Abstract
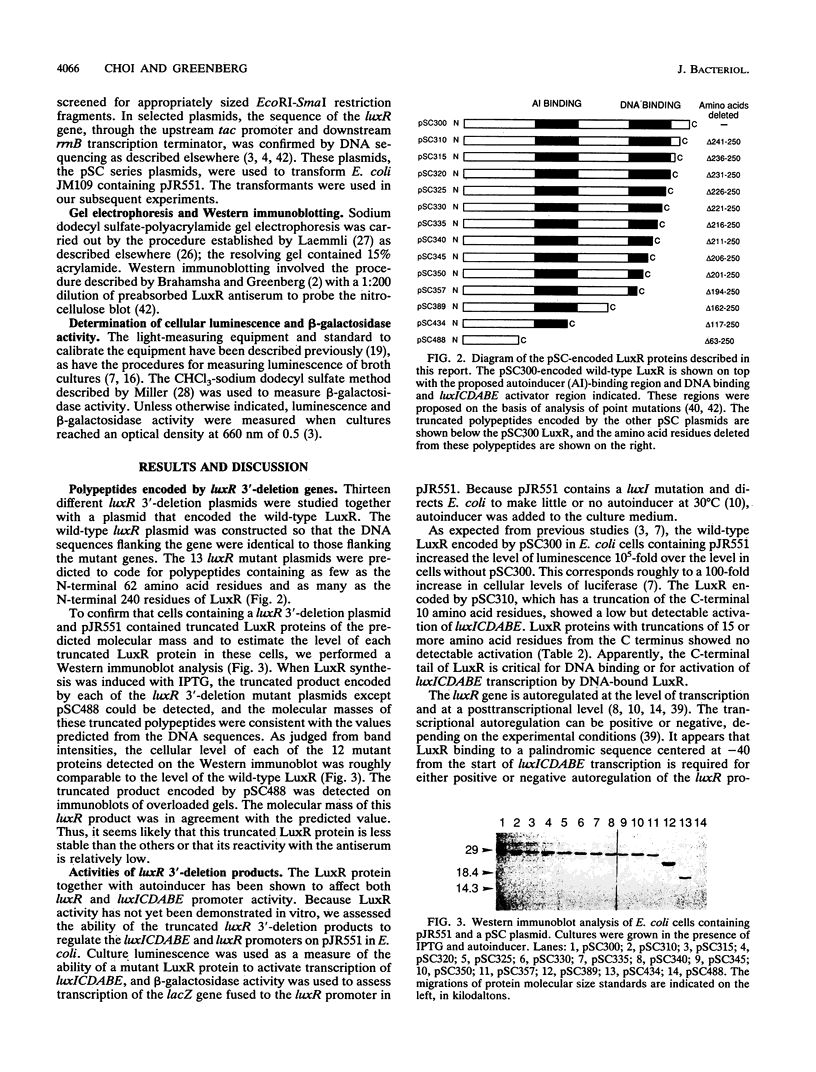
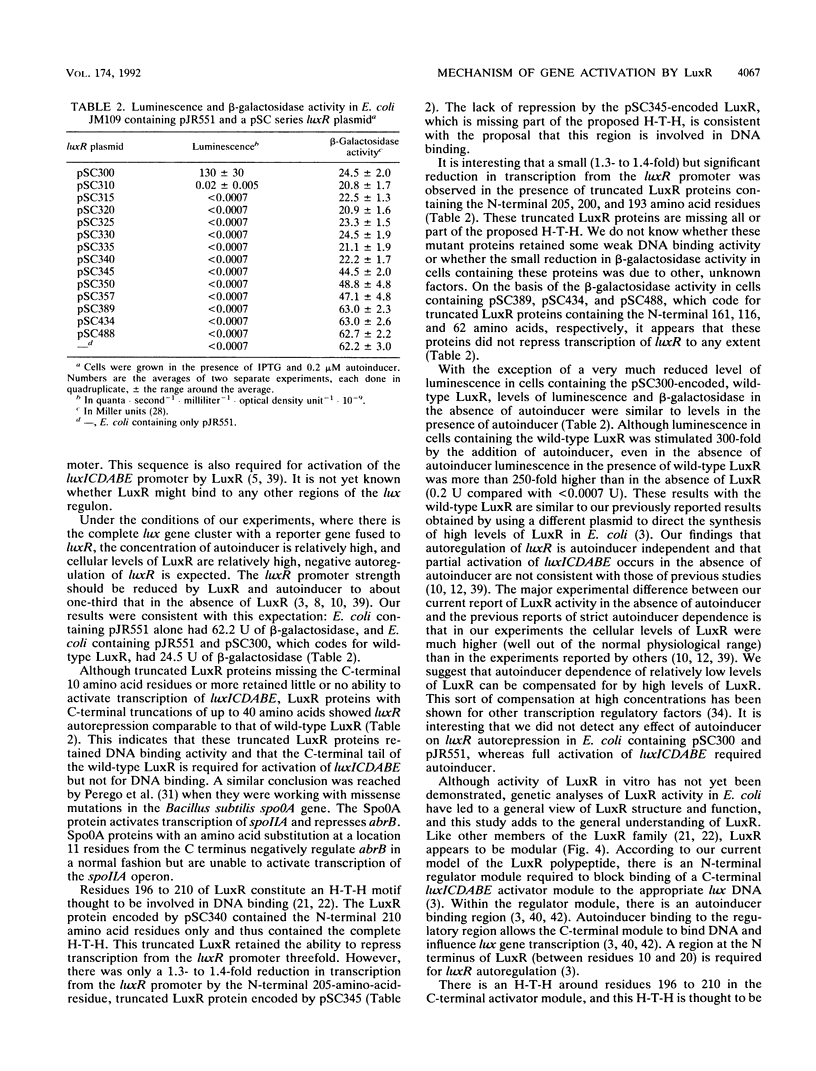
The Vibrio fischeri luminescence (lux) genes are regulated by the 250-amino-acid-residue LuxR protein and a V. fischeri metabolite termed autoinducer. The V. fischeri lux regulon consists of two divergently transcribed units. Autoinducer and LuxR activate transcription of the luxICDABE operon and autoregulate the luxR transcriptional unit. LuxR proteins with C-terminal truncations of up to 40 amino acid residues coded by plasmids with luxR 3'-deletion mutations are functional in negative autoregulation as demonstrated by using a luxR::lacZ transcriptional fusion as a luxR promoter probe in Escherichia coli. The truncated LuxR proteins showed little or no ability to activate transcription of luxICDABE, as indicated by using luminescence as a sensitive indicator of promoter strength in E. coli. Besides having no detectable activity as positive regulators of luxICDABE, LuxR proteins with C-terminal truncations of more than 40 amino acid residues had reduced or no detectable activity as negative autoregulators. The results suggest that amino acid residues in LuxR prior to no. 211 are sufficient for lux DNA binding. Residues in the region of 211 to 250 constitute a C-terminal tail that appears to be involved in activation of luxICDABE transcription either by interacting physically with the transcription initiation complex or by affecting lux DNA in the vicinity of the promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boettcher K. J., Ruby E. G. Depressed light emission by symbiotic Vibrio fischeri of the sepiolid squid Euprymna scolopes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3701–3706. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3701-3706.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Biochemical and cytological analysis of the complex periplasmic flagella from Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4023–4032. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4023-4032.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S. H., Greenberg E. P. The C-terminal region of the Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein contains an inducer-independent lux gene activating domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11115–11119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine J. H., Shadel G. S., Baldwin T. O. Identification of the operator of the lux regulon from the Vibrio fischeri strain ATCC7744. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Greenberg E. P. Control of Vibrio fischeri luminescence gene expression in Escherichia coli by cyclic AMP and cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.45-50.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Greenberg E. P. Control of Vibrio fischeri lux gene transcription by a cyclic AMP receptor protein-luxR protein regulatory circuit. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4040–4046. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4040-4046.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Ray J. M. Requirement for autoinducer in transcriptional negative autoregulation of the Vibrio fischeri luxR gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3549–3552. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3549-3552.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V. Regulation of luminescence by cyclic AMP in cya-like and crp-like mutants of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1199–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1199-1202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A. L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G. L., Nealson K. H., Oppenheimer N. J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2444–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory locus controlling expression of bacterial genes for bioluminescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10455–10467. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambello M. J., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR gene, a transcriptional activator of elastase expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):3000–3009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.3000-3009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Wallace J. C., Brown J. P. Finding protein similarities with nucleotide sequence databases. