Abstract
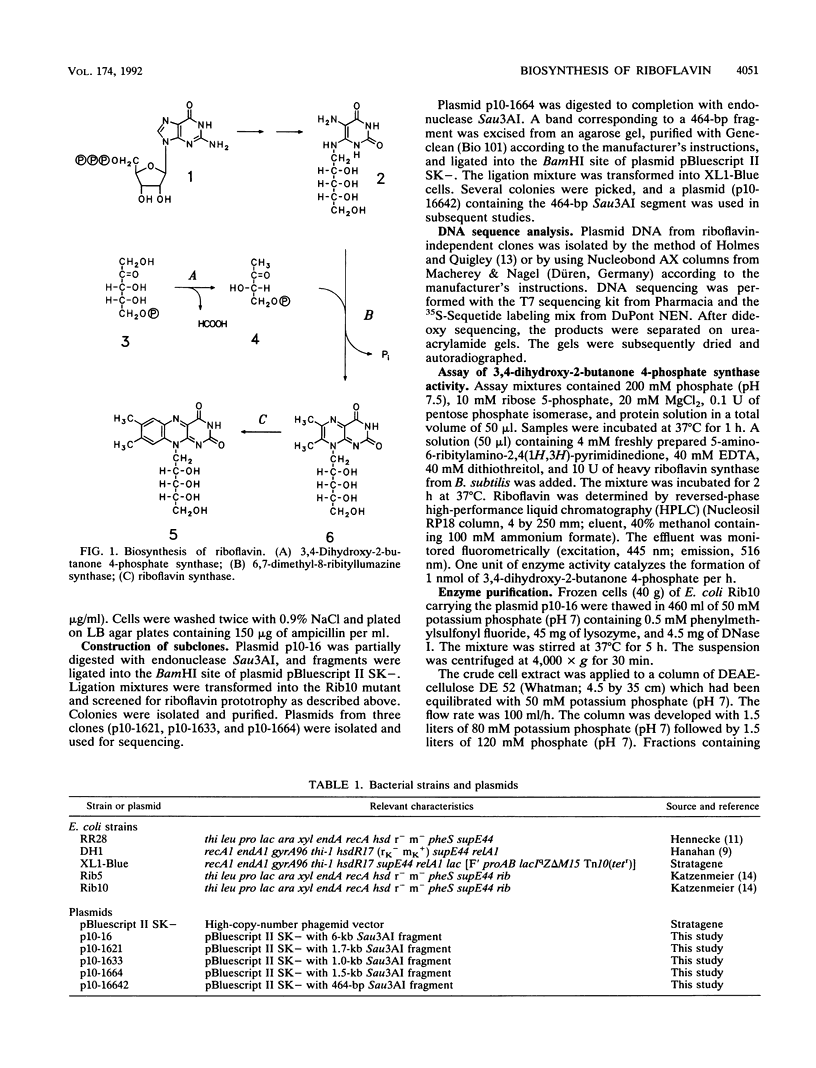
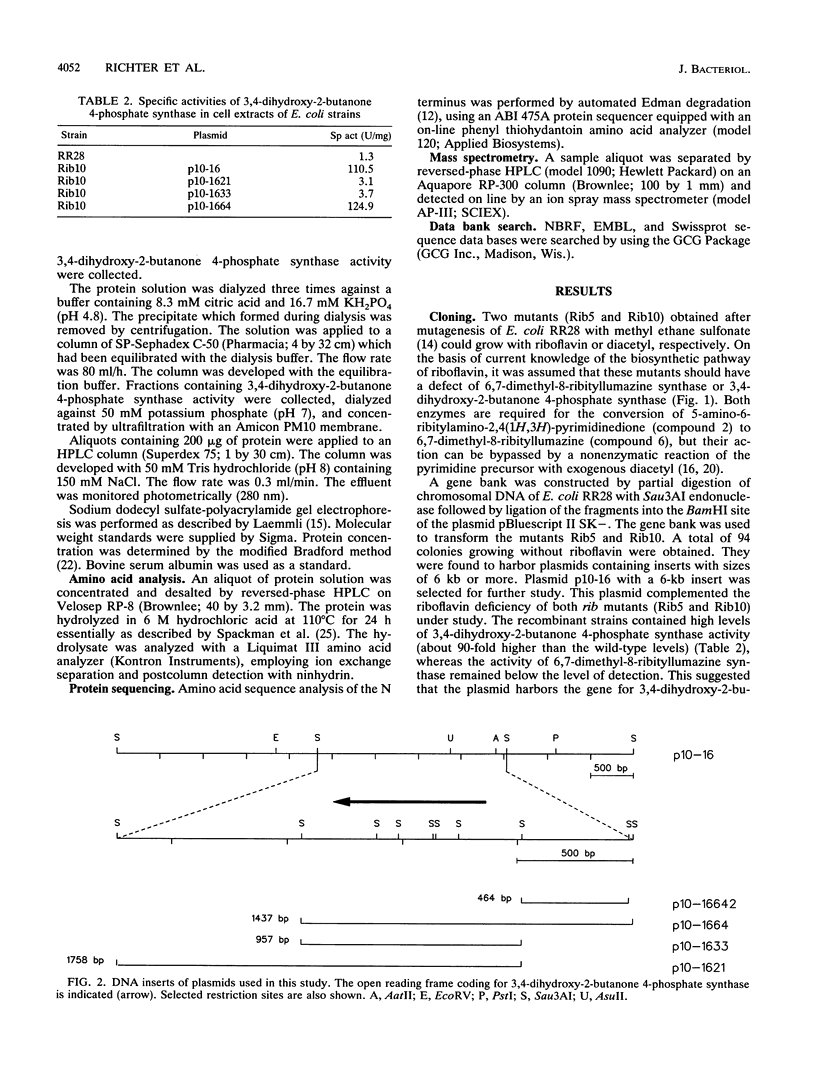
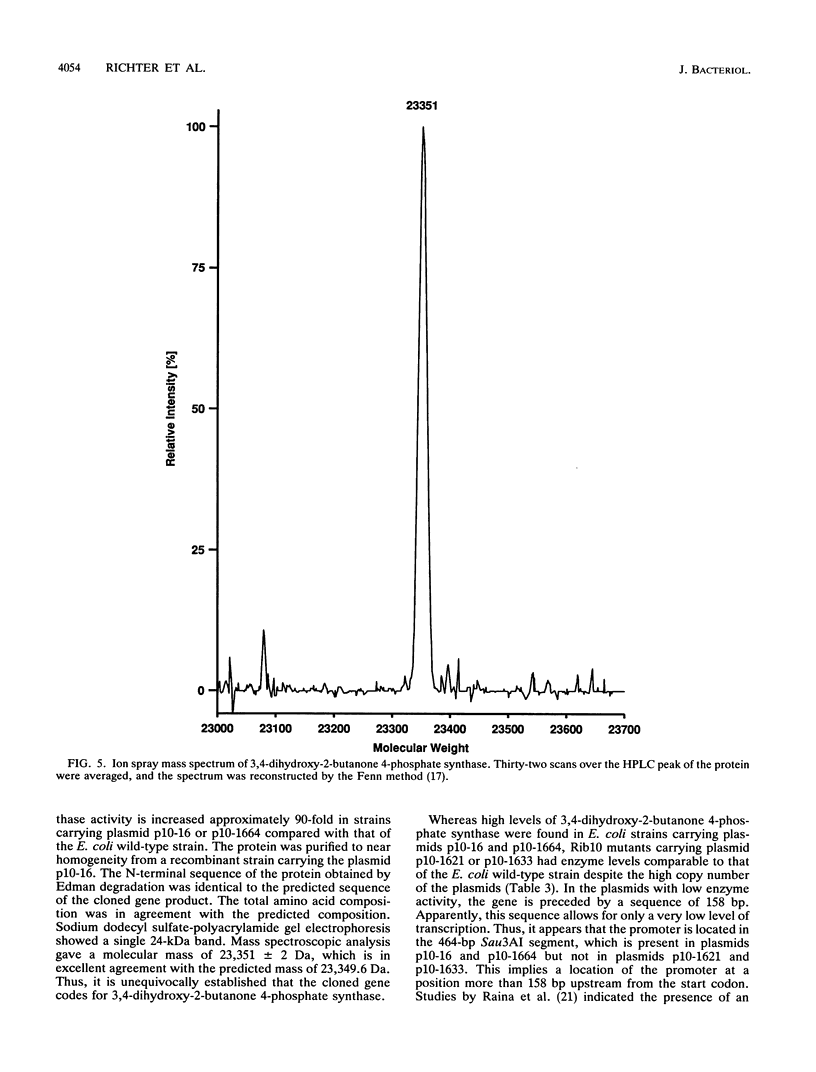
3,4-Dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate is biosynthesized from ribulose 5-phosphate and serves as the biosynthetic precursor for the xylene ring of riboflavin. The gene coding for 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli has been cloned and sequenced. The gene codes for a protein of 217 amino acid residues with a calculated molecular mass of 23,349.6 Da. The enzyme was purified to near homogeneity from a recombinant E. coli strain and had a specific activity of 1,700 nmol mg-1 h-1. The N-terminal amino acid sequence and the amino acid composition of the protein were in agreement with the deduced sequence. The molecular mass as determined by ion spray mass spectrometry was 23,351 +/- 2 Da, which is in agreement with the predicted mass. The previously reported loci htrP, "luxH-like," and ribB at 66 min of the E. coli chromosome are all identical to the gene coding for 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase, but their role had not been hitherto determined. Sequence homology indicates that gene luxH of Vibrio harveyi and the central open reading frame of the Bacillus subtilis riboflavin operon code for 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacher A., Baur R., Eggers U., Harders H. D., Otto M. K., Schnepple H. Riboflavin synthases of Bacillus subtilis. