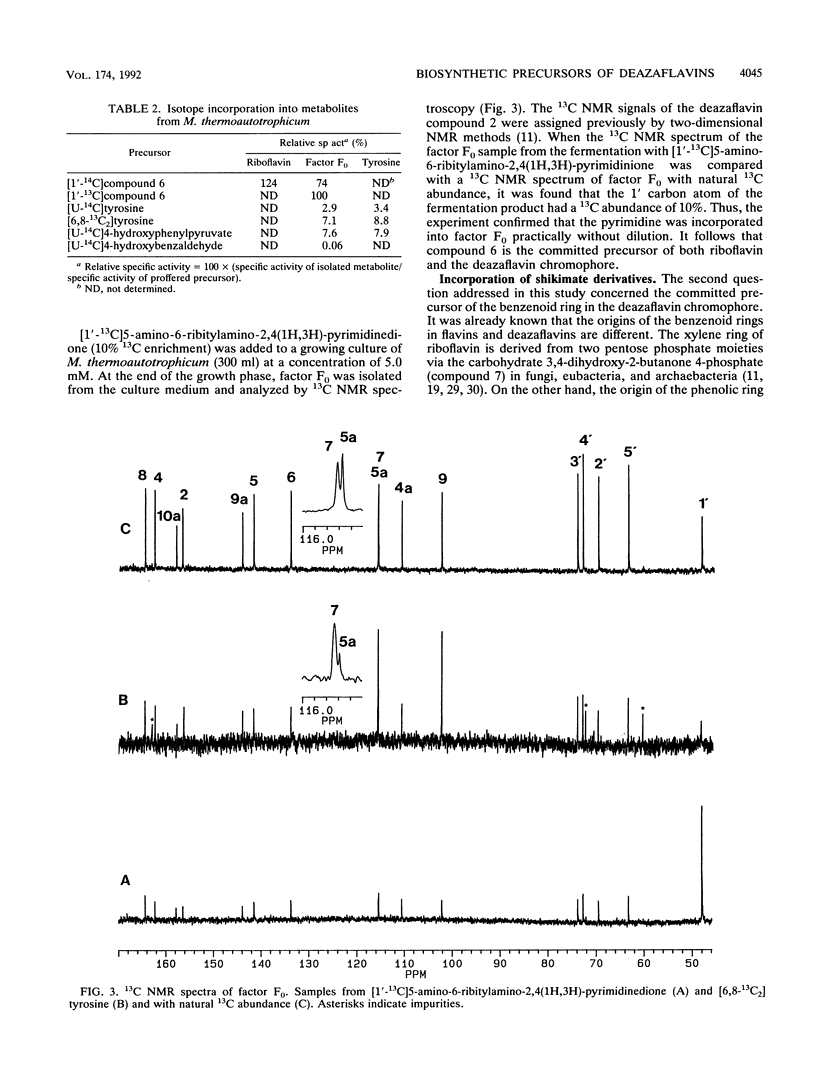
Abstract
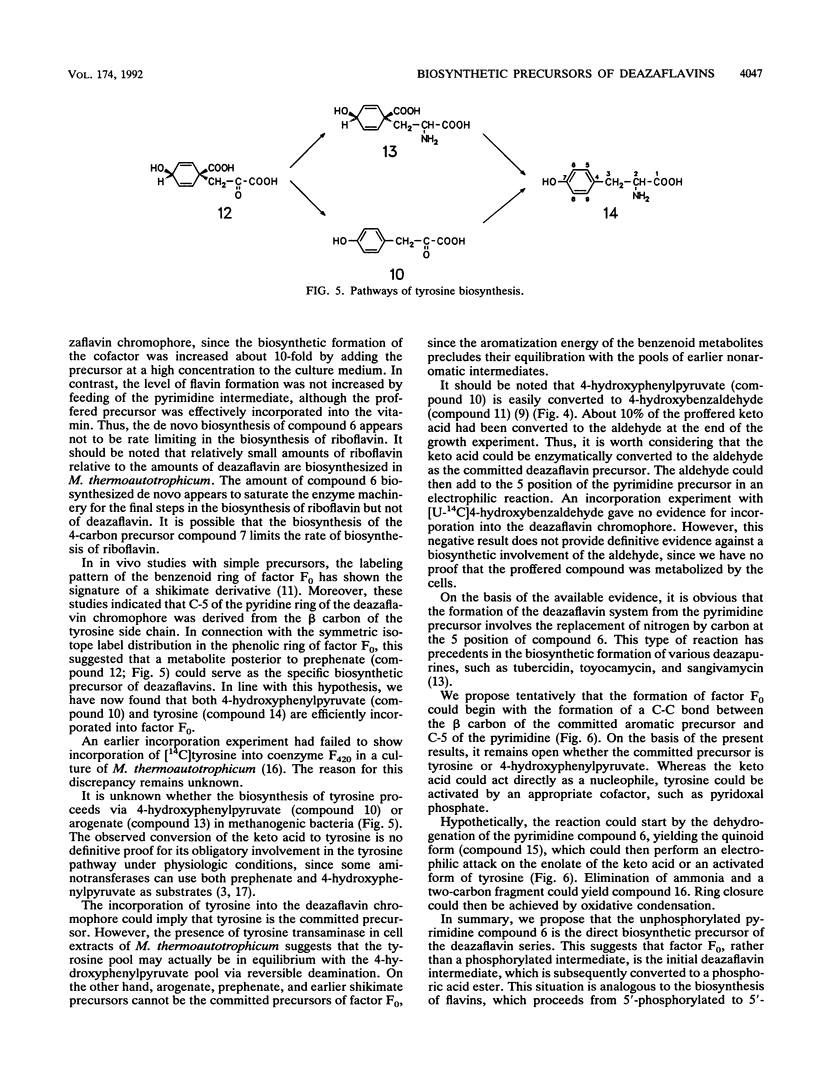
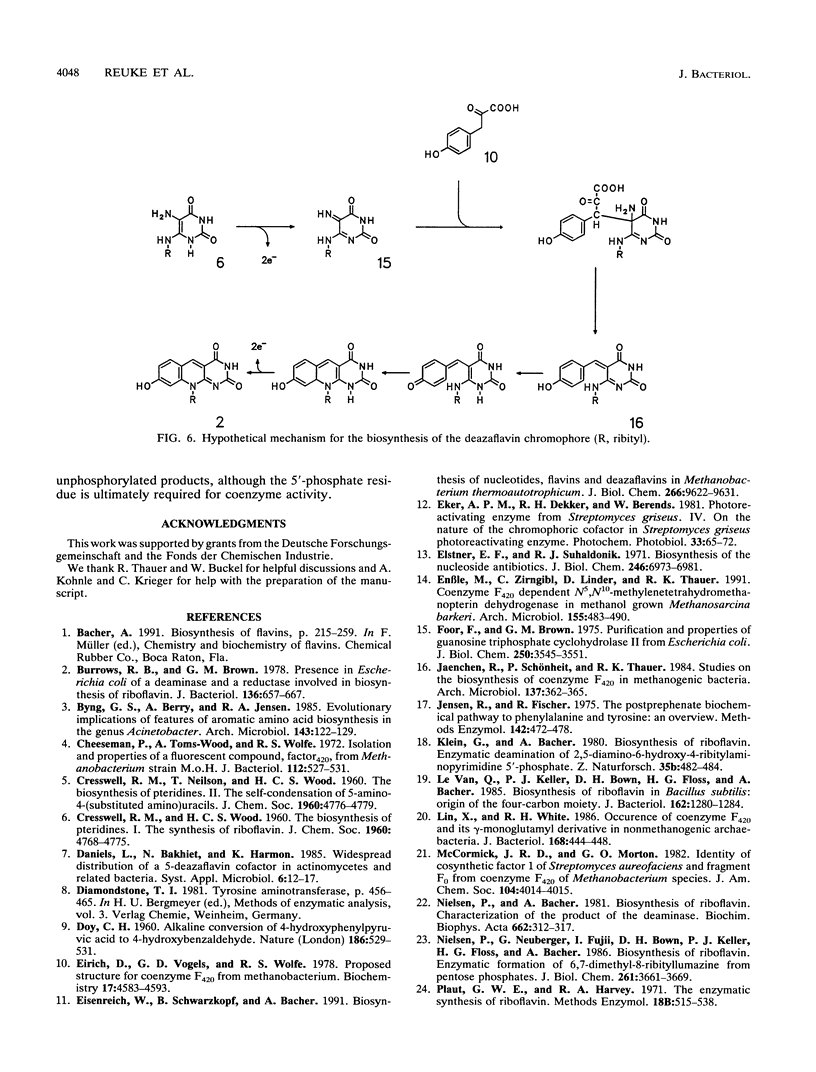
The incorporation of 13C- and 14C-labeled precursors into 5-deaza-7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxyriboflavin (factor F0) was studied with growing cells of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. 5-Amino-6-ribitylamino-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione was incorporated into the deazaflavin and into riboflavin without dilution. Tyrosine and 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate were incorporated into the deazaflavin and into cellular protein. 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde was not incorporated. A reaction mechanism is proposed for the formation of the deazaflavin chromophore from 5-amino-6-ribitylamino-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione and tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrows R. B., Brown G. M. Presence of Escherichia coli of a deaminase and a reductase involved in biosynthesis of riboflavin. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):657–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.657-667.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byng G. S., Berry A., Jensen R. A. Evolutionary implications of features of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the genus Acinetobacter. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Nov;143(2):122–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00411034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman P., Toms-Wood A., Wolfe R. S. Isolation and properties of a fluorescent compound, factor 420 , from Methanobacterium strain M.o.H. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.527-531.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
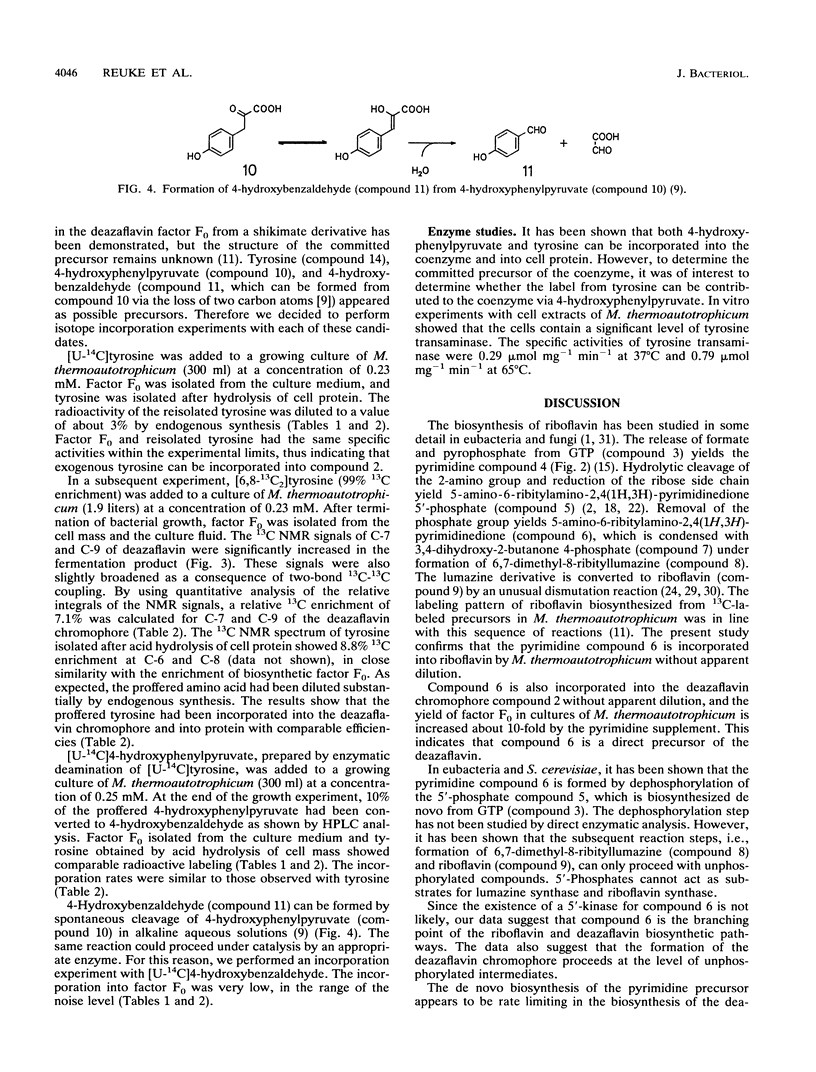