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:111–132. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Ditta G. Modular structure of FixJ: homology of the transcriptional activator domain with the -35 binding domain of sigma factors. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):987–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1210-1214.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. B., Greenberg E. P. Overproduction and purification of the luxR gene product: Transcriptional activator of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6639–6643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Parr T. R., Jr, Angus B. L., Hancock R. E., Ghiorse W. C., Greenberg E. P. Isolation of the outer membrane and characterization of the major outer membrane protein from Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):172–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.172-179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H. Autoinduction of bacterial luciferase. Occurrence, mechanism and significance. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00446657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Wu J. J., Spiegelman G. B., Hoch J. A. Mutational dissociation of the positive and negative regulatory properties of the Spo0A sporulation transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:207–212. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90368-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O. Nucleoprotein structures at positively regulated bacterial promoters: homology with replication origins and some hypotheses on the quaternary structure of the activator proteins in these complexes. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):455–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Richet E. Maltotriose is the inducer of the maltose regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3059–3061. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3059-3061.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Greenberg E. P., Hastings J. W. Planktonic marine luminous bacteria: species distribution in the water column. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):302–306. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.302-306.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol Bull. 1976 Dec;151(3):574–586. doi: 10.2307/1540507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadel G. S., Baldwin T. O. The Vibrio fischeri LuxR protein is capable of bidirectional stimulation of transcription and both positive and negative regulation of the luxR gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.568-574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadel G. S., Young R., Baldwin T. O. Use of regulated cell lysis in a lethal genetic selection in Escherichia coli: identification of the autoinducer-binding region of the LuxR protein from Vibrio fischeri ATCC 7744. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3980–3987. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3980-3987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slock J., VanRiet D., Kolibachuk D., Greenberg E. P. Critical regions of the Vibrio fischeri luxR protein defined by mutational analysis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3974–3979. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3974-3979.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Parales J., Jr, Merkel S. M. Structure of genes narL and narX of the nar (nitrate reductase) locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2229–2234. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2229-2234.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Torres-Cabassa A., Maurizi M. R., Gutnick D., Gottesman S. RcsA, an unstable positive regulator of capsular polysaccharide synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1738–1747. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1738-1747.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Richet E., Raibaud O. Two MalT binding sites in direct repeat. A structural motif involved in the activation of all the promoters of the maltose regulons in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90715-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