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):632–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandrin S. V., Rabinovich P. M., Stepanov A. I. Tri gruppy stsepleniia genov biosinteza riboflavina Escherichia coli. Genetika. 1983 Sep;19(9):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikindas M. L., Luk'ianov E. V., Rabinovich P. M., Stepanov A. I. Izuchenie oblasti 210 gradusov khromosomy Bacillus subtilis s pomoshch'iu rekombinantnykh plazmid. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1987 Feb;(2):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H., Günther I., Binder F. A novel cloning vector for the direct selection of recombinant DNA in E. coli. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingens F., Oltmanns O., Bacher A. Uber Zwischenprodukte der Riboflavin-Biosynthese bei Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Z Naturforsch B. 1967 Jul;22(7):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltmanns O., Bacher A., Lingens F., Zimmermann F. K. Biochemical and genetic classification of riboflavine deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;105(4):306–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00277585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantseva M. D., Rafailov A. M. Mutagennyi effekt radiatsii u myshei, podvergshikhsia gamma-oblucheniiu v émbrional'nyi period. Soobshchenie III. Chastota mozaikov po okraske shersti sredi geterozigotnykh po retsessivnym mutatsiiam myshei, podvergshikhsia oblucheniiu v raznye sroki émbriogeneza. Genetika. 1976;12(11):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina S., Mabey L., Georgopoulos C. The Escherichia coli htrP gene product is essential for bacterial growth at high temperatures: mapping, cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of htrP. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5999–6008. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5999-6008.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott K., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Bacher A. Riboflavin synthases of Bacillus subtilis. Purification and amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4204–4209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzman E., Miyamoto C., Graham A., Meighen E. Delineation of the transcriptional boundaries of the lux operon of Vibrio harveyi demonstrates the presence of two new lux genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3513–3517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesliar G. E., Shavlovskii G. M. Lokalizatsiia genov, kodiruiushchikh GTF-tsiklogidrolazu II i riboflavinsintazu na khromosome Escherichia coli K-12. Tsitol Genet. 1983 Sep-Oct;17(5):54–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk R., Bacher A. Biosynthesis of riboflavin. Studies on the mechanism of L-3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20610–20618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk R., Bacher A. Studies on the 4-carbon precursor in the biosynthesis of riboflavin. Purification and properties of L-3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19479–19485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