- DOY C. H. Alkaline conversion of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid to 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde. Nature. 1960 May 14;186:529–531. doi: 10.1038/186529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirich L. D., Vogels G. D., Wolfe R. S. Proposed structure for coenzyme F420 from Methanobacterium. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4583–4593. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenreich W., Schwarzkopf B., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of nucleotides, flavins, and deazaflavins in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9622–9631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Dekker R. H., Berends W. Photoreactivating enzyme from Streptomyces griseus-IV. On the nature of the chromophoric cofactor in Streptomyces griseus photoreactivating enzyme. Photochem Photobiol. 1981 Jan;33(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1981.tb04298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elstner E. F., Suhadolnik R. J. The biosynthesis of the nucleoside antibiotics. IX. Purification and properties of guanosine triphosphate 8-formylhydrolase that catalyzes production of formic acid from the ureido carbon of guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6973–6981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foor F., Brown G. M. Purification and properties of guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase II from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3545–3551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenchen R., Schönheit P., Thauer R. K. Studies on the biosynthesis of coenzyme F420 in methanogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Apr;137(4):362–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00410735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Fischer R. The postprephenate biochemical pathways to phenylalanine and tyrosine: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:472–478. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Van Q., Keller P. J., Bown D. H., Floss H. G., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin in Bacillus subtilis: origin of the four-carbon moiety. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1280–1284. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1280-1284.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X. L., White R. H. Occurrence of coenzyme F420 and its gamma-monoglutamyl derivative in nonmethanogenic archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):444–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.444-448.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin. Characterization of the product of the deaminase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 15;662(2):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P., Neuberger G., Fujii I., Bown D. H., Keller P. J., Floss H. G., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin. Enzymatic formation of 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine from pentose phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3661–3669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENTHESHANMUGANATHAN S. The purification and properties of the tyrosine-2-oxoglutarate transaminase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:619–625. doi: 10.1042/bj0770619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk R., Bacher A. Studies on the 4-carbon precursor in the biosynthesis of riboflavin. Purification and properties of L-3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19479–19485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. W. The biosynthesis of the vitamins thiamin, riboflavin, and folic acid. Nat Prod Rep. 1986 Aug;3(4):395–419. doi: 10.1039/np9860300395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Fuchs G., Kenealy W., Thauer R. K. Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.604-613.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


